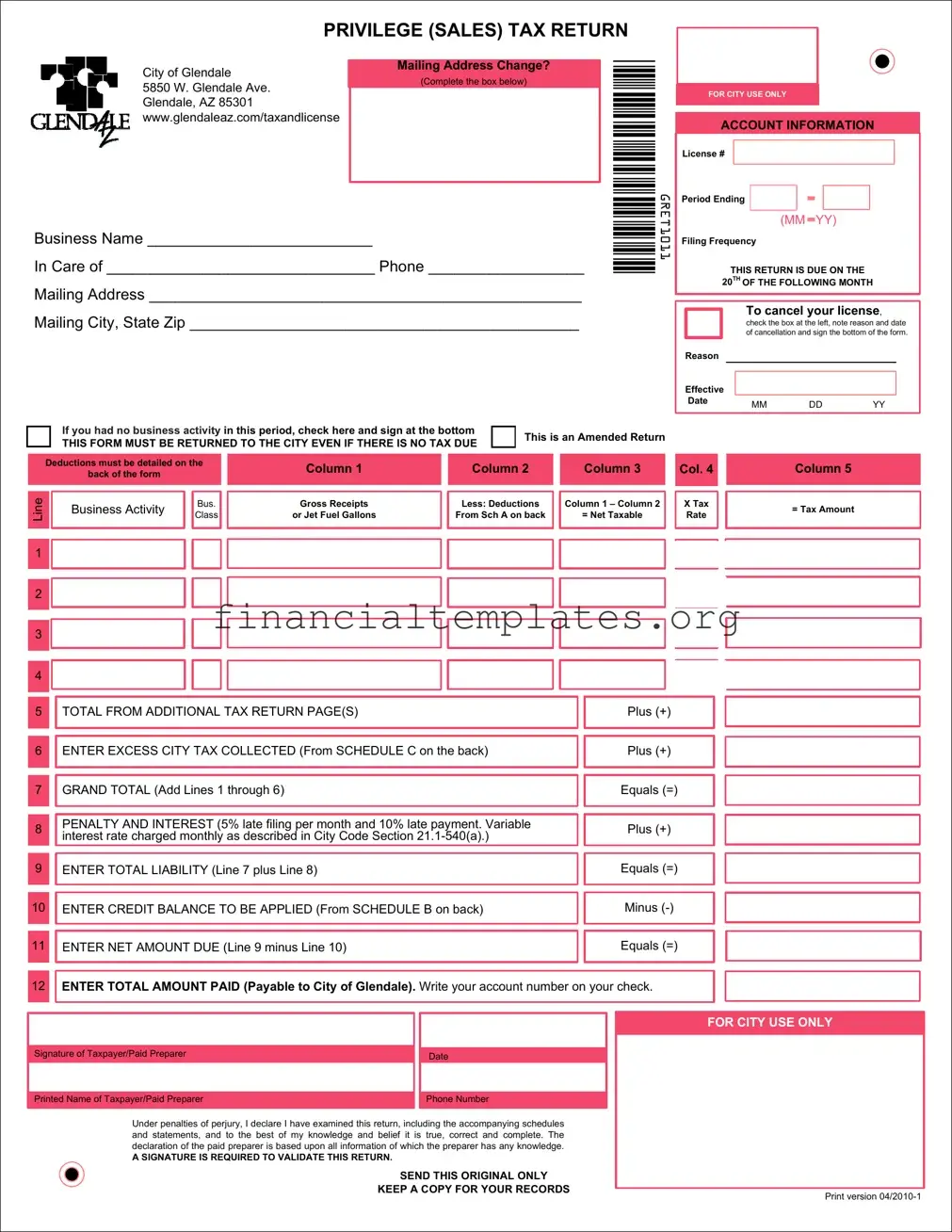
Get Privilege Sales Tax Return Form
In the complex landscape of business taxation, the privilege of conducting commerce comes with its share of responsibilities, one of which involves filing the Privilege Sales Tax Return form. This essential document serves as a bridge between businesses and tax authorities, detailing the sales and transactions over a certain period to calculate the tax owed to the government. Designed with precision, it covers a wide array of business activities ranging from transportation, mining, and utilities to retail sales, contracting, and even amusement. Each category is identified with a specific tax rate and allowable deduction codes, ensuring that businesses not only comply with their tax obligations but also benefit from applicable deductions. The form also caters to a variety of entities by including a comprehensive list for classifying the business's nature accurately, alongside identification codes for license applications, thereby streamlining the process. Additionally, instructions on selecting the appropriate tax rate for different business classes provide a roadmap for accurate tax calculation. This meticulous attention to detail underscores the importance of the Privilege Sales Tax Return form in the broader context of tax administration, embodying the balance between regulatory compliance and the support of business operations.
