Get Phoenix Tax Return Form
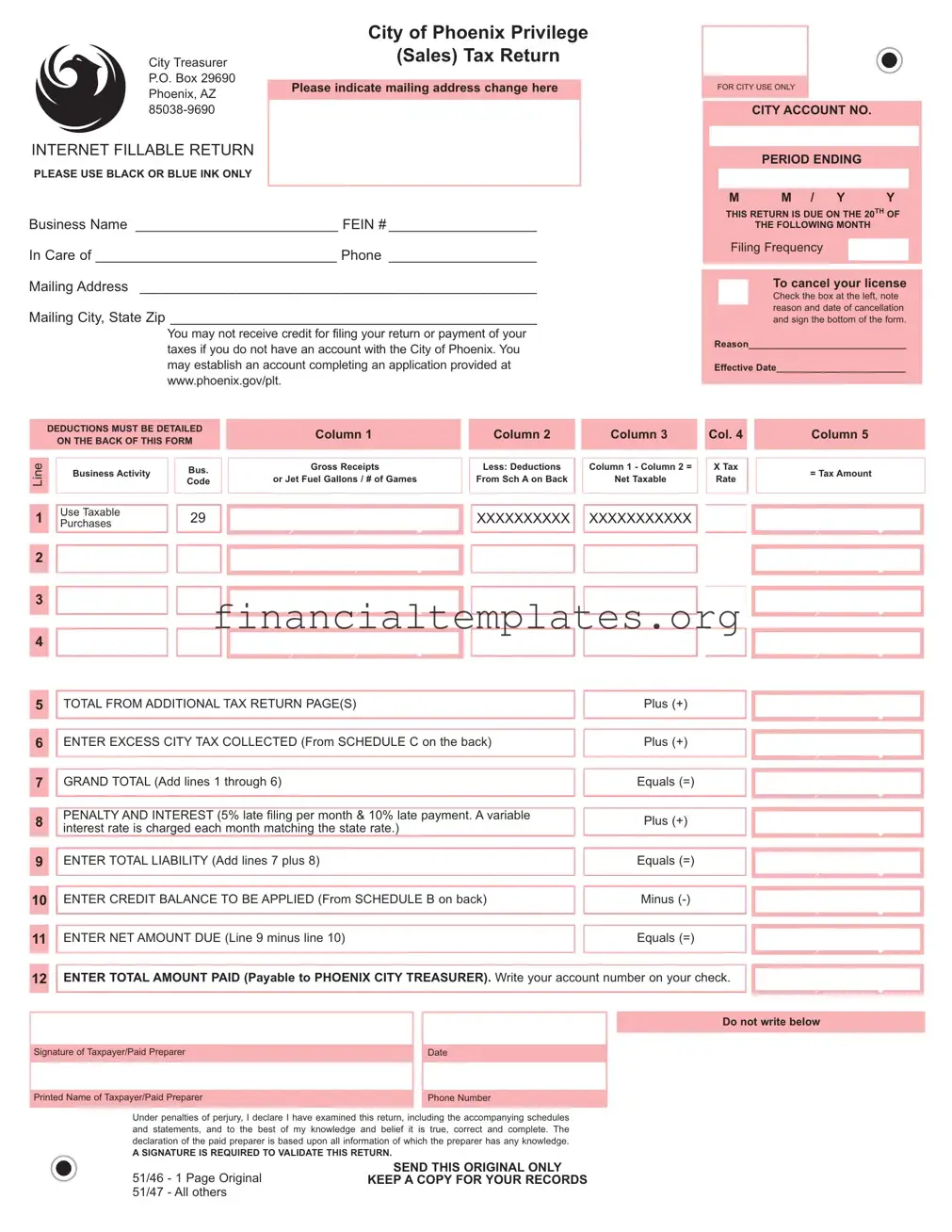
The City of Phoenix Tax Return form is an essential document for businesses operating within the city limits, designed to report privilege (sales) taxes due. Meticulously structured to facilitate accurate reporting and compliance, it necessitates the use of black or blue ink for its completion. Entities are required to update any changes in their mailing address directly on the form, indicating the importance of current contact information for efficient communication. The form clearly outlines due dates, emphasizing that returns are due on the 20th of the following month, thereby underscoring the significance of timely submissions to avoid penalties. Businesses must provide detailed information such as the Business Name, Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN), and specific details about their business activity including gross receipts and deductions. Additional instructions guide the taxpayer on how to cancel their license, apply for credits, and calculate net amount due, including penalties and interest for late filing or payment. Comprehensive instructions on the reverse side for detailing deductions underscore the city's effort to ensure that businesses accurately report their taxable and non-taxable sales. Furthermore, specifics on how to apply credits and report excess tax collected highlight the form’s exhaustive nature in handling various tax situations a business might encounter. Attention to detail, including the requirement for the preparer's signature to validate the return, reinforces the seriousness with which the City of Phoenix treats the accuracy and completeness of this financial document. Businesses are urged to retain a copy for their records, emphasizing the critical role this form plays in local tax administration.
