Get Sample Tax Return Transcript Form
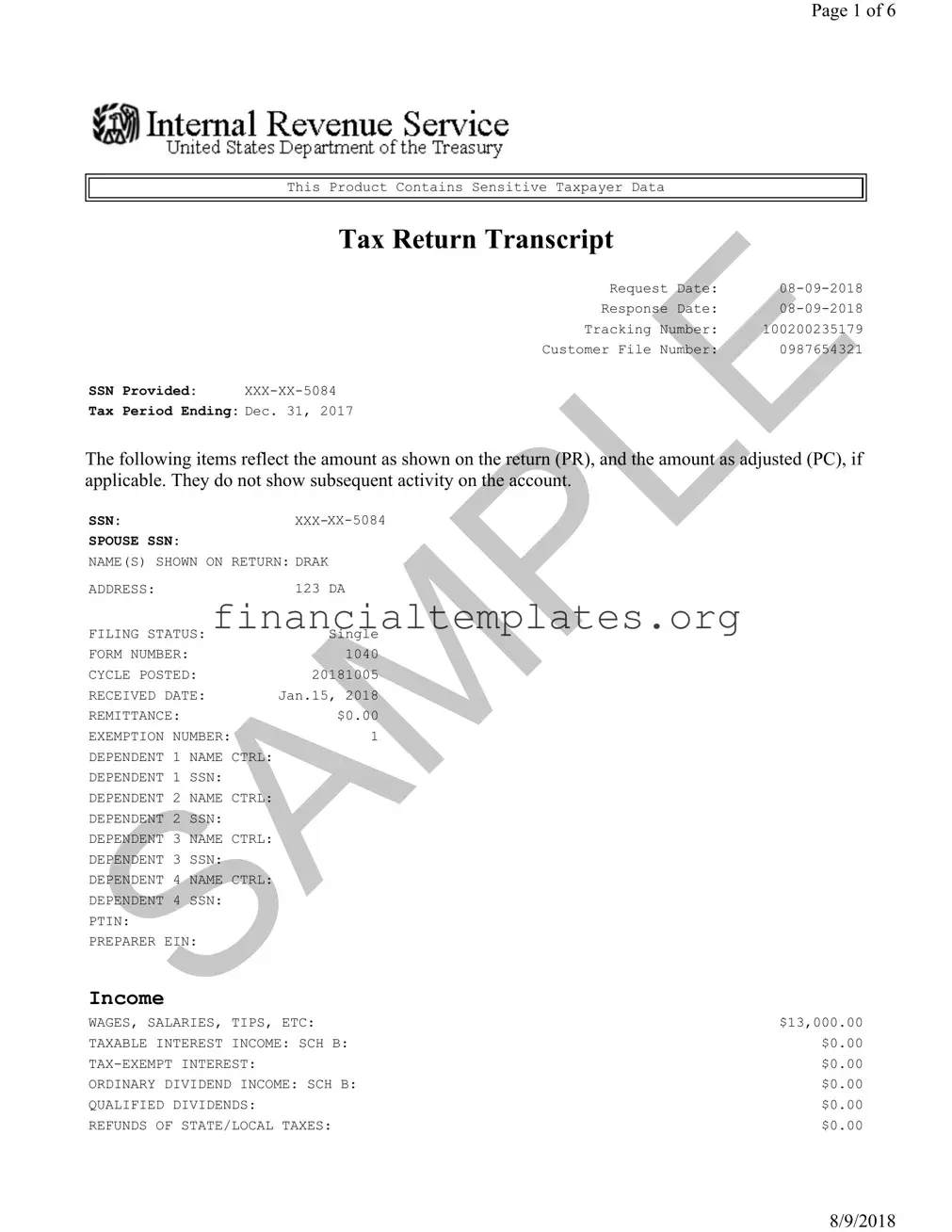
When navigating the complexities of tax documentation, understanding the Sample Tax Return Transcript form is essential for individuals seeking a comprehensive overview of their tax return details. This form, a snapshot provided by the IRS, includes critical data such as the request and response dates, tracking and customer file numbers, and the sensitive Social Security Numbers (SSNs) of the taxpayer and possibly their spouse, carefully redacted to ensure privacy. It summarizes the tax period ending on December 31, 2017, displaying key information like the filer’s name, address, filing status, and the detailed breakdown of income sources and adjustments. From wages, salaries, and tips to business income or loss and taxable interest, the form meticulously records initial amounts, adjustments if any, and the computed totals. Also outlined are deductions, tax credits, other taxes, and payments, culminating in the calculation of the return's outcome—whether there’s an amount owed or a refund due. Additionally, it includes specific sections for third-party designees, indicating whether another individual is authorized to discuss the return with the IRS. This document does not capture post-return activities but is invaluable for understanding the fundamental components of an individual's tax return, highlighting its importance for accurate tax filing and planning.
