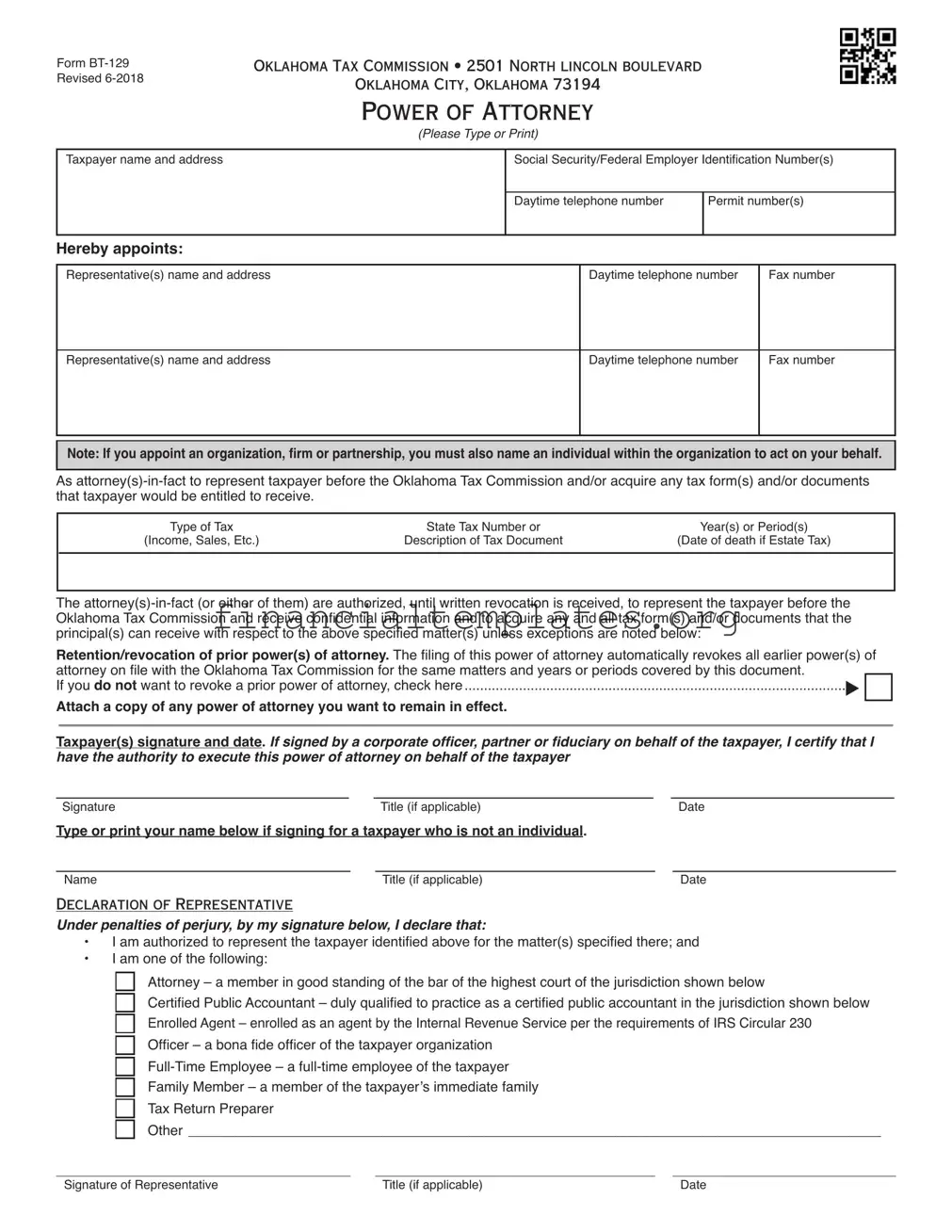
Get Tax POA form bt-129 Form
The Tax Power of Attorney (POA) form, known as BT-129, serves a critical role for individuals and businesses navigating the complexities of tax matters. It authorizes a designated representative, often a tax professional, to communicate with tax authorities, make decisions, and perform actions on behalf of the taxpayer. This empowerment covers a wide range of activities, from obtaining confidential tax information to representing the taxpayer in audits, negotiations, and settlements. Understanding the BT-129 form is essential for ensuring that this vital document is filled out correctly and that the right person is chosen for this responsibility. Not only does it streamline interactions with tax agencies by granting access to needed information, but it also relieves the stress of direct involvement in tax disputes or queries. Therefore, the BT-129 form acts as a bridge between the taxpayer, the tax professional, and the tax authority, ensuring that matters are handled efficiently and with the taxpayer's best interests in mind.
