Get Sbi Education Loan Form
Navigating the journey towards securing an education loan can be a crucial step for many students aiming to further their education. At the forefront of facilitating this process in India, the State Bank of India (SBI) offers a comprehensive Education Loan Application cum Appraisal Form, designed to gather all necessary particulars for loan consideration. This form demands detailed personal information from both the student and their parent or guardian, encompassing full names, detailed addresses, employment details, and educational qualifications, ensuring a thorough evaluation process. Financial information is meticulously collected, including monthly salaries, other incomes, and details of any immovable properties or securities offered as collateral. In addition, the form queries the proposed course of study, providing insights into the course details, the institution’s reputation, and the expected outcomes upon completion. The loan request section requires a breakdown of the course's costs against potential funding sources, ensuring transparency and planning. Notably, the form also seeks information on any existing loans and outlines the required documents for submission, ranging from academic records to financial statements and collateral security documents. Declarations by the applicant reinforce the accuracy and honesty of the information provided, a crucial aspect for the bank's appraisal process. Overall, the SBI Education Loan form stands as a pivotal document, initiating a bridge towards educational aspirations, underlined by a formal process seeking comprehensive, accurate details from the applicants.
Sbi Education Loan Example
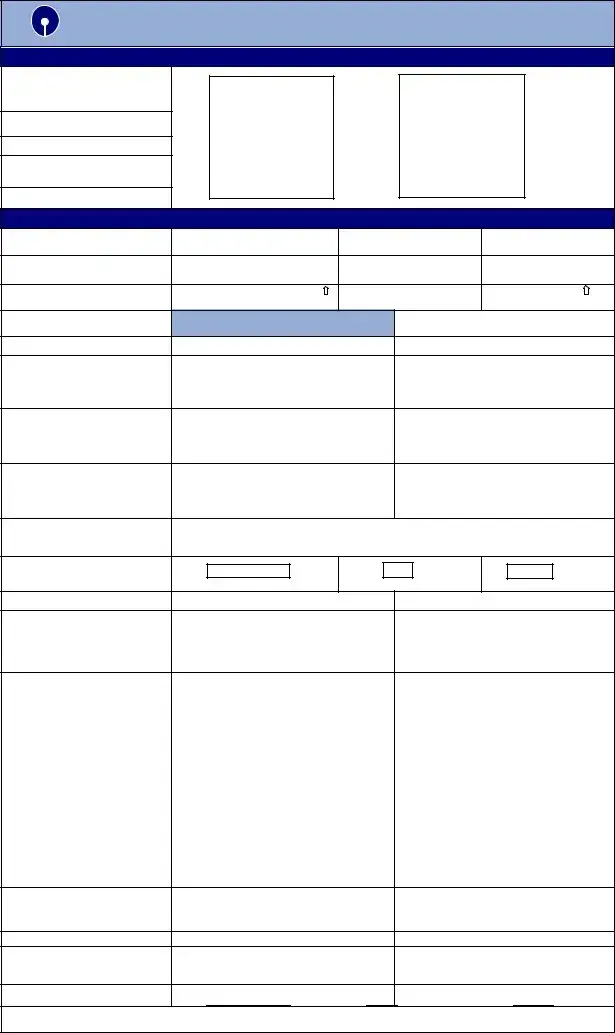
STATE BANK OF INDIA EDUCATION LOAN
APPLICATION CUM APPRAISAL FORM FOR EDUCATION LOAN
(PLEASE COMPLETE ALL PARTICULARS IN
BLOCK LETTERS AND TICKBOXES
WHEREEVER APPLICABLE)
CIF NO.(FOR OFFICE USE)
Signed photograph of Student
Signed photograph of Parent /
Guardian
ACCOUNT N0.(FOR OFFICE USE)
(1) PERSONAL INFORMATION OF THE APPLICANTS
Name in full of the Student
Name in full
MIDDLE NAME ( Father / Husband |
) |
FIRST NAME |
SURNAME |
Relationship with the student
PARTICULARS |
|
Student |
|
|
|
Parent / Guardian |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.Detailed Residential Address (House No., Road Name, Locality, City, PIN, District, State)
2.Office Address (House No., Road Name, Locality, City, PIN, District, State)
3.Permanent Residential Address (House No., Road Name, Locality, City, PIN, District, State)
4.The name in which the correspondence should be addressed ( Mention 1st or 2nd applicant)
5. Address for correspondence of (tick appropriate box)
Residential Address |
Office address |
Permanent Address |
6.E mail address
7.Date of birth ( DD / MM / YYYY)
8. |
Age |
|
|
Years |
|
|
Months |
|
|
Years |
|
|
|
Months |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9. |
Telephone Number ( Office & Residence) |
Office |
Residence |
Office |
|
|
Residence |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
9.A. Whether personal telephone is owned, if not the type of relationship with the owner :
10. |
Mobile No. |
|
|
|
Fax No. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fax No. |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11. |
Sex |
|
|
|
M |
|
|
F |
|
|
|
M |
|
|
|
F |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12. |
Marital Status ( Please also tick Single if no |
|
|
|
Single |
|
|
Married |
|
|
|
Single |
|
|
Married |
|||||||
living spouse) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13. |
Residential Status ( indicate date of |
|
|
|
|
|
Resident |
|
|
NRI / PIO |
|
|
|
Resident |
|
|
NRI / PIO |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
permanent return, if any) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14. |
Type of Identification Proof (Please indicate (a) |
|
|
|
|
Voter ID No. |
|
(a) |
|
|
Voter ID No. |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
name of the document at ( d), if any |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
(b) |
|
|
|
|
Pass Port No. |
|
(b) |
|
|
Pass Port No. |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
( c ) |
|
|
|
|
PAN |
|
( c ) |
|
|
PAN |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
(d) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.a. Particulars of Identification Proof, Issue date, place, expiry date,etc.
15.If you don't have PAN, reasons thereof
16. |
Do you belong to |
|
SC |
|
|
|
ST |
|
|
OBC** |
|
SC |
|
|
ST |
|
|
OBC** |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
17. |
Number of dependents |
|
|
Children |
|
|
Others |
|
Children |
|
|
|
Others |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
18 Educational / Professional qualifications
**If yes, please enclose proof thereof.

(2) FINANCIAL / INCOME INFORMATION OF THE PARENT / GUARDIAN
1. |
Monthly Gross Salary |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Monthly Net Salary |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
Particulars of deductions from gross salary |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