Sample Tax Return Transcript Example

Page 1 of 6
This Product Contains Sensitive Taxpayer Data
Tax Return Transcript
|
Request Date: |
|
|
Response Date: |
|
|
Tracking Number: |
100200235179 |
|
Customer File Number: |
0987654321 |
SSN Provided: |
|
Tax Period Ending: Dec. 31, 2017
The following items reflect the amount as shown on the return (PR), and the amount as adjusted (PC), if applicable. They do not show subsequent activity on the account.
SSN: |
|
|
SPOUSE SSN: |
|
|
NAME(S) SHOWN ON RETURN: DRAK |
||
ADDRESS: |
|
123 DA |
FILING STATUS: |
Single |
|
FORM NUMBER: |
|
1040 |
CYCLE POSTED: |
20181005 |
|
RECEIVED DATE: |
Jan.15, 2018 |
|
REMITTANCE: |
|
$0.00 |
EXEMPTION NUMBER: |
1 |
|
DEPENDENT 1 |
N ME CTRL: |
|
DEPENDENT 1 |
SSN: |
|
DEPENDENT 2 |
N ME CTRL: |
|
DEPENDENT 2 |
SSN: |
|
DEPENDENT 3 |
N ME CTRL: |
|
DEPENDENT 3 |
N: |
|
DEPENDENT 4 |
N ME CTRL: |
|
DEPENDENT 4 |
N: |
|
PTIN: |
|
|
PREPARER EIN: |
|
|
Income
WAGES, SALARIES, TIPS, ETC: |
$13,000.00 |
TAXABLE INTEREST INCOME: SCH B: |
$0.00 |
$0.00 |
|
ORDINARY DIVIDEND INCOME: SCH B: |
$0.00 |
QUALIFIED DIVIDENDS: |
$0.00 |
REFUNDS OF STATE/LOCAL TAXES: |
$0.00 |
8/9/2018
Page 2 of 6
ALIMONY RECEIVED: |
|
$0.00 |
BUSINESS INCOME OR LOSS (Schedule C): |
|
$2,500.00 |
BUSINESS INCOME OR LOSS: SCH C PER COMPUTER: |
|
$2,500.00 |
CAPITAL GAIN OR LOSS: (Schedule D): |
|
$0.00 |
CAPITAL GAINS OR LOSS: SCH D PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
OTHER GAINS OR LOSSES (Form 4797): |
|
$0.00 |
TOTAL IRA DISTRIBUTIONS: |
|
$0.00 |
TAXABLE IRA DISTRIBUTIONS: |
|
$0.00 |
TOTAL PENSIONS AND ANNUITIES: |
|
$0.00 |
SAMPLE |
$0.00 |
|
TAXABLE PENSION/ANNUITY AMOUNT: |
|
|
RENT/ROYALTY/PARTNERSHIP/ESTATE (Schedule E): |
|
$0.00 |
RENT/ROYALTY/PARTNERSHIP/ESTATE (Schedule E) PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
RENT/ROYALTY INCOME/LOSS PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
ESTATE/TRUST INCOME/LOSS PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|
$0.00 |
|
FARM INCOME OR LOSS (Schedule F): |
|
$0.00 |
FARM INCOME OR LOSS (Schedule F) PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
UNEMPLOYMENT COMPENSATION: |
|
$0.00 |
TOTAL SOCIAL SECURITY BENEFITS: |
|
$0.00 |
TAXABLE SOCIAL SECURITY BENEFITS: |
|
$0.00 |
TAXABLE SOCIAL SECURITY BENEFITS PER COM UTER: |
|
$0.00 |
OTHER INCOME: |
|
$0.00 |
SCHEDULE EIC SE INCOME PER COMPUTER: |
|
$2,323.00 |
SCHEDULE EIC EARNED INCOME PER COMPUTER: |
$15,323.00 |
|
SCH EIC DISQUALIFIED INC COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
TOTAL INCOME: |
$15,500.00 |
|
TOTAL INCOME PER COMPUTER: |
$15,500.00 |
|
Adjustments to Income
EDUCATOR EXPENSES: |
|
$0.00 |
||
EDUCATOR EXPENSES PER CO PUTER: |
$0.00 |
|||
RESERVIST AND OTHER |
BUSINESS EXPENSE: |
$0.00 |
||
HEALTH |
VINGS |
CCT |
DEDUCTION: |
$0.00 |
HEALTH S VINGS |
CCT |
DEDUCTION PER CO PTR: |
$0.00 |
|
MOVING EXPENSES: F3903: |
$0.00 |
|||
SELF EMPLOYMENT T X DEDUCTION: |
$177.00 |
|||
SELF EMPLOYMENT T X DEDUCTION PER COMPUTER: |
$177.00 |
|||
ELF EMPLOYMENT T X DEDUCTION VERIFIED: |
$0.00 |
|||
KEOGH/ EP CONTRIBUTION DEDUCTION: |
$0.00 |
|||
$0.00 |
||||
EARLY WITHDRAWAL OF |
AVINGS PENALTY: |
$0.00 |
||
ALIMONY PAID |
N: |
|
|
|
ALIMONY PAID: |
|
|
$0.00 |
|
IRA DEDUCTION: |
|
|
$0.00 |
|
IRA DEDUCTION PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
|||
STUDENT LOAN INTEREST DEDUCTION: |
$0.00 |
|||
STUDENT LOAN INTEREST DEDUCTION PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
|||
STUDENT LOAN INTEREST DEDUCTION VERIFIED: |
$0.00 |
|||
TUITION AND FEES DEDUCTION: |
$0.00 |
|||