Phoenix Tax Return Example

City Treasurer P.O. Box 29690 Phoenix, AZ
INTERNETFILLABLE RETURN
PLEASE USE BLACK OR BLUE INK ONLY
City of Phoenix Privilege
(Sales) Tax Return
|
|
|
Please indicate mailing address change here |
|
FOR CITYUSE ONLY |
|
|
|
CITYACCOUNT NO.
PERIOD ENDING
M |
M / Y |
Y |
Business Name __________________________ FEIN #___________________ |
|
THIS RETURN IS DUE ON THE 20TH OF |
|
||
|
|
THE FOLLOWING MONTH |
|
||
In Care of _______________________________ Phone ___________________ |
|
Filing Frequency |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mailing Address ____________________________________________________ |
|
|
To cancel your license |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Check the box at the left, note |
|
|
Mailing City, State Zip ________________________________________________ |
|
|
reason and date of cancellation |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
and sign the bottom of the form. |
|
||
You may not receive credit for filing your return or payment of your |
|
|
|
|
|
taxes if you do not have an account with the City of Phoenix. You |
Reason______________________________ |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
may establish an account completing an application provided at |
Effective Date_________________________ |
|
|||
www.phoenix.gov/plt. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DEDUCTIONS MUST BE DETAILED |
|
|
Column 1 |
|
|
Column 2 |
|
Column 3 |
|
Col. 4 |
|
Column 5 |
|
|
|||
|
|
ON THE BACK OF THIS FORM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Line |
|
Business Activity |
|
Bus. |
|
|
Gross Receipts |
|
|
Less: Deductions |
|
Column 1 - Column 2 = |
|
X Tax |
|
= Tax Amount |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Code |
|
or Jet Fuel Gallons / # of Games |
|
From Sch Aon Back |
|
Net Taxable |
|
Rate |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
Use Taxable |
|
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
XXXXXXXXXX |
|
XXXXXXXXXXX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchases |
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
5 |
|
TOTALFROM ADDITIONALTAX RETURN PAGE(S) |
|
|
|
|
Plus (+) |
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
6 |
|
ENTER EXCESS CITYTAX COLLECTED (From SCHEDULE C on the back) |
|
Plus (+) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
7 |
|
GRAND TOTAL(Add lines 1 through 6) |
|
|
|
|
|
Equals (=) |
|
|
|
, |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
8 |
|
PENALTYAND INTEREST(5% late filing per month & 10% late payment. Avariable |
|
Plus (+) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
interest rate is charged each month matching the state rate.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
9 |
|
ENTER TOTALLIABILITY(Add lines 7 plus 8) |
|
|
|
|
Equals (=) |
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
10 |
|
ENTER CREDITBALANCE TOBE APPLIED (From SCHEDULE B on back) |
|
Minus |
|
|
|
, |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
11 |
|
ENTER NETAMOUNTDUE (Line 9 minus line 10) |
|
|
|
|
Equals (=) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
,
12ENTER TOTALAMOUNT PAID (Payable to PHOENIX CITY TREASURER). Write your account number on your check.