Other Income as per I.T. return |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
Annual Income as per I.T.return |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
(3) EMPLOYMENT DETAILS OF THE PARENT / GUARDIAN |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
Name of the employer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Name of the department |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
Designation & Employee No.(if available) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
No.of years of present employment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
Date of retirement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
(4) DETAILS OF SECURITY OFFERED |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) IMMOVABLE PROPERTY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Title deed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Estimated Market |
||
|
Plot / Flat / House No. |
|
|
|
|
|
In the name of |
|
Address |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
value |
||||||
|
|
|
|
Lease / Freehold |
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B) VEHICLE / CAR - Please give details |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
including registration number,etc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C) OTHER SECURITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name of the Security |
|
Serial No. |
|
|
|
Name of the holder |
|
Maturity value |
Estimated Market |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Value |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(5) DETAILS OF THE COURSE / STUDY |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
Name of the Proposed Course of Study |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Name of the Institution, University, Country |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
Reasons for selection of Institution / |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
University |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
Ranking of the Institution or course |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
Duration of course |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. |
Date of commencement of course |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7. |
Expected monthly income of student after |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
completion of the course |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. |
Employment potential after |
completion |
of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
course |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(6) LOAN REQUEST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
COST OF THE COURSE |
|
|
|
|
|
SOURCES |
|||||
1. |
Tution fees |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Details of non repayable studentship / |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fellowship, etc. available to the Student |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Essential Books, Stationery, |
equipments, |
if |
|
|
|
2. |
Details of |
|
repayable studentship |
/ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
any |
|
|
|
|
|
fellowship, etc. available to the Student |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
Examination fees |
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
Details of |
funds available from family |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
sources for the course |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
Maintenance expenditure |
|
|
|
|
|
4. Amount of loan applied for |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
5. |
Insurance premia for the duration of loan and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
start up period |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL (Should tally with the sources) |
|
|
|
|
TOTAL (Should tally with the cost) |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

(7) DETAILS OF FINANCIAL WORTH OF THE PARENT / GUARDIAN
PARTICULARS |
|
|
Details ( Bank, branch, etc.) |
|
Amount (Rupees ) |
|
|
Bank's assessment |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Savings in Bank (Savings Bank + |
Fixed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Deposits) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1.a. How long the Account has been maintained |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Immovable property |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Current PF balance(Your share) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Investment in NSCs/Share / Debentures / |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
bonds, etc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
5. Jewellary / gold ornaments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. LIC / Postal life, etc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7. Capital in various firms (your share), |
HUF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