TUITION AND FEES DEDUCTION PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
|||
DOMESTIC PRODUCTION ACTIVITIES DEDUCTION: |
$0.00 |
|||
8/9/2018
Page 3 of 6
DOMESTIC PRODUCTION ACTIVITIES DEDUCTION PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
OTHER ADJUSTMENTS: |
|
|
$0.00 |
||
ARCHER MSA DEDUCTION: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
ARCHER MSA DEDUCTION PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
TOTAL ADJUSTMENTS: |
|
|
$177.00 |
||
TOTAL ADJUSTMENTS PER COMPUTER: |
|
$177.00 |
|||
ADJUSTED GROSS INCOME: |
$15,323.00 |
||||
ADJUSTED GROSS INCOME PER COMPUTER: |
$15,323.00 |
||||
SAMPLE |
|
||||
Tax and Credits |
|
|
|||
|
|
NO |
|||
BLIND: |
|
|
|
|
NO |
SPOUSE |
|
|
NO |
||
SPOUSE BLIND: |
|
|
NO |
||
STANDARD DEDUCTION PER COMPUTER: |
|
$4,850.00 |
|||
ADDITIONAL STANDARD DEDUCTION PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
TAX TABLE INCOME PER COMPUTER: |
$10,473.00 |
||||
EXEMPTION AMOUNT PER COMPUTER: |
|
$3,100.00 |
|||
TAXABLE INCOME: |
|
|
$7,373.00 |
||
TAXABLE INCOME PER COMPUTER: |
|
$7,373.00 |
|||
TOTAL POSITIVE INCOME PER COMPUTER: |
$15,500.00 |
||||
TENTATIVE TAX: |
|
|
$749.00 |
||
TENTATIVE TAX PER COMPUTER: |
|
$749.00 |
|||
FORM 8814 ADDITIONAL TAX AMOUNT: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
TAX ON INCOME LESS SOC SEC INCOME PER COM UTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
FORM 6251 ALTERNATIVE MINIMUM TAX: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
FORM 6251 ALTERNATIVE INI UM TAX PER CO UTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
FOREIGN TAX CREDIT: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
FOREIGN TAX CREDIT PER CO PUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
FOREIGN INCOME EXCLUSION PER CO PUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
FOREIGN INCOME EXCLUSION TAX PER CO PUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
EXCESS ADVANCE PREMIUM TAX CREDIT REPAY ENT OUNT: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
EXCESS |
DV NCE PREMIUM T X CREDIT REP Y ENT VERIFIED A OUNT: |
|
$0.00 |
||
CHILD & DEPENDENT C RE CREDIT: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
CHILD & DEPENDENT C RE CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
CREDIT FOR ELDERLY |
ND DIS BLED: |
|
$0.00 |
||
CREDIT FOR ELDERLY |
ND DIS BLED PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
||
EDUCATION CREDIT: |
|
|
$0.00 |
||
EDUCATION CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
GRO EDUC TION CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
RETIREMENT |
AVINGS CNTRB CREDIT: |
|
$0.00 |
||
RETIREMENT |
AVINGS CNTRB CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
||
PRIM RET |
|
AV CNTRB: F8880 LN6A: |
|
$0.00 |
|
EC RET |
AV CNTRB: F8880 LN6B: |
|
$0.00 |
||
TOTAL RETIREMENT |
AVINGS CONTRIBUTION: F8880 CMPTR: |
|
$0.00 |
||
RESIDENTIAL ENERGY CREDIT: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
RESIDENTIAL ENERGY CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
CHILD TAX CREDIT: |
|
|
$0.00 |
||
CHILD TAX CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
ADOPTION CREDIT: F8839: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
ADOPTION CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
|||
8/9/2018
Page 4 of 6
FORM 8396 MORTGAGE CERTIFICATE CREDIT: |
$0.00 |
|
FORM 8396 MORTGAGE CERTIFICATE CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
|
F3800, F8801 AND OTHER CREDIT AMOUNT: |
$0.00 |
|
FORM 3800 GENERAL BUSINESS CREDITS: |
$0.00 |
|
FORM 3800 GENERAL BUSINESS CREDITS PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