Tax POA form bt-129 Example

Form |
OKLAHOMA TAX COMMISSION • 2501 NORTH LINCOLN BOULEVARD |
Revised |
OKLAHOMA CITY, OKLAHOMA 73194 |
|
POWER OF ATTORNEY
(Please Type or Print)
Taxpayer name and address |
Social Security/Federal Employer Identification Number(s) |
|
|
|
|
|
Daytime telephone number |
Permit number(s) |
|
|
|
Hereby appoints:
Representative(s) name and address |
Daytime telephone number |
Fax number |
|
|
|
Representative(s) name and address |
Daytime telephone number |
Fax number |
|
|
|
Note: If you appoint an organization, firm or partnership, you must also name an individual within the organization to act on your behalf.
As
Type of Tax |
State Tax Number or |
Year(s) or Period(s) |
(Income, Sales, Etc.) |
Description of Tax Document |
(Date of death if Estate Tax) |
|
|
|
The
Retention/revocation of prior power(s) of attorney. The filing of this power of attorney automatically revokes all earlier power(s) of |
|||
attorney on file with the Oklahoma Tax Commission for the same matters and years or periods covered by this document. |
|
|
|
▼ |
□ |
|
|
If you do not want to revoke a prior power of attorney, check here |
|
||
Attach a copy of any power of attorney you want to remain in effect. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Taxpayer(s) signature and date. If signed by a corporate officer, partner or fiduciary on behalf of the taxpayer, I certify that I have the authority to execute this power of attorney on behalf of the taxpayer
Signature |
Title (if applicable) |
Date |
Type or print your name below if signing for a taxpayer who is not an individual.
Name |
Title (if applicable) |
Date |
DECLARATION OF REPRESENTATIVE
Under penalties of perjury, by my signature below, I declare that:
•I am authorized to represent the taxpayer identified above for the matter(s) specified there; and
•I am one of the following:
□

□

□
□
□

□

□
□
Attorney – a member in good standing of the bar of the highest court of the jurisdiction shown below
Certified Public Accountant – duly qualified to practice as a certified public accountant in the jurisdiction shown below
Enrolled Agent – enrolled as an agent by the Internal Revenue Service per the requirements of IRS Circular 230
Officer – a bona fide officer of the taxpayer organization
Family Member – a member of the taxpayer’s immediate family
Tax Return Preparer
Other _________________________________________________________________________________________
Signature of Representative |
Title (if applicable) |
Date |
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Tax Power of Attorney (POA) form BT-129 is designed to authorize an individual (typically a tax professional) to represent a taxpayer before tax authorities, allowing them to receive and inspect confidential tax information and to make decisions and actions regarding the taxpayer's tax matters. |
| Governing Law | The form is governed by the state's tax code and regulations that outline the specific requirements and limitations for the use of a Power of Attorney in tax matters. The exact law and section might vary depending on the state. |
| Validity Period | This form usually has a specified validity period set by the principal (the tax payer) or until the purpose for which it was issued is fulfilled or revoked. Some states automatically revoke or require renewal of the form after a certain period. |
| Revocation | The taxpayer can revoke the Tax POA at any time. This action often requires the taxpayer to inform the tax authority and the previously authorized representative in writing. |
| State-Specific Requirements | While the core purpose of Tax POA forms like BT-129 is consistent, the form and procedure might vary by state. Each state could have specific requirements for execution, such as notarization, witnesses, or specific filing procedures with the state's tax authority. |
Guide to Writing Tax POA form bt-129
Upon deciding to grant someone the power to handle your tax matters, the Tax Power of Attorney (POA) Form BT-129 is a critical document to complete. Filling out this form properly ensures that your chosen representative can perform actions such as filing taxes, obtaining confidential information, and making decisions about tax payments on your behalf. This process, while important, can be approached methodically to reduce any potential stress or confusion.
- Begin by gathering all necessary information including your full legal name, address, and taxpayer identification number (SSN or EIN).
- Provide the same information for your chosen representative, ensuring accuracy to prevent any issues with identification by the tax authorities.
- Specify the tax matters and years or periods for which the POA is granted. This could include, for instance, income tax for the years 2020 through 2023.
- Detail any specific powers you are granting your representative. This may include the ability to receive and inspect confidential tax documents, negotiate and agree on matters with the tax authority, and make payments or refunds.
- If you wish to limit any of these powers, clearly describe the limitations in the provided section. This ensures that your representative's authority is clearly defined according to your preferences.
- It is essential to sign and date the form. If you are appointing more than one representative, ensure that all parties sign the form. The signature officially grants the powers listed to the chosen representative(s).