share and Share in Associate Concern |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8) ADDITIONAL DETAILS OF BANK ACCOUNTS OF THE PARENT / GUARDIAN |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name of the a/c holder |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Type of a/c |
|
|
Name of Bank and branch |
|
|
A/c Number |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(9) DETAILS OF EXISTING LOANS ( FROM STATE BANK OF INDIA OR OTHER BANKS) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purpose |
|
|
Bank Name / other details and a/c No. |
Date of loan |
|
Loan Amt |
|
|
Present |
Mode of payment |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
outstandings |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Housing loan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Car loan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PF Loan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Borrowings from friends and relatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Credit Society |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Others (Please specify) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other details |
|
|
|
EMI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Details of security charged |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Housing loan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Car loan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PF Loan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Borrowings from friends and relatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Credit Society |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Others (Please specify) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(10) PROPOSED / PREFERRED REPAYMENT AND PAYMENT OF INTEREST |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mode of Repayment (How many months or how many EMIs ?) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Payment of full interest as and when applied during the |
|
|
No interest will be paid during |
|||||||||
|
By Student |
|
|
By Guardian |
|
|
|
|
moratorium |
|
|
|
moratorium |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(11) GENERAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Do you have an existing relationship with SBI, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
if so, details thereof |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
4. Do you wish to open a Savings Bank with SBI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. Is any guarantee given to SBI/Other bank |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If yes, details |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
|
|
No. |
thereof |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(12) DOCUMENTS REQUIRED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mark sheet of last qualifying examination for school and graduate studies in India |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Copies of letter conferring scholarship, free ship, etc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Documents evidencing duration of course of |
commencement |
thereof, viz. Prospectus or |
Certificate from the competent |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
authority of the Institution. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Copy of ranking of the University / Institution |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proof of admission to the course |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Schedule of expenses for the course |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Two copies of pass port size photograph of the student / parent/ guardian /guarantor |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Salary certificate & form 16 of previous year ( in case of employed) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I.T.Returns for the last 2 years ( if I.T.Assessee) duly accepted by the ITO |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Statement of bank account for the last six months of the guardian / parent |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Original sale deed and other document of title to property in respect of immvoable property offered as collateral security.
Proof of residnece ( identity Card / Passport / Voter Identification Card / Driving licence
Tax paid receipts etc. (Advance IT / Property Tax / Municipal Tax, etc.)
Others
DECLARATION
I / We hereby apply for a loan from State Bank of India to the extent indicated in the Loan Request Section of this application form. I / We declare that the foregoing particulars and information furnished in this application form are true, accurate and complete and that they shall form the basis of any loan State Bank of India may decide to sanction to me / us. I / We confirm that I / We have / had no insolvency proceedings against me / us. Nor have, I / We been adjudicated insolvent. I / We further confirm that I
/We have read the terms and conditions and understood the contents therein. I / We am / are aware that if I / We opt for loan at floating rates of interest, the Equated Monthly Instalment will comprise Principal and Interest based on State Bank Advance Rate which is subject to change from time to time.