|
PRIOR YR MIN TAX CREDIT: F8801: |
$0.00 |
|
PRIOR YR MIN TAX CREDIT: F8801 PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
|
F8936 |
ELECTRIC MOTOR VEHICLE CREDIT AMOUNT: |
$0.00 |
F8936 |
ELECTRIC MOTOR VEHICLE CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
SAMPLE |
$0.00 |
|
F8910 |
ALTERNATIVE MOTOR VEHICLE CREDIT AMOUNT: |
|
F8910 |
ALTERNATIVE MOTOR VEHICLE CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
OTHER CREDITS: |
$0.00 |
|
TOTAL CREDITS: |
$0.00 |
|
TOTAL CREDITS PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
|
INCOME TAX AFTER CREDITS PER COMPUTER: |
$749.00 |
|
Other Taxes
SE TAX: |
|
$354.00 |
SE TAX PER COMPUTER: |
|
$354.00 |
SOCIAL SECURITY AND MEDICARE TAX ON UNREPORTED TIPS: |
|
$0.00 |
SOCIAL SECURITY AND MEDICARE TAX ON UNRE ORTED TI |
ER COM UTER: |
$0.00 |
TAX ON QUALIFIED PLANS F5329 (PR): |
|
$0.00 |
TAX ON QUALIFIED PLANS F5329 PER COM UTER: |
|
$0.00 |
IRAF TAX PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
TP TAX FIGURES (REDUCED BY IRAF) PER COM UTER: |
|
$1,103.00 |
IMF TOTAL TAX (REDUCED BY IRAF) PER COM UTER: |
|
$1,103.00 |
OTHER TAXES PER COMPUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
UNPAID FICA ON REPORTED TIPS: |
|
$0.00 |
OTHER TAXES: |
|
$0.00 |
RECAPTURE TAX: F8611: |
|
$0.00 |
HOUSEHOLD EMPLOYMENT TAXES: |
|
$0.00 |
HOUSEHOLD EMPLOYMENT TAXES PER CO PUTER: |
|
$0.00 |
HEALTH C RE RESPONSIBILITY PEN LTY: |
|
$0.00 |
HEALTH C RE RESPONSIBILITY PEN LTY VERIFIED: |
|
$0.00 |
HEALTH COVER GE REC PTURE: F8885: |
|
$0.00 |
RECAPTURE T XES: |
|
$0.00 |
TOTAL SSESSMENT PER COMPUTER: |
|
$1,103.00 |
TOTAL T X LI BILITY TP FIGURES: |
|
$1,103.00 |
TOTAL T X LI BILITY TP FIGURES PER COMPUTER: |
|
$1,103.00 |
Payments
FEDERAL INCOME TAX WITHHELD: |
$1,000.00 |
|
HEALTH CARE: INDIVIDUAL RESPONSIBILITY: |
$0.00 |
|
HEALTH CARE |
0 |
|
E TIMATED TAX |
PAYMENT : |
$0.00 |
OTHER PAYMENT CREDIT: |
$0.00 |
|
REFUNDABLE EDUCATION CREDIT: |
$0.00 |
|
REFUNDABLE EDUCATION CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
|
REFUNDABLE EDUCATION CREDIT VERIFIED: |
$0.00 |
|
EARNED INCOME CREDIT: |
$0.00 |
|
EARNED INCOME CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
|
EARNED INCOME CREDIT NONTAXABLE COMBAT PAY: |
$0.00 |
|
8/9/2018
Page 5 of 6
SCHEDULE 8812 |
NONTAXABLE COMBAT PAY: |
$0.00 |
EXCESS SOCIAL |
SECURITY & RRTA TAX WITHHELD: |
$0.00 |
SCHEDULE 8812 |
TOT SS/MEDICARE WITHHELD: |
$0.00 |
SCHEDULE 8812 |
ADDITIONAL CHILD TAX CREDIT: |
$0.00 |
SCHEDULE 8812 |
ADDITIONAL CHILD TAX CREDIT PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
SCHEDULE 8812 |
ADDITIONAL CHILD TAX CREDIT VERIFIED: |
$0.00 |
AMOUNT PAID WITH FORM 4868: |
$0.00 |
|
FORM 2439 REGULATED INVESTMENT COMPANY CREDIT: |
$0.00 |
|
FORM 4136 CREDIT FOR FEDERAL TAX ON FUELS: |
$0.00 |
|
SAMPLE |
$0.00 |
|
FORM 4136 CREDIT FOR FEDERAL TAX ON FUELS PER COMPUTER: |
||
HEALTH COVERAGE TX CR: F8885: |
$0.00 |
|
PREMIUM TAX CREDIT AMOUNT: |
$0.00 |
|
PREMIUM TAX CREDIT VERIFIED AMOUNT: |
$0.00 |
|
PRIMARY NAP FIRST TIME HOME BUYER INSTALLMENT AMT: |
$0.00 |
|
SECONDARY NAP |
FIRST TIME HOME BUYER INSTALLMENT AMT: |
$0.00 |
FIRST TIME HOMEBUYER CREDIT REPAYMENT AMOUNT: |
$0.00 |
|
FORM 5405 TOTAL HOMEBUYERS CREDIT REPAYMENT PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
|
SMALL EMPLOYER HEALTH INSURANCE PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
|
SMALL EMPLOYER HEALTH INSURANCE PER COMPUTER (2): |
$0.00 |
|
FORM 2439 AND |
OTHER CREDITS: |
$0.00 |
TOTAL PAYMENTS: |
$1,000.00 |
|
TOTAL PAYMENTS PER COMPUTER: |
$1,000.00 |
|
Refund or Amount Owed
AMOUNT YOU OWE: |