Privilege Sales Tax Return Example
64
,(% ( ;
)<)>C4.
4.E<)'>%
*6,
*+/+/
F!
B#DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD
6DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD"DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD 1.DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD 16 EDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD
*GRET1011*
+*+,+
! =
%( |
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*11A77, |
|
||
*(*% > ! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
).+) 4?)+*)*++@,+)
!! %!
!"# |
|
|
|
." |
11 |
$$ |
77 |
|
!"#""$ %&! !' % ("" "" |
|
"% |
|
|
|
.!"" " "
!'" %
B. |
|
B |
|
|
6 |
||
|
|
|
|
% ! $"
%6 "*
4 |
|
3 |
|
01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
:. !" |
|
94 |
|
7 |
*%!!' |
|
8 "7 |
|
" |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2
87"
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
& |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"*+, |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
5 |
|
3#303263 |
|
|
|
"*+, |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3:*;, |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
< |
|
"3#.7.#$#303 *)=%>=? |
|
|
|
"*+, |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
66 |
&%%@)(>*,, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3:*;, |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
%> |
|
|
|
|
1*@, |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
%% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3:*;, |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
%& |
|
+,+. "" 0C |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*+/+/ |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"# |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
!"" |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"# |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
"#!"" |
|
|
"# |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.+.)0
.)++/
<+/*+/++.
">(!&>%>@%
*GRET1012* |
J |
" %# ( 7 |
"%9$( 4 |
! A . " !":" %" !"! " (% !$"(%"%# ( 70
*%,
" :
). |
$ 6 |
|
. !". !%$" |
||
"* ,6* |
5( |
|
, |
||
|
4A
3A
1A
55
0
0@
)(
0
$.
*,
5'
)&
9(
GH
5)
4
)>=
)5
#.
5A
))
B$"
<%
')=66
9>
"
6! B
00*
4,
1?4
/
9%
5&
)'
)A
G
"63:
9'
1$"G
"$
)<
5<
,!0. !"A 7$ B
+..+$"*%"
).
7! 7 !"
4
|
.6 |
|
|
|
B |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
B6 |
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
6"6 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
||||
|
"! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
*%>, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
6 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ 1
"!
*5,
+,<+..+*,/*0
*+&:64*5&',A'>@'%A>*"%,7*5&',A'>@&%A9/*5&',A'>@&%<5
BBB0( C0!D"7!
">(!&>%>@%
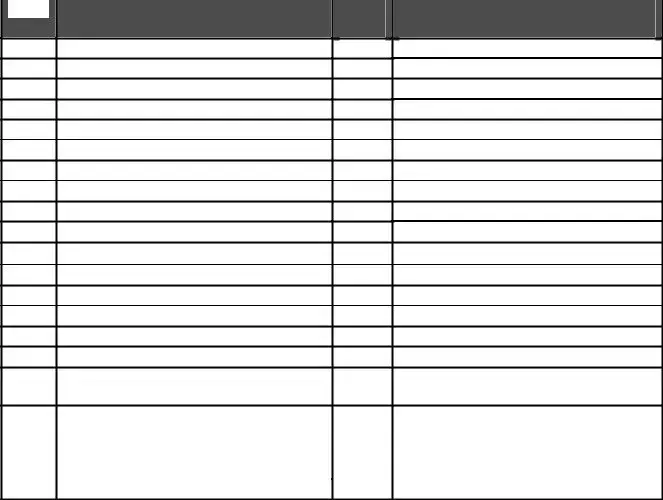
The chart below is intended to assist you in selecting the proper tax rate for your business class/ activity.
When printing this document set Page Scaling=”None”.