I / We agree that State Bank of India may at its discretion conduct discreet inquiries in respect of this application. I / We undertake to inform as to any change in my / our occupation / employment, residential address and to provide any further information that the Bank may require. State Bank of India will be at liberty to take such action as it may deem necessary if my / our above statements are found to be untrue. I / We agree that State Bank of India shall have the sole discretion to reject / reduce loan amount / our loan application without assigning any reason thereof. I / We further agree that my / our loan transactions shall be governed by the rules of State Bank of India which may be in force from time to time. I also hereby give my consent to send the application to RACPC for sanction if in order and disbursement on sanction from RACPC or any Branch as per process prescribed by State Bank of India. I may carry out future transactions at the above mentioned Branch as Home Branch.
|
|
Signature of the student |
|
|
|
|
Signature of the Guardian |
|||
|
|
Place |
|
|
|
|
Place |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
17. FOR OFFICE USE ONLY |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Signature/s of the applicant/s obtained in our presence and verified and sent to RACPC |
|
|
|
||||
At Branch / OSF - |
|
|
on ______________ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name & Signature ( Branch / OSF) |
||
At RACPC ( Data related |
|
VIP Code ( 0 for No , 1 for |
|
Customer |
|
Relative |
Code |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
to CIF Creation) |
|
|
Yes) |
|
Type |
- |
|
(father / spouse) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Personal |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Greetings required |
|
|
|
|
Occupancy |
|
Customer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(home |
owner, |
|
evaluation required |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tenant,etc.) |
|
|
|
|
|
CIS Organization code |
|
|
|
|
Segment Code |
|
CIBIL Reference |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
made |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Date _______________ |
|
|
|
SIGNATURE OF THE |
APPRAISING OFFICER |
||||
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Details |
|---|---|
| Form Purpose | Application cum appraisal form for education loan. |
| Applicant Personal Information | Includes detailed residential, office, and permanent addresses, along with contact information and personal details like date of birth, marital status, etc. |
| Financial Information of the Parent/Guardian | Contains sections on monthly gross/net salary, other income, and annual income as per tax returns. |
| Employment Details of the Parent/Guardian | Details about the employer, department, designation, employee number, years of present employment, and date of retirement. |
| Details of Security Offered | Information on immovable property, vehicles/cars, and other securities being offered as collateral. |
| Course/Study Details | Includes the name of the course, institution, reasons for selection, ranking, duration, and expected employment potential. |
| Loan Request Details | Specifies the cost of the course, sources of funds, and the amount of loan applied for. |
| Financial Worth of the Parent/Guardian | Outlines the parent’s/guardian's financial assets, including bank savings, immovable property, investments, etc. |
| Documents Required | List of documents required for the loan application, including mark sheets, income proof, property documents, and others. |
| Declaration and Consent | Applicant and guardian must declare the accuracy of information provided and consent to the terms and conditions of the loan. |
Guide to Writing Sbi Education Loan
Filling out the State Bank of India Education Loan Application Form is a significant step towards financing your education and achieving your dreams. This form is detailed, intending to capture all relevant information about the student and the parent or guardian. It includes personal, financial, educational, and course-related details, as well as required documentation to support the loan application. To ensure a smooth process, it's crucial to fill out the form accurately and thoroughly. Here are step-by-step instructions to guide you through each section of the form:
- Start with Section 1 (Personal Information of the Applicants):
- Enter the full name of the student and the parent/guardian in block letters.
- Provide the detailed residential, office, and permanent addresses.
- Choose the address for correspondence and provide the email address, date of birth, telephone and mobile numbers for both the student and the parent/guardian.
- Indicate sex, marital status, residential status, and type of identification proof along with its particulars.
- If applicable, mark the box corresponding to your category (SC, ST, OBC) and include the number of dependents.
- Move to Section 2 (Financial/Income Information of the Parent/Guardian):
- Fill in the monthly gross and net salary, particulars of deductions from gross salary, other income, and annual income as per IT return of the parent/guardian.