$103.00 |
APPLIED TO NEXT YEAR'S ESTIMATED TAX: |
$0.00 |
ESTIMATED TAX PENALTY: |
$0.00 |
TAX ON INCOME LESS STATE REFUND PER CO UTER: |
$0.00 |
BAL DUE/OVER PYMT USING TP FIG PER CO PUTER: |
$103.00 |
BAL DUE/OVER PYMT USING CO PUTER FIGURES: |
$103.00 |
FORM 8888 TOTAL REFUND PER CO PUTER: |
$0.00 |
Third Party Designee
THIRD P RTY DESIGNEE ID NU BER: |
|
AUTHORIZ TION INDIC TOR: |
0 |
THIRD RTY DESIGNEE N ME: |
|
Schedule
OCIAL |
ECURITY NUMBER: |
|
EMPLOYER |
ID NUMBER: |
|
BU INE |
NAME: |
|
DE CRIPTION OF BU INE /PROFESSION: |
DRAK |
|
NAICS CODE: |
000000 |
|
ACCT MTHD: |
|
|
FIR T TIME CHEDULE C FILED: |
N |
|
TATUTORY EMPLOYEE IND: |
N |
|
INCOME
GROSS RECEIPTS OR SALES: |
$2,700.00 |
RETURNS AND ALLOWANCES: |
$0.00 |
NET GROSS RECEIPTS: |
$0.00 |
COST OF GOODS SOLD: |
$0.00 |
SCHEDULE C FORM 1099 REQUIRED: |
NONE |
8/9/2018
Page 6 of 6
SCHEDULE C FORM 1099 FILED: |
NONE |
OTHER INCOME: |
$0.00 |
EXPENSES
CAR AND TRUCK EXPENSES: |
$0.00 |
DEPRECIATION: |
$0.00 |
INSURANCE (OTHER THAN HEALTH): |
$0.00 |
MORTGAGE INTEREST: |
$0.00 |
LEGAL AND PROFESSIONAL SERVICES: |
$0.00 |
SAMPLE |
$0.00 |
REPAIRS AND MAINTENANCE: |
|
TRAVEL: |
$0.00 |
MEALS AND ENTERTAINMENT: |
$0.00 |
WAGES: |
$0.00 |
OTHER EXPENSES: |
$0.00 |
TOTAL EXPENSES: |
$200.00 |
EXP FOR BUSINESS USE OF HOME: |
$0.00 |
SCH C NET PROFIT OR LOSS PER COMPUTER: |
$2,500.00 |
AT RISK CD: |
|
OFFICE EXPENSE AMOUNT: |
$0.00 |
UTILITIES EXPENSE AMOUNT: |
$0.00 |
COST OF GOODS SOLD
INVENTORY |
AT |
BEGINNING OF |
YEAR: |
$0.00 |
INVENTORY |
AT |
END OF YEAR: |
|
$0.00 |
Schedule
SSN OF |
|
NET FARM PROFIT/LOSS: SCH F: |
$0.00 |
CONSERVATION RESERVE PROGRAM PAY ENTS: |
$0.00 |
NET NONFARM PROFIT/LOSS: |
$2,500.00 |
TOTAL SE INCOME: |
$2,500.00 |
SE QUARTERS COVERED: |
4 |
TOTAL SE TAX PER COMPUTER: |
$353.12 |
SE INCOME COMPUTER VERIFIED: |
$0.00 |
SE INCOME PER COMPUTER: |
$2,308.00 |
TOTAL NET E RNINGS PER CO PUTER: |
$2,308.00 |
LONG FORM ONLY
TENTATIVE |
CHURCH RNINGS: |
$0.00 |
|
TOTAL SOC |
SEC & RR W GES: |
$0.00 |
|
E |
T X |
COMPUTER: |
$286.19 |
E MEDIC RE INCOME PER COMPUTER: |
$2,308.00 |
||
E MEDICARE TAX PER COMPUTER: |
$66.93 |
||
E FARM OPTION METHOD U ED: |
0 |
||
E OPTIONAL METHOD INCOME: |
$0.00 |
||
Form 8863 - Education Credits (Hope and Lifetime Learning Credits)
PART III - ALLOWABLE EDUCATION CREDITS
GROSS EDUCATION CR PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
||
TOTAL EDUCATION CREDIT AMOUNT: |
$0.00 |
||
TOTAL EDUCATION CREDIT AMOUNT PER COMPUTER: |
$0.00 |
|
|
|
This Product Contains Sensitive Taxpayer Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8/9/2018
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Request and Response Dates | The Tax Return Transcript was requested and responded to on August 9, 2018. |
| Privacy Notice | This document contains sensitive taxpayer data, indicating a high level of confidentiality. |
| Income Reporting | Wages, salaries, tips, etc. are reported at $13,000.00 with additional business income or loss reported at $2,500.00. |
| Adjusted Gross Income | The adjusted gross income calculated is $15,323.00 as reflected by the income and adjustments listed. |
Guide to Writing Sample Tax Return Transcript
Filing out the Sample Tax Return Transcript form is a crucial step in many financial or documentation processes. This task requires careful attention to detail and accuracy to ensure that all information reflects the taxpayer's previous filings accurately. To fill out the form correctly, follow these detailed steps one by one, and rest assured, knowing the process is being handled properly.