- Review the form to ensure that all information is correct and that no necessary sections have been inadvertently skipped.
- Finally, submit the completed form to the appropriate tax authority. The submission process may vary by state or jurisdiction, so it is advisable to check the specific requirements of the tax authority to which you are submitting.
Following submission, the tax authority will process your Tax POA Form BT-129. During this period, it's wise to maintain communication with your representative, ensuring they're prepared to act on your behalf once the form is processed. This foundational step empowers them to manage your tax affairs efficiently and in accordance with your wishes. Remember, it's about laying the groundwork for a smooth relationship between your representative, the tax authorities, and yourself, yielding peace of mind regarding your tax matters.
Understanding Tax POA form bt-129
-
What is the Tax POA Form BT-129?
The Tax Power of Attorney (POA) Form BT-129 is a document that allows individuals or businesses to grant authority to another person, known as an agent or attorney-in-fact, to handle their tax matters with the tax authorities. This can include filing taxes, obtaining confidential tax information, and making decisions regarding tax payments and disputes.
-
Who can be appointed as an agent on the Form BT-129?
Individuals can appoint almost anyone as their agent, including family members, friends, or professionals like accountants or attorneys. The selected agent should be someone the individual trusts to manage their tax issues competently and confidentially.
-
How does one complete the Form BT-129?
Completing the Form BT-129 typically involves providing detailed information about the taxpayer authorizing the power, the appointed agent, and the specific tax matters the agent is allowed to handle. It might also require specifying the tax periods covered under the authorization and may need to be signed by both the taxpayer and the agent.
-
Is there a fee to file Form BT-129?
Generally, there is no fee required to submit Form BT-129 to the tax authorities. However, if you are using a professional, like a lawyer or an accountant, to fill out the form or act as your agent, they may charge a fee for their services.
-
How long does the authority granted on Form BT-129 last?
The duration of the authority granted can vary. It might be set to expire on a specific date or upon the completion of a certain act, like filing a tax return. It is possible to specify the duration of authority when completing the form, based on the individual's needs.
-
Can the authority granted on Form BT-129 be revoked?
Yes, the individual who granted authority through Form BT-129 can revoke it at any time. Revocation typically requires notifying the tax authorities and the agent in writing that the POA is no longer in effect.
-
Do both parties need to sign the Form BT-129?
Yes, both the individual granting authority (the principal) and the appointed agent must sign the Form BT-129. Depending on the jurisdiction, the form might also need to be notarized or witnessed.
-
What happens if the appointed agent on Form BT-129 misuses their power?
If an agent misuses their power, they can be held legally accountable for their actions. The principal can revoke the POA and take legal action against the agent for any misconduct or harm caused.
-
Can a business use Form BT-129?
Yes, businesses can also use Form BT-129 to authorize someone to handle their tax matters. The form might be completed slightly differently for businesses, including providing information about the business and its authorized representative.
-
Where can one find Form BT-129?
Form BT-129 can usually be obtained from the local tax authority's office or website. Some tax preparation services and legal professionals can also provide this form and assist in filling it out correctly.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Tax Power of Attorney (POA) form is a critical step in managing your tax matters, allowing a person you trust, often a professional, to handle these affairs on your behalf. However, several common mistakes can complicate this process or render the form invalid. Awareness of these errors can ensure the form is completed accurately and effectively.
Not verifying the representative’s information: It’s imperative to ensure that the information related to the representative, including their name, address, and phone number, is accurate and current. Any discrepancy in this information can lead to communication issues with the taxation authority, potentially causing delays or misunderstandings.
Incorrectly specifying the tax matters: The form requires you to specify which tax matters and years the POA covers. A common mistake is either providing vague descriptions or incorrect years, limiting the representative’s ability to act effectively or covering periods not intended by the taxpayer.
Omitting the taxpayer’s details: Sometimes, in the rush to complete the form, taxpayers may forget to include essential information such as their full legal name, Social Security Number (SSN), or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN). This omission can result in the form being rejected or significant delays.
Failing to revoke previous POAs: If you have previously granted a POA for the same tax matters to another individual but wish to replace them with a new representative, it is necessary to formally revoke prior authorizations. Failing to do so can lead to confusion and conflicting instructions to the taxation authority.
Not signing or dating the form: Perhaps the simplest yet most critical step is properly signing and dating the form. An unsigned or undated form is typically considered invalid, which means the representative cannot take any action on your behalf until the oversight is corrected.
Ensuring these common mistakes are avoided can streamline the process, allowing your representative to act on your behalf without unnecessary delays or complications.