- Fill out Section 3 (Employment Details of the Parent/Guardian):
- Detail the employment information including the name of the employer, department, designation, employee number, years of present employment, and date of retirement.
- Complete Section 4 (Details of Security Offered) if applicable:
- Provide information about any immovable property, vehicle/car and other securities being offered as collateral for the loan.
- In Section 5 (Details of the Course/Study):
- Include the name of the proposed course of study, the institution, reasons for selecting the institution/university, ranking, duration of course, date of commencement, expected monthly income after completion, and employment potential.
- Proceed to Section 6 (Loan Request Cost of the Course / Sources):
- Detail the financial requirements including tuition fees, books, examination fees, maintenance expenditure, and insurance premium, as well as the sources of funds.
- Fill Section 7 (Details of Financial Worth of the Parent/Guardian):
- Provide information about savings in bank, immovable property, current PF balance, investments, jewelry/gold ornaments, and other financial assets.
- Provide Section 8 (Additional Details of Bank Accounts of the Parent/Guardian):
- Include details of the bank accounts held by the parent/guardian.
- In Section 9 (Details of Existing Loans):
- Detail any existing loans including purpose, bank name/details, date of loan, loan amount, present outstandings, mode of payment, and details of security charged.
- Complete Section 10 (Proposed / Preferred Repayment and Payment of Interest):
- Indicate the preferred mode of repayment and how interest will be handled during the moratorium period.
- Answer questions in Section 11 (General) regarding your existing relationship with SBI, wishes to open an SBI Savings Bank account, and if any guarantees are given to SBI or other banks.
- Review the Documents Required list and ensure you have all necessary documentation ready to submit with the application.
- Carefully read the Declaration at the end of the form, and once satisfied, sign the application form along with the guardian at the designated places. Make sure to fill in the place and date.
Once all sections are completed and documents are gathered, submit the application form to the designated State Bank of India branch for processing. Remember, providing accurate and complete information will facilitate a smoother loan approval process.
Understanding Sbi Education Loan
What is the State Bank of India Education Loan Application cum Appraisal Form?
This form is used by individuals who are seeking financial assistance for educational purposes from the State Bank of India (SBI). It gathers comprehensive information about the applicant and their parent or guardian, including personal, financial, and course-related details, to evaluate the loan application.
Who needs to fill out this form?
Students looking to pursue further education and require financial support to cover their educational expenses should fill out this form. It must also be accompanied by the relevant financial and personal details of the applicant's parent or guardian.
What sections does the form include?
- Personal Information
- Financial/Income Information of the Parent/Guardian
- Employment Details of the Parent/Guardian
- Details of Security Offered
- Details of the Course/Study
- Loan Request and Sources of Funds
- Details of the Financial Worth of the Parent/Guardian
- Additional Details of Bank Accounts of the Parent/Guardian
- Details of Existing Loans
- Proposed/Preferred Repayment and Payment of Interest
- General Information
- Documents Required
- Declaration
What documents are required along with the form?
Applicants need to provide academic records, proof of admission, financial documents, and any supporting documents for scholarships or fellowships. Also required are identification proofs, photographs, and any collateral security documentation if applicable.
How is the applicant's eligibility determined?
Eligibility is determined based on the financial information provided by the parent or guardian, the academic credentials of the student, the reputation of the institution, and the potential earning capacity upon course completion.
What is the importance of stating the relationship with SBI, if any?
Declaring an existing relationship with SBI can assist in the loan approval process, as it may reflect the applicant's or the parent/guardian's financial reliability and trustworthiness based on their banking history with the bank.
Can students studying abroad apply for this loan?
Yes, students aiming to pursue their studies abroad can apply for an education loan using this form. They need to provide details of the overseas institution and the course, along with other mandatory information.
What are the repayment terms?
The form asks applicants to mention their preferred mode of repayment and whether they plan to pay interest during the study period. The actual repayment terms, including duration and EMIs, will be finalized based on the loan agreement with SBI.