- Begin with the Tax Return Transcript Request Date: Record the request date as "08-09-2018".
- Next, note down the Response Date: This should also be "08-09-2018".
- Enter the Tracking Number: Input "100200235179" carefully.
- Fill in the Customer File Number: Use the number "0987654321".
- Locate the section marked SSN Provided and write "XXX-XX-5084".
- For the Tax Period Ending, indicate "Dec. 31, 2017".
- Under the taxpayer information, enter the SSN, Spouse SSN (if applicable), and the Name(s) shown on return as "Drak".
- Fill out the address section with "123 Da".
- Select the correct Filing Status, which in the sample is "Single".
- Document the Form Number used, which is "1040".
- Record the received date as "Jan. 15, 2018" and remittance as "$0.00".
- Move on to the income section and report wages, salaries, and tips as "$13,000.00". If there are entries for other types of income (e.g., business income or loss, capital gains, alimony received), fill these in as indicated in the sample.
- Under the Adjustments to Income section, enter any applicable adjustments like educator expenses or self-employment tax deduction. According to the sample, self-employment tax deduction is "$177.00".
- In the Tax and Credits section, input all relevant tax computations and credits as shown on your transcript sample, such as the standard deduction and taxable income.
- For the Other Taxes section, include specifics about self-employment tax, if applicable.
- Proceed to the Payments segment, noting the federal income tax withheld and any other payments or credits.
- In the section detailing Refund or Amount Owed, indicate the amount you owe or expect to be refunded, and note any amounts applied to next year’s estimated taxes or penalties incurred.
- Finally, if there’s a Third Party Designee, provide their details including ID number and name.
- Should there be additional schedules or details pertinent to your tax situation (such as Schedule C for business profit or loss), ensure these are accurately completed as well.
After completing these steps, verify all the information for accuracy against your records. This form serves as a comprehensive overview of your tax return as filed, so accuracy is essential. Once filled out completely, you're ready to proceed to the next steps of your financial or legal process with confidence.
Understanding Sample Tax Return Transcript
What is a Tax Return Transcript?
A Tax Return Transcript shows most line items from the original tax return you filed, along with any forms and schedules. It includes information such as your income, tax payments, and refund amount. Adjustments made by you or the IRS after the original return was filed are also included. However, it doesn't reflect changes made after the processing of the original return.
How can I use a Tax Return Transcript?
This document can be used as a proof of income and tax filing status for mortgage applications, student or small business loan applications, and to apply for government benefits. Many institutions require a copy of this form to verify your financial status.
What information does the Tax Return Transcript include?
It consists of sensitive taxpayer data, including your Social Security number (partially hidden), name, address, filing status, details of income sources, adjustments to income, total income, tax and credits, other taxes, payments, and the amount owed or refund. Specific forms and schedules related to your income and deductions are also detailed.
Is there a difference between a Tax Return Transcript and a Tax Account Transcript?
Yes, there's a significant difference. A Tax Return Transcript shows most items from your original tax return, while a Tax Account Transcript shows basic data such as return type, marital status, adjusted gross income, taxable income, and all payment types. It also records any adjustments made after the return was filed.
How can I request a Tax Return Transcript?
You can request it online, by phone, or through mail via the IRS website. You'll need to provide your Social Security Number, date of birth, and the mailing address from your latest tax return. Keep in mind, there's no cost to request or receive this document.
Can I request a Tax Return Transcript for a previous tax year?
Yes, the IRS provides access to tax return transcripts for the current tax year and up to six years prior. You must specify the year when requesting the transcript to ensure you receive the correct document.
Is it safe to share my Tax Return Transcript?
Because it contains sensitive financial information, caution is advised when sharing your Tax Return Transcript. Only provide it to trusted institutions for necessary financial applications. The IRS partially hides social security numbers to enhance privacy and protect your information.
Common mistakes
Filling out forms related to taxes, like the Sample Tax Return Transcript form, can be complex and might lead to errors if not done carefully. Here are four common mistakes that often occur:
Incorrect Information: One of the most common mistakes is entering incorrect information. This could range from misspelling names to inputting wrong Social Security numbers (SSNs). The SSN provided, as well as the SSN for the spouse if applicable, must match the numbers on the Social Security card to avoid processing delays.