Class |
Activity |
Tax |
Allowable Deduction Codes |
|
|
Rate |
(Definitions listed in schedule A) |
01 |
Transportation |
2.2% |
52, 53, 64, 75, 81 |
02 |
Mining |
0.1% |
52, 53, 64, 74, 75, 81 |
03 |
Jet Fuel (cents per gallon) |
0.021 |
52, |
04 |
Utilities |
2.2% |
|
05 |
Telecommunications |
5.4% |
|
06 |
Manufactured Buildings |
2.2% |
|
09 |
Publishing |
2.2% |
|
10 |
Printing |
2.2% |
|
11 |
Restaurant/Bars |
3.2% |
52, 53, 64, 65, 74, 75, 81 |
12 |
Amusement |
2.2% |
52, 53, 64, 75, 81 |
13 |
Residential Rental of Real Property |
2.2% |
|
14 |
Rental of Personal Property |
2.2% |
|
15 |
Contracting |
2.2% |
|
17 |
Retail Sales |
2.2% |
|
18 |
Advertising |
2.2% |
52, 53, 64, 69, 75, 81 |
25 |
Hotel/Motel |
5.6% |
52, 53, 64, 75, 81 |
30 |
Retail Sales- Food for Home |
1.8% |
52, 53, 56, 64, 65, 74, 75, 81 |
|
Consumption |
|
|
35 |
Contracting |
1.8% |
|
|
(Contracts prior to 11/1/07) |
|
|
40 |
Commercial Rental of Real Property |
2.2% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
99 |
Use Tax |
2.2% |
Not Applicable |
City of Glendale Arizona
License Application Codes
Title Code: |
|
Government Issued ID Type: |
|
Accountant/CPA |
ACC |
Driver License |
DRLC |
Agent |
AGT |
Misc. Foreign ID |
MFID |
Attorney |
ATT |
Military ID |
MIID |
Audit Contact |
AUD |
Matricula Consular |
MTCL |
Bankruptcy Attorney |
BKA |
Passport |
PPRT |
Bankruptcy Trustee |
BKT |
Permanent Resident |
PRES |
Chief Executive Officer |
CEO |
Resident Alien |
RESA |
Chief Financial Officer |
CFO |
US Employment Authorization |
USEA |
Chairman of Board |
COB |
US |
USID |
Controller |
CON |
Visa |
VISA |
Director |
DIR |
Miscellaneous US ID |
MUID |
Employee |
EMP |
|
|
General Partner |
GEN |
Color of Eyes: |
|
General Manager |
GMR |
|
|
Limited Partner |
LIM |
Black |
BL |
Liquor Agent |
LQA |
Brown |
BR |
Member |
MBR |
Blue |
BU |
Management Co |
MCO |
Green |
GN |
Manager |
MGR |
Gray |
GR |
Managing Member |
MMB |
Hazel |
HZ |
Managing Agent |
MNA |
Pink |
PK |
Owner |
OWN |
Violet |
VT |
President |
PRE |
|
|
Partner |
PRT |
Color of Hair: |
|
Statutory Agent |
SAG |
|
|
Secretary |
SEC |
Bald |
BA |
Shareholder |
SHH |
Blond |
BD |
Treasurer |
TRE |
Black |
BL |
Trustee |
TRU |
Brown |
BR |
VPR |
Gray |
GR |
|
|
|
Red |
RD |
|
|
White |
WH |
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Tax Rate Selection | The form provides a detailed chart to assist businesses in selecting the correct tax rate for their specific class/activity, including rates and allowable deduction codes. |
| Governing Law | State-specific governing laws apply to the completion and submission of the Privilege Sales Tax Return form, ensuring compliance with local tax statutes. |
| Identification Codes | Includes an extensive list of identification codes for businesses and individuals, ranging from Government Issued ID types to roles such as CEO, Attorney, or Partners. |
| Deductible Categories | Provides a wide array of categories for allowable deductions, indicating inclusivity of various business expenses across different sectors. |
Guide to Writing Privilege Sales Tax Return
The process of completing a Privilege Sales Tax Return form signifies a vital step for businesses to comply with local tax obligations. This structured document requires careful attention to detail, ensuring that every section is accurately filled out to reflect the business's sales activities and applicable taxes. Below is a sequential guide designed to navigate the complexities of filling out this form.
- Begin by locating the form number, GRET1011 or GRET1012, to ensure you are working on the correct document for your filing period.
- Enter the Business Name, Address, City, State, and ZIP Code in the designated fields at the top of the form.
- Proceed by providing your City of Glendale Arizona License Number and Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) in their respective spaces.
- Fill in the reporting period date including the month, day, and year to accurately represent the tax period being reported.