,
.
.
Do not write below
Signature of Taxpayer/Paid Preparer
Printed Name of Taxpayer/Paid Preparer
Date
Phone Number
Under penalties of perjury, I declare I have examined this return, including the accompanying schedules and statements, and to the best of my knowledge and belief it is true, correct and complete. The declaration of the paid preparer is based upon all information of which the preparer has any knowledge.
ASIGNATURE IS REQUIRED TO VALIDATE THIS RETURN.
SEND THIS ORIGINAL ONLY
51/46 - 1 Page Original KEEPACOPY FOR YOUR RECORDS 51/47 - All others

Account
No.
City of Phoenix Privilege (Sales) Tax Return — page 2
Schedule A - Details of deductions: Enter the deductions included in the gross used in computing your city
privilege (sales) tax. Please note: Not all deductions are available to all business classifications.
The line numbers at the top of each column correspond with the line numbers on the front page (no Line 1 is listed).
SCHEDULE A |
Ded Code |
||
Deduction Description |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total combined tax |
64 |
||
(State, county and city) |
|||
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Bad debt on which tax was |
|
81 |
|
paid |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Sales for resale |
54 |
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Repair, service or installation |
63 |
||
labor |
|
||
|
|
||
Discounts/Refunds/Returns |
52 |
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
Freight out or delivery |
74 |
||
charges |
|||
|
|||
|
|
||
Sales to qualified health org. |
65 |
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
Sales to U.S. Govt. |
56 |
||
Byretailer 50% deductible |
|||
|
|
||
Sales to U.S. Govt. |
57 |
||
By manufacturer (100% deductible) |
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
Out of state sales |
55 |
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
82 |
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
35% Construction Contracting |
70 |
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
Exempt Subcontracting |
71 |
||
Income |
|||
|
|||
|
|
||
62 |
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
Food stamp sales |
93 |
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Sales of motor vehicle |
59 |
||
gasoline and use fuel |
|||
|
|||
|
|
||
Sales/Leases of exempt |
73 |
||
machinery & equipment |
|||
|
|||
|
|
||
Prescription drugs/prosthetics |
58 |
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
Lottery ticket sales |
68 |
||
|
|
|
|
Misc. Deductions - Please Explain here
|
|
Line 2 Bus. Code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
Line 3 Bus. Code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
Line 4 Bus. Code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
. |
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
. |
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
. |
|
TOTAL DEDUCTIONS (Copy to Front)
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
. |
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
. |
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
. |
|
SCHEDULE B Credit Details (please verify credit before claiming)
|
Account Credit |
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
B |
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Schedule B |
|
|
|
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
(copy total to front, line 10) |
|
. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCHEDULE C
Excess Tax Collected |
|
|
Line 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
By business class code |
|
C |
Line 3 |
|
|
|
+ Line 4 |
|
|
|
|
Total Schedule C |
|
|
|
(copy total to front, line 6)
,
,
,
,
.
.
.
.
POSTMARKS ARE NOT ACCEPTED AS EVIDENCE OF TIMELY FILING.
FOR ASSISTANCE, CALL: City of Phoenix
Document Specifics
| Fact Number | Fact Detail |
|---|---|
| 1 | The form is used for the City of Phoenix Privilege (Sales) Tax Return. |
| 2 | It must be filled out using black or blue ink only. |
| 3 | Businesses need to update their mailing address on this form if it has changed. |
| 4 | This return is due on the 20th of the month following the reporting period. |
| 5 | It includes sections for business name, taxpayer identification (FEIN), and mailing address. |
| 6 | To cancel a license, the form requires checking a box, noting the reason and effective date of cancellation. |
| 7 | Deductions must be detailed on the back of the form, with specific columns for calculation. |
| 8 | Penalties include a 5% late filing fee per month and a 10% late payment fee plus variable interest. |
| 9 | Payments must be made payable to PHOENIX CITY TREASURER, with the account number included on the check. |
| 10 | The form must be signed under penalty of perjury, affirming its completeness and accuracy. |
Guide to Writing Phoenix Tax Return
Filling out the Phoenix Tax Return form is important for businesses operating in Phoenix, AZ, as it ensures compliance with local tax regulations. It might seem daunting at first, but by following these steps carefully, you can complete it accurately. Remember, timely submission of this form helps avoid potential penalties and interest charges due to late filing or payment. Here are the steps you need to follow:
- Use only black or blue ink when filling out the form to ensure all information is legible.