Omitting Information: Another frequent error is leaving sections blank that should have been filled out. For instance, income details, such as wages, salaries, tips, etc., should be carefully entered. Additionally, adjustments to income and credits, such as the Earned Income Credit (EIC), should not be overlooked.
Miscalculating Totals: Calculating totals incorrectly is also a common issue. This includes sums for total income, taxable income, and the total tax liability. Remember, the amount as shown (PR) and the adjusted amount (PC), if applicable, have to be carefully calculated to reflect the accurate financial situation.
Failing to Report All Income Sources: Sometimes, individuals might forget to report all sources of income. This includes not only wages and salaries but also less common types such as business income or loss (Schedule C), alimony received, capital gain or loss, and any other incomes like unemployment compensation or Social Security benefits. All these contribute to the total income calculation, which is crucial for accurate tax assessment.
Attention to these areas can improve the accuracy of the Tax Return Transcript form submission significantly. It's always a good idea to review every section, ensure all income is reported, and double-check calculations before submission. Seeking professional advice or assistance might also be beneficial in avoiding these common errors.
Documents used along the form
When individuals and professionals dive into the complexities of tax documentation, a Tax Return Transcript is a commonly requested form, especially when verifying income for loans or financial aid. However, it often travels in the company of other essential documents, each with its unique role in the broader scenario of financial analysis or tax preparation. Let’s explore some of these additional documents that are frequently used alongside the Tax Return Transcript.
- W-2 Form: The Wage and Tax Statement is issued by employers to report an employee's annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld from their paycheck. It's crucial for accurately reporting one's income and tax liability.
- Form 1099: This is a series of documents that report various types of income other than wages, salaries, and tips. For example, Form 1099-MISC is used to report payments made to independent contractors, while 1099-INT reports interest income.
- Schedule C (Form 1040): Profit or Loss from Business is utilized by sole proprietors. It details the income, costs, and expenses related to their business, and it's essential for calculating the taxable profit or deducible loss from their business operations.
- Form 4868: Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. This form is critical for taxpayers who need additional time to file their income tax returns. It does not extend the time to pay any taxes owed, but it helps avoid late filing penalties.
Understanding these forms can illuminate the financial stories of individuals and businesses alike. From detailing the earnings of an employee to shedding light on the intricacies of business operations and beyond, each form contributes its piece to the puzzle. Whether for loan applications, financial aid, or ensuring compliance with tax regulations, these documents, along with the Tax Return Transcript, provide a comprehensive view of financial affairs.
Similar forms
The Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, is a document closely resembling the sample Tax Return Transcript in its content and purpose. Both provide detailed information about an individual's income, deductions, and tax liability for a specific tax year. However, the Form 1040 is the original filing document, whereas the transcript is a summary provided by the IRS upon request, noting amounts as shown on the return and as adjusted.
W-2 forms, issued by employers, report an employee's annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld from their paycheck. These forms are akin to the information found in the Tax Return Transcript, which includes income data such as wages, salaries, and tips. Both documents are essential for understanding an individual's income situation and are used in preparing or verifying tax return details.
Schedule C (Profit or Loss From Business) is part of an individual's tax return that outlines the income and expenses of a sole proprietorship. Like the Tax Return Transcript, Schedule C provides a detailed record of business operations affecting the taxpayer's overall tax situation. Both documents are crucial for accurate reporting and understanding of taxable business income or loss.
Form 1099, particularly the 1099-MISC, reports income from sources other than wages, salaries, and tips. It's similar to the Tax Return Transcript in that both contain information about an individual's income. However, while 1099 forms are issued by payers to the taxpayer and the IRS, the transcript is a consolidated summary provided by the IRS, capturing various income sources, including those reported on different 1099 forms.
The Schedule D (Capital Gains and Losses) form and the Tax Return Transcript both provide information on an individual's investment income, including capital gains or losses from the sale of assets. Schedule D details transactions that contribute to the capital gains or losses, while the transcript summarizes the outcome as it affects the individual's tax liability.
Form 8962 (Premium Tax Credit) is used to reconcile the amount of health insurance premium credits received with the amount one is eligible for. Like the Tax Return Transcript, it concerns adjustments that affect the taxpayer's final tax calculation. Both documents may include adjustments to income or tax credits that impact the overall tax situation.
The Schedule EIC (Earned Income Credit) shows eligibility for a tax credit aimed at low- to moderate-income families, similar to the transcript's function of detailing various tax credits the taxpayer has claimed. The Tax Return Transcript consolidates this information, showing the outcome of such claims including the Earned Income Credit.
Lastly, the Schedule SE (Self-Employment Tax) complements the Tax Return Transcript by providing details on self-employment taxes owed by those who work for themselves. Both documents are interconnected, with Schedule SE addressing how self-employment income and taxes contribute to the overall tax scenario detailed in the transcript.