Is there any special consideration for students belonging to SC/ST/OBC categories?
Applicants belonging to SC/ST/OBC categories are required to indicate their background in the form and may be eligible for certain governmental schemes or concessions as per SBI's policies and the loan scheme criteria.
Common mistakes
Failing to complete all sections in BLOCK LETTERS can lead to misunderstandings or delays. The form clearly instructs applicants to fill it out in block letters, which enhances readability.
Not ticking the appropriate boxes, especially in sections like correspondence address preferences, misunderstands the applicant's intentions.
Omitting the personal information section, including the detailed residential and office addresses, reduces the bank's ability to communicate effectively.
Ignoring financial/income information of the parent/guardian can lead to an incomplete assessment of eligibility for the education loan.
Forgetting to attach identification proof or not specifying the type, such as Voter ID, Passport, or PAN, can halt the application process.
Incorrectly filling out the loan request cost and sources section may misrepresent the financial requirement and availability, affecting the loan sanction process.
Leaving the course details, including name, institution, and expected monthly income after completion, blank or partially filled, might lead to an undervaluation of the education's worth.
Not detailing the collateral security offered under the security details, if any, can lead to a rejection or delay in loan processing.
Providing incomplete or inaccurate information in the existing loans section misrepresents the applicant's financial obligations and may affect the loan's approval.
Attention to detail and thorough review before submission can significantly improve the likelihood of a successful education loan application with the State Bank of India.
Documents used along the form
When applying for an education loan with the State Bank of India (SBI), the application form is a comprehensive document designed to gather extensive information from the applicant. To support the information provided and comply with the bank's requirements, several other forms and documents are often needed. These additional documents play a critical role in ensuring the application process is thorough, enabling the bank to assess the applicant's eligibility and financial capacity accurately.
- Admission Letter: This document from the educational institution confirms the student's admission to the course. It typically includes details such as the course name, duration, and commencement date.
- Academic Records: Transcripts and mark sheets from previous educational qualifications (e.g., high school, undergraduate degree) are required to establish the student's academic history and performance.
- Scholarship Documents: If the student has been awarded a scholarship, documents confirming the scholarship amount and terms are needed. This information is essential for calculating the loan amount.
- Income Proof of the Parent/Guardian: Documents such as salary slips, tax returns, and proof of other income sources of the parent or guardian are required to assess the repayment capacity.
- Bank Account Statements: Recent bank statements of the parent or guardian are needed to examine the financial health and transaction history.
- Pan Card: A copy of the PAN card of the student and the parent/guardian serves as an identity and financial status check.
- Proof of Identity and Address: Valid government-issued documents like passports, voter ID cards, or driving licenses are required for both student and parent/guardian to verify identity and residency.
- Affidavit of Claim: In some cases, an affidavit stating that no other education loan has been availed or that the student does not have any pending legal liabilities can be asked for.
- Collateral Documents: If the education loan requires collateral, documents related to the collateral (like property deeds, valuation reports, etc.) need to be submitted for legal verification and valuation.
Together, these documents supplement the SBI Education Loan Application Form, enabling the bank to have a holistic view of the applicant's background, financial situation, and the educational course undertaken. Accurate and timely submission of these documents facilitates a smoother loan approval process, helping students to embark on their educational journeys without undue financial strain.
Similar forms
An auto loan application form shares similarities with the SBI Education Loan form by requiring personal information about the applicant, such as name, address, contact details, and employment information. Both forms assess an applicant's financial situation, including monthly income and other sources of income, to determine their ability to repay the loan. Just as the education loan form asks for details regarding the educational course and expenses, the auto loan form requires information about the vehicle being purchased, including its cost and details.
The mortgage application form, used when applying for a home loan, resembles the SBI Education Loan form in its requirement for comprehensive personal and financial information about the applicant. It includes details on income, employment, and existing debts, similar to the education loan form. Additionally, both forms demand information on the security offered for the loan, with the mortgage application focusing on the property to be purchased.