- Under the Class Activity section, select the tax rate applicable to your business activity. Reference the chart provided at the bottom of the instruction document for assistance in selecting the correct rate based on your business class/activity. Examples include Transportation at a 2.2% rate or Hotel/Motel at a 5.6% rate.
- Record your gross sales, adjustments, deductions, and taxable sales in their respective columns, ensuring you adhere to the allowable deduction codes listed for your chosen class/activity.
- If your business is eligible for deductions, reference Schedule A for definitions and applicable codes. Enter the deduction amounts next to the corresponding codes in the Deductions section of the form.
- Calculate the amount of tax owed by applying the tax rate to your taxable sales, taking into account any credits or prepayments that may apply.
- Verify all inputted information for accuracy and completeness. An oversight or mistake could result in incorrect tax liability or processing delays.
- Sign and date the form in the designated area, making sure to provide your title or position within the company.
- Last, submit the form by the due date to the City of Glendale, using the prescribed submission method, whether it be electronic filing or through mail submission.
This methodical approach to completing the Privilege Sales Tax Return form is designed to ensure that businesses meet their tax obligations accurately and efficiently. Compliance with local tax laws not only supports the operation of public services but also maintains the integrity of the business's financial obligations.
Understanding Privilege Sales Tax Return
What is the Privilege Sales Tax Return form?
The Privilege Sales Tax Return form is a document businesses use to report and pay taxes on revenue earned from specific types of activities that are considered privileges by the governing authority. These activities include but aren't limited to transportation, mining, utilities, telecommunications, and retail sales. This form helps ensure compliance with local tax regulations and contributes to public funding.
How do I know which tax rate applies to my business?
The tax rate varies depending on your business's specific class or activity. Here's a brief guide to help you identify your applicable tax rate:
- Transportation: 2.2%
- Restaurant/Bars: 3.2%
- Retail Sales: 2.2% for general sales, 1.8% for food for home consumption
- Hotel/Motel: 5.6%
Each business class or activity comes with allowable deduction codes that can adjust your taxable amount. Refer to the form for specific deduction codes that apply to your business category.
Are there different types of information required for completing the Privilege Sales Tax Return?
Yes, depending on your business's nature and the transactions completed within the reporting period, you may need to provide various details, such as:
- Total revenue generated
- Class activity code
- Applicable tax rate
- Allowable deductions and corresponding deduction codes
- Tax amount due after deductions
Accurate completion of these sections is crucial for correct tax calculation and compliance.
Can I apply for deductions on my Privilege Sales Tax Return?
Yes, businesses can apply for deductions on their Privilege Sales Tax Return. The form lists specific deduction codes related to each class of business activity, such as costs of goods sold, out-of-state sales, and sales to other licensed dealers, which are not subject to tax. It's essential to review the schedule provided within the form to identify which deductions you're eligible for, enhancing your tax return accuracy and potentially reducing the amount of tax owed.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Privilege Sales Tax Return form correctly is crucial for business owners to comply with tax regulations. However, certain mistakes can occur during the process, leading to potential errors. Below are eight common mistakes people make:
- Incorrectly selecting the business class/activity: Each business activity has a specific tax rate associated with it. Selecting the wrong category may result in paying more or less tax than required.
- Overlooking allowable deductions: The form lists allowable deductions for each business category. Failing to account for these can lead to overpayment of taxes.
- Misunderstanding the tax rate: Each category has its designated tax rate. Misinterpreting these rates can lead to calculation errors.
- Error in calculation: Simple mathematical errors in addition, subtraction, or percentage calculation can lead to incorrect tax amounts being reported.
- Missing deadlines: Late submission of the tax return can result in penalties and interest charges. Knowing the due date is crucial.
- Not updating business information: If business details change (e.g., address, ownership, or business activity) and the form is not updated accordingly, it may lead to issues with the tax return.
- Forgetting to sign the document: An unsigned tax return form is considered incomplete and can lead to delays or rejection of the submission.
- Failing to print the document correctly: The instruction to set Page Scaling to “None” is vital to ensure that the form prints correctly. Ignoring this step can result in a form that is not properly formatted, leading to potential rejection.
Avoiding these mistakes is imperative to ensure compliance with tax obligations and to avoid unnecessary penalties. It is beneficial for business owners to review the form thoroughly before submission and consult with a professional if any uncertainties arise.