- Start by entering your business name and Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) in the designated spaces.
- Check the box for a mailing address change if applicable and fill in the new address details.
- If cancelling your license, mark the cancellation box, provide a reason, and the effective date of cancellation.
- Enter your City Account Number and the period ending date (MM/YY).
- Complete the section assigning a person in care of the account if necessary, along with a phone number for contact.
- In the business activity section, list each type of activity, corresponding gross receipts, allowances for deductions, and calculate the net taxable amount, applying the correct tax rate to find the tax amount due.
- Add any additional tax from other return pages if applicable.
- Include any excess city tax collected as per Schedule C from the back of the form.
- Sum all values to find the grand total, then calculate any penalties and interest if your filing is late, and add this to your total liability.
- If you have a credit balance to be applied, subtract this from your total liability to find the net amount due.
- Enter the amount paid, ensuring it matches the net amount due calculated. Preparing your payment, make sure to write your account number on your check for proper identification.
- Sign and date the bottom of the form, acknowledging under penalties of perjury that the information you've provided is complete and accurate to the best of your knowledge. A preparer should also sign if applicable.
- Keep a copy of the completed form for your records and send the original to the address provided: City Treasurer, PO Box 29690, Phoenix, AZ 85038-9690.
After submitting your tax return form, it's important to keep track of the due dates for future payments and returns. Regularly visit the City of Phoenix website or contact their office for any updates regarding tax rates, filing procedures, or new taxes that may apply to your business. Timely and accurate filing helps keep your business in good standing and ensures that all applicable city taxes are accounted for.
Understanding Phoenix Tax Return
What is the City of Phoenix Privilege (Sales) Tax Return?
This form is used by businesses to report and pay the sales tax they have collected from customers on behalf of the City of Phoenix. It covers various business activities and requires detailed information about gross receipts, deductions, and the net taxable amount.
When is the Phoenix Tax Return due?
The return is due on the 20th day of the month following the end of the reporting period. For example, if you are reporting for the month of January, your return must be submitted by February 20th.
What types of payments are accepted for the City of Phoenix Privilege (Sales) Tax?
Payments can be made by check. It's important to write your city account number on your check to ensure your payment is correctly applied to your account.
How can I change my mailing address or cancel my license on the form?
To update your mailing address, simply fill in the new address in the designated area on the form. If you wish to cancel your license, check the appropriate box, note the reason and effective date of cancellation, and ensure you sign at the bottom of the form.
What are the penalties for late filing or late payment?
Late filing attracts a penalty of 5% per month, and late payment incurs a 10% penalty. Additionally, variable interest rates that match the state’s rate are charged each month for overdue payments.
Are there any specific ink colors I should use when filling out the form?
Yes, the form specifies that you should use black or blue ink only to ensure legibility and the proper processing of your return.
How can I establish a City of Phoenix tax account?
If you do not already have an account, you can establish one by completing an application available at the City of Phoenix’s official website: www.phoenix.gov/plt.
What information is required for deductions on the Phoenix Tax Return?
Detailed information about deductions must be provided on the back of the form. This includes listing the type of business activity, business gross receipts, deductions, and net taxable amounts. Specific codes and descriptions for common deductions are provided to help classify them correctly.
Who must sign the City of Phoenix Privilege (Sales) Tax Return?
The form must be signed by the taxpayer or the paid preparer. By signing, the signer declares that, to the best of their knowledge, the return is true, correct, and complete. This signature is required to validate the return.