A personal loan application form is somewhat similar to the education loan form, focusing on the borrower's personal and financial information but used for a broader range of purposes. Both require details about employment, income, and existing debts to evaluate the applicant's repayment capacity. However, personal loan forms might not always ask for collateral information, unlike the education loan form which requires details on offered security.
The credit card application form seeks personal and employment information to establish creditworthiness, akin to the education loan application. Like the SBI form, credit card applications inquire about the applicant's income and existing loans or credits, aiming to understand their financial stability and ability to take on new debts. However, they generally involve less comprehensive details about financial resources and security.
Business loan application forms, though primarily aimed at businesses and entrepreneurs, share the essence of the education loan form in collecting detailed financial information. These forms require knowledge of the business's financial statements, current debts, and collateral, paralleling the education form in its scrutiny of the applicant's financial health and securities offered.
The scholarship application form, while not a loan form, necessitates thorough personal and academic information from applicants, echoing the education loan form's requirement for educational qualifications and the course's details. Both forms assess the potential benefits of the funding (loan or scholarship) towards the applicant's education and future career prospects.
The tenant application form is used by landlords to vet potential renters. It requests personal information, employment and income verification similar to the loan form, ensuring the applicant's ability to pay rent. Though it’s for housing, not a loan, the principle of assessing financial stability is shared with the SBI Education Loan form.
A grant application form, submitted by individuals or organizations seeking non-repayable funds, requires detailed project information and a financial plan, reflecting the Education Loan form's requirement for course and financial details. Both aim to assess the feasibility and financial planning of the proposed project or education pathway.
The investment account application form, for those looking to open brokerage or retirement accounts, gathers personal, employment, and financial information to comply with legal requirements and assess risk tolerance. Similar to education loan forms, these applications consider the individual's financial situation to tailor services accordingly.
Lastly, the debt consolidation loan application form, designed for individuals seeking to consolidate multiple debts into one loan, mirrors the SBI form in its collection of personal, financial, and employment information. It assesses the applicant's overall financial health, existing debts, and security offered for the loan to streamline their financial obligations.
Dos and Don'ts
Filling out the SBI Education Loan form correctly is crucial for a smooth application process. Here are ten dos and don'ts to keep in mind:
Do's:- Fill out the form in block letters to ensure legibility.
- Make sure to tick the appropriate boxes where applicable, indicating your selections clearly.
- Review the list of required documents carefully and ensure every document is complete and up to date.
- Provide a detailed residential address and, if different, a correspondence address.
- Include accurate financial information about the parent or guardian, including income details and any other income sources.
- Disclose any existing loans from SBI or other banks in the Details of Existing Loans section.
- Be honest about your educational background and professional qualifications.
- Read through the declaration section thoroughly before signing to ensure you understand the terms.
- Double-check the form for any errors or omissions before submitting.
- Make sure you understand the repayment and interest payment terms and select the option that best suits your situation.
- Do not leave any mandatory fields blank. If a section does not apply to you, mark it as N/A (Not Applicable).
- Avoid providing false or misleading information—this could lead to your application being rejected.
- Do not forget to sign and date the form in the designated areas for both the student and the guardian.
- Avoid overlooking the need for signatures on photographs and other required documents.
- Do not ignore the instructions regarding filling out the form in block letters and ticking the appropriate boxes where applicable.
- Avoid submitting outdated or expired identification documents. Always check the validity dates.
- Do not neglect to review the financial worth section for accuracy in reporting assets.
- Do not be vague about the course details; provide specific information about the institution, course duration, and employment potential post-completion.
- Avoid rushing through the form without reading the instructions and understanding each section.
- Do not forget to discuss the loan application with a co-applicant or guarantor beforehand, ensuring they are fully informed and agreeable.
Misconceptions
Many people have misconceptions about the State Bank of India (SBI) Education Loan application process, which can lead to confusion and misinformation. Here are eight common myths dispelled to help applicants understand the process better:
- Myth 1: Only students with exceptionally high grades qualify for an SBI Education Loan.