Documents used along the form
When preparing the Privilege Sales Tax Return, various other forms and documents might be necessary to ensure comprehensive compliance and accuracy. These forms play a pivotal role in the process, each serving its specific purpose, from detailing exemptions to providing critical business information. Below is a list of some of these essential forms and brief descriptions of their uses.
- Business License Application: This document is required for any business to legally operate. It captures basic information about the business, such as the name, location, type of business, and owner details.
- Exemption Certificates: These forms are used by a seller to document that a sale was legally exempt from sales tax. They are crucial for businesses that sell goods or services which may qualify for a sales tax exemption.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN) Confirmation Letter: Issued by the IRS, this letter confirms a business’s EIN, an essential identifier for tax reporting.
- Sales and Use Tax Worksheet: A preparatory document that helps businesses calculate the amount of sales and use tax owed. It’s a critical step in ensuring accurate tax reporting.
- Annual Financial Statement: This comprehensive report details a business's financial activities over the year and is essential for accurate tax reporting and preparation.
- Transaction Privilege Tax (TPT) License: Specific to Arizona, this license is necessary for businesses to legally collect tax on sales. It’s important for compliance with state tax laws.
- City or Municipal Business License: In addition to a general business license, some localities require a specific license to operate within their jurisdiction, further legitimizing the business for tax purposes.
Accurately preparing and filing the Privilege Sales Tax Return necessitates a thorough documentation process. By understanding and utilizing these accompanying forms, businesses can ensure they meet all regulatory requirements, thereby avoiding costly penalties and ensuring their operations remain in good standing.
Similar forms
The Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return, often referred to as Form 941, shares similarities with the Privilege Sales Tax Return form. Both documents are vital for reporting tax liabilities, although they focus on different taxes. The Form 941 reports on federal income tax withheld from employees, social security, and Medicare taxes, while the Privilege Sales Tax Return is concerned with the tax collected from sales activities. Each serves to ensure businesses comply with tax reporting and payment obligations at different government levels.
The State Unemployment Tax Act (SUTA) filing is another document resembling the Privilege Sales Tax Return in its purpose of calculating and reporting taxes due. While SUTA deals with unemployment insurance taxes at the state level to provide benefits to unemployed workers, the Privilege Sales Tax Return addresses the collection of taxes on sales and services. Both documents are essential for business compliance with tax regulations, supporting societal and economic structures within their respective scopes.
Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement, also parallels the Privilege Sales Tax Return. It summarizes an employee's annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld from their paycheck. In contrast, the Privilege Sales Tax Return tallies the tax collected on sales. Though one focuses on income and the other on sales, both forms are crucial for accurately reporting tax information to the government and ensuring transparency and fairness in tax collection processes.
The Business License Renewal forms that many local governments require can be likened to the Privilege Sales Tax Return form. These forms are necessary for the ongoing authorization to operate within a specific jurisdiction. Similarly, the Privilege Sales Tax Return ensures that businesses comply with local sales tax laws, contributing to their legitimacy and operation within a community.
The Corporate Income Tax Return is another document with functions similar to the Privilege Sales Tax Return, albeit focusing on different types of tax. This form calculates the income tax liability based on a corporation's earnings, whereas the Privilege Sales Tax Return calculates tax based on sales. Both are critical for determining a business's tax obligations to the government.
Form 1099, used for reporting various types of income other than wages, salaries, and tips, shares a common goal with the Privilege Sales Tax Return: ensuring appropriate tax collection and compliance. The Privilege Sales Tax Return specifically targets sales tax collection, while Form 1099 encompasses a broader range of income sources, from independent contractor earnings to dividend income.
The Value Added Tax (VAT) Return, applicable in many countries outside the United States, is akin to the Privilege Sales Tax Return in its function and importance. Both forms are concerned with the tax on goods and services, though VAT is a multi-stage tax on value addition, and sales tax is typically a single-stage tax at the point of sale. Their accurate completion ensures businesses contribute fairly to the tax revenues of their respective governments.
The Excise Tax Return is another document similar to the Privilege Sales Tax Return, focusing on specific goods, services, and activities. While the excise tax is levied on particular items like gasoline, alcohol, and tobacco, the sales tax applies more broadly to sales transactions. Both forms play a role in the taxation system, ensuring businesses pay the correct taxes for their operations and sales.