Common mistakes
Filling out tax forms can sometimes feel like navigating through a maze. When it comes to the Phoenix Tax Return form, a few common mistakes often trip people up. Understanding these errors can help taxpayers avoid them and ensure their tax filing process is smooth. Below are five common mistakes made when completing the Phoenix Tax Return:
- Using the wrong ink color: The form specifies that only black or blue ink should be used. Although it may seem trivial, using any other color can lead to processing issues or even return rejection.
- Incorrect account information: Failure to include a valid City of Phoenix account number can lead to credits not being properly applied or returns not being processed. This often occurs when taxpayers overlook or inaccurately fill in their account details.
- Not detailing deductions: Deductions must be itemized and detailed on the back of the form. A common mistake is either not detailing these deductions or providing insufficient explanation, leading to lost tax benefits or queries from the city.
- Failing to sign the return: The form states that a signature is required to validate the return. An unsigned tax form is considered incomplete and will not be processed, thus delaying any refunds or acknowledgments of filing.
- Missing the filing deadline: The return is due on the 20th of the following month. Late submissions are subject to penalties and interest, yet it is a frequent oversight by many filers.
Avoiding these common mistakes can make the tax return process less daunting and help ensure your financial obligations to the City of Phoenix are met accurately and on time.
Documents used along the form
When filing the Phoenix Tax Return form, other important documents and forms often play a crucial role in ensuring completeness and compliance with the City of Phoenix's requirements. These documents support and provide detailed insight into the figures reported on the tax return. Understanding these documents is vital for an accurate and audit-proof tax filing process.
- W-9 Form: Used to provide the correct Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) of the person or entity conducting business, ensuring accurate tax reporting to the IRS and preventing backup withholding.
- Sales and Use Tax Worksheet: Helps taxpayers calculate the total sales tax due from business operations, including applicable deductions and exemptions, ensuring accuracy in reporting taxable and nontaxable sales.
- Income Statement: This financial statement provides a detailed report of the company's revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period, supporting the gross receipts reported on the tax return.
- Balance Sheet: Offers a snapshot of the company’s financial condition at the end of a particular period, detailing assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity, which can affect tax liability.
- Bank Statements: Serve as a third-party verification of the cash flow in and out of the business accounts, supporting the income and deductions claimed on the tax return.
- 1099-MISC Forms: These are necessary for businesses that have hired independent contractors, showing non-employee compensation that may be deductible as a business expense.
- Schedule of Deductions Detail: Provides a thorough breakdown of deductions claimed on the tax return, including descriptions and amounts, to substantiate deductions for specific business activities.
Collectively, these documents are integral to the tax filing process. They ensure that the information reported on the Phoenix Tax Return form is accurate and backed by solid documentation. Proper preparation and organization of these records streamline the filing process and help avoid complications with tax authorities.
Similar forms
The form is similar to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) 1040 Form, which is used by U.S. taxpayers to file an annual income tax return. Both documents require detailed financial information, including income, deductions, and applicable taxes owed. They also include sections for the taxpayer's personal information and a declaration that the information is true and correct to the best of their knowledge.
Comparable to a State Sales Tax Return, this document collects sales-related financial details from businesses operating within the city. Both forms demand the reporting of gross receipts, allowable deductions, and calculation of taxes due. They serve the purpose of remitting sales tax collected from customers to the respective government authority.
Similar to the Employee’s Withholding Allowance Certificate (W-4 Form), it collects crucial taxpayer information for tax-related purposes. While the W-4 focuses on payroll tax withholdings, both forms meticulously detail personal and financial information to comply with tax regulations and ensure accurate tax collection and/or payments.
It has parallels with the Business License Application forms found in many municipalities. Both require information about the business, including the FEIN, business name, and contact details. These documents are integral to obtaining the necessary authorization for legal business operations within the city or area specified.
It resembles a Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) Tax Return, with both requiring detailed financial reporting for tax purposes. They collect different types of tax, but each plays a critical role in ensuring businesses contribute to federal or municipal financial obligations, thus funding government services or benefits.
Also akin to a Quarterly Estimated Tax Payment voucher, which individuals and businesses use to remit payments towards their expected tax liability before the annual filing. Both encourage compliance with tax obligations throughout the fiscal period, preventing substantial cumulative dues at the fiscal year's end.