- Myth 2: The SBI Education Loan only covers tuition fees.
- Myth 3: You must have a bank account with SBI to apply for an Education Loan.
- Myth 4: You need to provide collateral for all SBI Education Loans.
- Myth 5: The student alone must repay the education loan.
- Myth 6: The interest rates for SBI Education Loans are fixed.
- Myth 7: SBI Education Loans are only for studying within India.
- Myth 8: Once the loan application is submitted, there is no need to interact with the bank until the loan is disbursed.
This is not true. While academic performance can be a factor in loan approval, SBI also considers other aspects like the potential income after course completion, the reputation of the institution, and the course of study. The decision is based on a comprehensive appraisal, not solely on academic achievements.
Contrary to this belief, the loan covers a wide range of expenses including books, equipment, examination fees, and even insurance premium for the student. The aim is to support the overall educational expenses to ease the financial burden on the student and their family.
Having an account with SBI is not a prerequisite for applying for an education loan. However, it might facilitate a smoother transaction and communication process. The bank encourages applicants to open an account for better service but does not make it mandatory.
Collateral is not required for all education loans. It depends on the loan amount and the creditworthiness of the applicant and their family. For loans below a certain threshold, which is subject to change, you might not need to provide any collateral.
This misconception overlooks the fact that the responsibility of loan repayment can also fall upon the parent or guardian. The repayment plan is often customized based on the financial situation of the student’s family, and in many cases, parents or guardians co-sign the loan and share the repayment responsibility.
Interest rates for education loans can be either fixed or floating, depending on the chosen scheme. This implies that the interest rate can change in accordance with the financial market conditions and RBI regulations. Applicants have the choice to opt for the type of interest rate they are comfortable with.
SBI offers education loans for studying abroad as well as within India. The bank has specific loan schemes designed to cater to students who aspire to study at foreign universities and institutions.
The process of loan approval involves various steps including verification of documents, appraisal of the financial status, and assessment of the loan amount needed. The bank may require additional documents or clarifications during this process. Hence, it's essential to maintain communication with the bank until the loan disbursement is complete.
Understanding these aspects of the SBI Education Loan process can make the application process smoother and more predictable for applicants, helping them to plan their education financing with more clarity and confidence.
Key takeaways
When applying for an education loan with the State Bank of India (SBI), it is crucial to prepare adequately and understand the process and requirements. Here are some key takeaways to consider when filling out the SBI Education Loan Application cum Appraisal Form:
- Complete all sections thoroughly: Every field in the SBI Education Loan application form must be filled out in block letters. It’s important to provide detailed and accurate information in every section, including personal, educational, and financial details.
- Prepare necessary documents: Alongside the application, several documents need to be submitted, including signed photographs of the student and the parent/guardian, proof of identity, proof of residence, and academic records. Preparing these documents in advance can significantly streamline the application process.
- Demonstrate financial eligibility: The financial/income information of the parent or guardian plays a critical role in the appraisal process. Accurate details regarding monthly gross and net salary, other sources of income, and annual income as per I.T. returns should be meticulously documented.
- Provide details about the course and institution: The form requires specific information about the course of study, including the name of the institution, the duration of the course, and expected employment opportunities post-completion. Selecting a reputable institution and course can positively impact the loan appraisal.
- Understand loan terms and repayment options: The application form outlines repayment terms and interest payment options. Applicants should carefully review these sections to understand their obligations and choose a repayment plan that suits their future financial outlook.
By keeping these key points in mind, applicants can ensure a smoother process when applying for an education loan with the State Bank of India, paving the way for their academic and professional growth.
Popular PDF Documents
Trillium Drug Program Application Online - A simplified guide for seniors 65 and older in Ontario to apply for reduced prescription medication costs, detailing both the application process and eligibility criteria.
Purchase Requisition - Submitting this form kicks off the review process to ensure the purchase aligns with company goals.
How Much Does It Cost to Register a Business in Texas - The Texas SOS Payment 807 form is designed for processing various document requests with options for expedited or regular handling.