Documents used along the form
When navigating the complexities of tax matters, the Tax Power of Attorney (POA) Form BT-129 plays a crucial role by authorizing an individual, usually a tax professional, to handle tax affairs on behalf of someone else. It's an essential document for ensuring that tax-related matters are handled effectively and according to the individual's wishes. Often, handling tax affairs requires more than just the Tax POA. Several other forms and documents frequently complement the Tax POA to ensure thorough management and compliance with tax laws and regulations.
- IRS Form 2848, Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative: This form allows individuals to authorize someone else, usually a tax attorney or accountant, to represent them before the IRS, making it a crucial document for tax matters at the federal level.
- Form W-9, Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification: Often used in conjunction with the Tax POA, this form is necessary for verifying the taxpayer's identification number or Social Security Number, crucial for accurate tax reporting.
- Form 4506-T, Request for Transcript of Tax Return: This document allows individuals or their authorized representatives to request a transcript of their tax returns, which is often necessary for loan applications, financial verifications, or legal matters.
- Form 8821, Tax Information Authorization: Similar to the Tax POA, this form authorizes any individual or organization to inspect and/or receive confidential tax information, though it does not allow them to represent the taxpayer.
- Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return: As the standard federal income tax form used by citizens, it's often the subject of representation or discussion by the authorized representative under a Tax POA.
- State-specific Tax Power of Attorney Forms: Many states have their own versions of the Tax POA for state tax matters, requiring separate authorization to handle state tax issues.
- Annual Filing Season Program Record of Completion: For professionals authorized under a Tax POA, having this record can enhance their credibility by demonstrating their commitment to maintaining current knowledge of tax laws and regulations.
Each of these documents serves a specific purpose in the broader context of managing tax affairs. From designating a representative to dealing with the IRS, to ensuring correct taxpayer identification and accessing tax return information, these documents collectively ensure a comprehensive approach to tax management. Whether for individual or business tax matters, understanding and utilizing these documents in conjunction with the Tax POA can significantly streamline the process, ensure compliance, and safeguard the taxpayer's interests.
Similar forms
The Tax Power of Attorney (POA) form BT-129 is quite similar to a General Power of Attorney document in the sense that it allows an individual to grant authority to another person to handle certain affairs on their behalf. However, while the General Power of Attorney can be broad, encompassing a wide range of personal, business, and financial decisions, the Tax POA is specifically designed for tax-related matters. This includes authority to access confidential tax information and make decisions regarding taxes on behalf of the grantor.
Another document akin to the Tax POA is the Healthcare Power of Attorney. This document permits an individual to appoint someone else to make healthcare decisions for them, should they become unable to do so. Although it covers a completely different area of one’s life, the similarity lies in the specific delegation of decision-making authority. Both types of POA allow individuals to choose someone they trust to act in their best interests within a defined scope, healthcare for one and tax matters for the other.
The Limited Power of Attorney shares a strong resemblance with the Tax POA, as both specify a confined scope of authority. The Limited Power of Attorney allows individuals to grant someone else the power to act on their behalf for a particular purpose or event, often for a short duration. Similarly, the Tax POA provides someone else authority but strictly confines this to tax-related activities, highlighting the main similarity in their limitation of scope and purpose.
Similar to the Tax POA, the Durable Power of Attorney is designed to remain in effect even if the grantor becomes incapacitated. However, the Durable Power of Attorney encompasses a broader range of powers that can include making financial and medical decisions, among others, not just those pertaining to taxes. The similarity here is in its durability; both documents ensure representation for the individual, albeit in different capacities, should they be unable to make decisions for themselves.
Finally, the Financial Power of Attorney is closely comparable to the Tax POA form in that it specifically deals with a person's financial matters, including but not limited to tax issues. The Financial Power of Attorney grants someone the right to handle financial transactions, manage bank accounts, and make investment decisions. The key similarity lies in its focus on financial affairs, with the Tax POA being a more specialized form that zeroes in on tax-related matters within the broader financial arena.
Dos and Don'ts
When you're tasked with filling out the Tax Power of Attorney (POA) Form BT-129, accuracy and completeness are crucial. This form allows you to grant someone else the authority to handle your tax matters, which can include talking to the tax department, getting information, and making decisions on your behalf. To ensure that this process goes smoothly, here are eight dos and don'ts to keep in mind:
- Do ensure that all information provided on the form is accurate and up to date. Mistakes can lead to delays or misunderstandings.
- Do clearly identify the individual or organization you're appointing as your representative. This includes their full name, address, and phone number.