Lastly, the Property Tax Declaration form, which reports the value of a business's property to calculate property tax, has its similarities with the Privilege Sales Tax Return. While focusing on different types of assets (property vs. sales), each form allows for the appropriate assessment and collection of taxes, supporting public services and infrastructure within their communities.
Dos and Don'ts
When preparing to fill out the Privilege Sales Tax Return form, it's important to pay close attention to detail and ensure compliance with all tax regulations. Below are ten key dos and don'ts to guide you through this process:
- Do carefully review the entire form before starting to make sure you understand all the requirements.
- Do gather all necessary documents, such as sales records and receipts, to accurately report your sales and deductions.
- Do use the correct tax rate for your business class/activity. Refer to the chart provided for proper tax rate selection based on your business activities.
- Do double-check your calculations to avoid errors. This includes computing the tax owed and any deductions with precision.
- Do ensure that your business information, including the license number and legal name, is accurate and matches the records.
- Do not leave any fields blank. If a section does not apply, indicate this with “N/A” or “0,” as appropriate.
- Do not guess if you are unsure about how to report something. It's better to consult the instructions or contact a tax professional for guidance.
- Do not use pencil to fill out the form; all entries should be made in ink to ensure permanence and legibility.
- Do not round off figures. Report all numbers with exact amounts to ensure accurate tax calculation.
- Do not forget to sign and date the form. An unsigned form is considered incomplete and will not be processed.
Adhering to these guidelines can help streamline the filing process and avoid common pitfalls that can lead to errors or delays in processing your Privilege Sales Tax Return.
Misconceptions
There are common misconceptions about the Privilege Sales Tax Return form that can lead to confusion. Here is a list of ten such misconceptions and the truths behind them:
- Only retail businesses need to file: Not true. While retail businesses do need to file, this form is also required for various other business activities including manufacturing, utilities, telecommunications, and even rental of real property.
- It's the same as income tax: This is incorrect. The Privilege Sales Tax is a tax on the privilege of doing business in a specific area, not a tax on income.
- One rate fits all: Each type of business activity is taxed differently. Rates vary depending on the business class/activity as outlined in the tax rate chart.
- Filing is only annual: The filing frequency can vary. Depending on your business, you might need to file monthly, quarterly, or annually.
- Online filing isn't an option: Many jurisdictions now offer online filing as a convenient way to submit the Privilege Sales Tax Return form.
- There are no deductions allowed: This is false. There are allowable deduction codes for different business activities that can reduce your taxable amount.
- You don't need to file if no tax is due: Even if no tax is owed, you typically still need to file a return to report your business activity.
- Out-of-state businesses are exempt: If you're conducting business within the jurisdiction, regardless of where your business is based, you may still need to file.
- Late filing penalties are negligible: Penalties can be significant and include both fines and interest on the unpaid tax amount.
- The form is too complicated to fill out without a professional: While it may seem daunting, resources and assistance are available to help businesses fill out and file the form correctly.
Understanding these key points can help ensure that your business complies with local tax obligations and avoids unnecessary penalties.
Key takeaways
Filling out the Privilege Sales Tax Return correctly is crucial for complying with tax obligations. Here are six key takeaways to remember:
- Ensure all business information is accurate, including the business class/activity code which determines the tax rate applicable to your business.
- Pay close attention to allowable deduction codes related to your business activity, as these can significantly impact the amount of tax owed.
- Before printing the document, set Page Scaling to “None” to ensure that the tax rates and codes are correctly displayed and readable.
- Different business activities have different tax rates and allowable deductions; verify these carefully to avoid errors in tax calculation.
- Use the chart provided within the form to select the proper tax rate for your business based on the class activity. Incorrect selection could lead to under or overpayment of taxes.
- Documentation such as Government Issued ID, and other specifics like License Application Codes, must be correctly noted to avoid processing delays or audits.
Remember, timely and correct submission of the Privilege Sales Tax Return helps in maintaining compliance with state tax regulations and avoids potential fines and audits.
Popular PDF Documents
Broward Tax Collector Plantation - Special provisions for events like fairs or circuses, requiring start and end date information for proper event coverage.
Arkansas Tax Forms - Methods to determine net tax, report Arkansas income tax withheld, and estimated tax paid are clear.
1065 Tax Form - Real estate investors use this form to document rental income received throughout the tax year, as well as expenses incurred in the course of renting property.