Dos and Don'ts
When dealing with the Sample Tax Return Transcript form, it's essential to follow a comprehensive approach to ensure accuracy and compliance. Here are some dos and don'ts to keep in mind:
Do:- Review the entire form before filling it out to ensure you understand all the requirements and have all the necessary information at hand.
- Use accurate and up-to-date information, especially when entering personal details such as your Social Security Number (SSN), address, and income figures.
- Double-check the figures you input against your records to ensure there are no discrepancies in income reported, tax calculations, or credits claimed.
- Sign and date the form if required, as an unsigned form may not be processed.
- Keep a copy of the completed form for your records. This could be crucial for future reference or in the case of an audit.
- Seek professional advice if you're unsure about any aspects of the form. Tax professionals can offer valuable assistance.
- Submit the form before the deadline to avoid potential penalties for late submission.
- Leave sections blank that apply to you. If a particular section is not applicable, it's better to fill it with "N/A" or "0" as instructed.
- Omit your SSN or inaccurately report it, as this could lead to delays in processing or mistakes in your tax records.
- Guess on figures. Always use actual data from your financial records to avoid issues with the IRS.
- Forget to review the tax credits or deductions you're eligible for, as this could result in overpaying taxes.
- Ignore the IRS guidelines for specific lines or entries, as these provide crucial instructions on how to accurately fill out the form.
- Use pencil or erasable ink to fill out the form. This could raise questions about the authenticity of the information provided.
- Overshare information not requested on the form, as it could complicate the processing of your tax return.
Misconceptions
When it comes to understanding tax documents like the Sample Tax Return Transcript, it's easy to get confused by the abundance of information and specific terms used. However, it's essential to clear up some common misconceptions to ensure that everyone has a correct understanding of what these documents represent and how they should be used. Here are four misconceptions that often come up.
- Everything listed reflects current account status. The amounts shown on the Sample Tax Return Transcript for items such as wages, deductions, and credits represent the amounts reported or adjusted as of the date the return was processed. They do not reflect any changes or transactions that may have occurred after that date. So, if you're looking at this transcript to understand your current tax situation, it may not provide a complete picture if there have been additional activities on your account.
- Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) is my taxable income. This is a common area of confusion. Your AGI, as indicated on the transcript, is simply your total income minus specific adjustments, such as educator expenses or contributions to a retirement account. However, your AGI is not the amount you're taxed on. The taxable income, a separate figure on the transcript, further subtracts either the standard or itemized deductions and exemptions you're eligible for. This figure is closer to what your income tax is based on.
- The transcript is a substitute for my return. While a Tax Return Transcript includes most of the line items from your original tax return, it is not a one-for-one copy. It's formatted differently and may not include every form or attachment you submitted. For certain purposes, such as mortgage applications or financial aid, this transcript will suffice, but it's not an exact replica of your filed return.
- Information about payments and refunds is up-to-date. The payments and refund information shown on the transcript reflect what was processed as of the return or document date. This does not account for any payments made or refunds issued after that time. For the most current information regarding payments, refunds, or any amount you may owe, it's recommended to check directly with the IRS or through your IRS online account.
Understanding these aspects of the Sample Tax Return Transcript can help demystify some of the complexities surrounding tax documentation and ensure that taxpayers have a clearer idea of what their transcript represents. Remember, if there's ever doubt about your taxes or how to interpret tax documents, seeking guidance from a tax professional is a wise course of action.
Key takeaways
Understanding the Sample Tax Return Transcript form is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance. Here are nine key takeaways to help guide you:
- Request and Response Dates are prominently displayed, indicating when the transcript was requested and when it was provided.
- The Tracking Number and Customer File Number are unique identifiers for each request, ensuring precise tracking and referencing of each transcript.
- Personal information, including the Social Security Number (SSN) and filing status, is masked for privacy yet maintains enough detail for verification purposes.
- Income details reflect both the originally reported amounts and the adjusted amounts, showing any updates or corrections made post-submission.
- Adjustments to Income show deductions and credits applied, affecting the adjusted gross income, highlighting the importance of accurate claim submissions for tax benefits.
- Tax and Credits section describes calculations affecting tax liability, including the standard deduction, taxable income, and credits reducing the tax owed.
- The transcript details various types of Other Taxes and Payments, including self-employment tax and federal income tax withheld, offering a complete picture of an individual’s tax situation.
- Amount Owed or Refund displays the final tax result, showing whether an individual owes additional taxes or is entitled to a refund, crucial for financial planning.
- The inclusion of Third Party Designee information indicates permission granted to another individual to discuss this return with the IRS, emphasizing the importance of authorized representation in tax matters.
Understanding each section of the Tax Return Transcript can empower individuals and tax preparers alike in managing and planning for tax obligations more efficiently.
Popular PDF Documents
Irs 944 Instructions - Failure to file Form 944 when required, or inaccurately reporting tax information, may result in penalties.
Eft Authorization - Streamlines the process for Healthfirst providers to both receive payments electronically and manage remittance advice efficiently.