- Do specify the tax matters and years for which the authorization applies. Being precise helps avoid any confusion regarding the extent of the powers granted.
- Do sign and date the form. An unsigned form is invalid.
- Don't leave any sections incomplete. Each question on the form provides important information that's necessary for legal and administrative purposes.
- Don't appoint a representative who is not trustworthy or lacks the appropriate knowledge and skills to handle your tax matters effectively.
- Don't forget to revoke any previous POA forms if you are naming a new representative to avoid any confusion about who has the authority.
- Don't ignore the instructions that come with the form. They provide valuable guidance on how to fill out the form correctly and what steps to take afterwards.
By following these guidelines, you will ensure that your Tax Power of Attorney Form BT-129 is filled out correctly and effectively grants the necessary authority to your chosen representative. This careful attention to detail can help prevent future legal or financial issues related to your tax matters.
Misconceptions
When navigating the complexities of tax documentation, individuals often find themselves entangled in misconceptions about specific forms, such as the Tax Power of Attorney (POA) Form BT-129. Clear comprehension of this document is crucial for effective tax management and legal representation. Here are eight common misconceptions about the Tax POA Form BT-129, demystified:
- It grants unlimited power: A common misconception is that the Tax POA Form BT-129 provides the agent with unlimited power over the principal's tax matters. In reality, the scope of authority is specifically outlined within the form, limiting the agent's actions strictly to those tax-related activities the principal has authorized.
- It's effective indefinitely: Many believe once the Tax POA Form BT-129 is signed, it remains effective indefinitely. This is incorrect. The form usually specifies the duration for which it is valid, or it may be terminated upon the completion of certain conditions or events specified within the document.
- Only for individuals with complex tax situations: Another misconception is that the Tax POA Form BT-129 is only necessary for individuals with complex tax situations or large estates. However, anyone may require this form to authorize a representative, for a variety of reasons such as travel, illness, or convenience.
- It requires legal expertise to complete: While it's advisable to consult with a tax professional or attorney when dealing with legal documents, the Tax POA Form BT-129 is designed to be straightforward. Individuals can complete it without requiring extensive legal knowledge, provided they follow the instructions carefully.
- It's only for elderly or incapacitated individuals: There's a false belief that the Tax POA is exclusively for elderly or incapacitated persons. In truth, any individual, regardless of age or health status, might find it beneficial to delegate the authority to manage tax affairs to a trusted representative.
- It allows the agent to transfer POA to someone else: Some think that once someone is granted power of attorney through Form BT-129, they can transfer that authority to another person. This is inaccurate; the power of attorney cannot be transferred unless the original document explicitly allows it, which is uncommon.
- It's the same as a general POA: People often confuse the Tax POA Form BT-129 with a general power of attorney. The Tax POA is specifically for tax purposes and does not grant the agent authority over other aspects of the principal's personal or financial matters.
- All family members can use one form: A final misconception is that a single Tax POA Form BT-129 can cover all family members. In reality, each individual must complete their own form to authorize representation for their tax matters separately.
Dispelling these misconceptions is essential for individuals to make informed decisions regarding their tax affairs and representation. Careful consideration and proper action regarding the Tax POA Form BT-129 can ensure that tax matters are handled accurately and legally, reflecting the principal's best interests.
Key takeaways
Understanding the purpose of the Tax POA (bt-129) form is crucial. This document grants another person or entity the authority to handle your tax matters with the tax authority. It's typically used when individuals need a professional to discuss, dispute, or negotiate taxes on their behalf.
Completing the form accurately is paramount. Ensure all the required fields are filled out with current and correct information. This includes your personal information, the designated representative’s details, and the specific tax matters and years you are authorizing them to handle.
Choosing the right representative is critical. The individual or firm you select should have the necessary knowledge and experience in tax matters similar to yours. Their competence and integrity will directly influence the outcome of your tax issues.
Be specific about the powers you are granting. The form allows you to specify the tax issues and periods for which the representative will have authority. Limiting this scope as needed can provide you with additional peace of mind.
The duration of the power of attorney should not be overlooked. Although some forms may grant an indefinite period, it’s wise to specify a termination date or condition to ensure that the power is only in effect for as long as necessary.
Filing the completed form according to the instructions is essential. This may involve sending it to a specific office or department. Ensure it is received and processed by following up if necessary, as failing to do so may result in delays or a lack of representation.
Popular PDF Documents
IRS 1065 - By filing this form, partnerships provide transparency to the IRS, building a foundation of trust and compliance.
Irs Form 4506 - Meet your career goals in real estate appraisal by adhering to the application requirements set forth in State Form 45016.