It mirrors the functionality of a Property Tax Declaration form closely, wherein property owners report the value of their property to determine tax liability. Both types of forms help the corresponding government entities to assess and collect taxes based on reported values or income, ensuring funding for public services.
Similar to a Worker’s Compensation Insurance Report, this form requires businesses to provide specifics regarding their operations, albeit for differing intents. Both are compliance documents essential for operating within legal and regulatory frameworks, ensuring financial responsibilities, whether taxes or insurance premiums, are accurately reported and paid.
It aligns with Customs Declaration forms used for international trade, where businesses must declare the value of goods being shipped. While serving different government entities and purposes, both facilitate the accurate collection of dues—taxes in one scenario and duties in the other—based on declared values or transactions.
Dos and Don'ts
Filling out the Phoenix Tax Return form accurately is crucial for meeting tax obligations and ensuring compliance with city regulations. Here are some essential tips to guide you through the process:
Do:- Use black or blue ink only, as specified on the form, to ensure clarity and readability.
- Double-check the city account number and ensure it's correctly entered to avoid processing delays.
- Report gross receipts accurately in the relevant sections and ensure that all income is accounted for.
- Detail your deductions on the back of the form, as incomplete information could result in disallowed deductions.
- Include deductions such as bad debt, sales for resale, and other allowable items, precisely as guided in Schedule A.
- Calculate penalties and interest correctly if the submission is late to avoid further discrepancies and additional fines.
- Sign the form. An unsigned form is considered invalid and could lead to penalties.
- Keep a copy for your records. It's essential for tracking your tax obligations and any future inquiries.
- Verify any credit balance to be applied as stated in Schedule B to avoid mistakes in your payment due.
- Check the box for mailing address change if applicable, to ensure all correspondence reaches you.
- Forget to enter the business name and FEIN# at the top of the form; these identifiers are crucial for processing your return.
- Mistake the filing frequency or the period ending, as this could lead to your return being processed for the wrong period.
- Omit phone numbers or contact information which could delay resolution if there are issues with your return.
- Leave the deduction details area on the back of the form blank; specificity is required for validation.
- Include non-eligible deductions; ensure you understand which deductions are allowable for your business classification.
- Miscalculate the net taxable amount or tax due. Accurate calculations prevent additional charges or audit flags.
- Underestimate penalty and interest charges for late filings. Always aim to file and pay on time to avoid these costs.
- Overlook excess city tax collected as reported in Schedule C. This amount needs accurate reporting and remittance.
- Ignore instructions for credit balances and net amounts due. Misinterpretation can lead to underpayment or overpayment.
- Delay sending your form until the last minute. Postmarks are not accepted as evidence of timely filing.
Following these guidelines can help streamline the tax filing process and ensure compliance with the City of Phoenix's requirements. Always consult a tax professional if you have specific questions or concerns regarding your situation.
Misconceptions
When navigating the intricacies of the Phoenix Tax Return form, individuals and businesses might encounter several misconceptions that can lead to confusion or errors in their filing. Understanding these misconceptions can ensure accurate and timely submissions, avoiding potential penalties and complications.
Only Phoenix-based businesses are required to file: It's a common misunderstanding that only businesses physically located within Phoenix need to file this return. In reality, any business engaging in taxable activities within Phoenix's jurisdiction must complete the form, regardless of their base location.
Filing frequency is fixed: Many assume that the frequency of their tax returns is set permanently. However, the City of Phoenix may adjust a business's filing frequency based on its reported sales volume or compliance history, necessitating adaptability from the business.
All deductions require detailed documentation on the back of the form: While the form does state that deductions must be detailed, not every deduction necessitates extensive backup in the submission. Key is providing enough information to justify the deduction without overburdening the process.
Digital submissions are less valid than paper submissions: There's a misconception that electronically filed returns are somehow less official or are scrutinized more than paper filings. Both digital and paper formats are equally valid, and the City of Phoenix encourages electronic submissions for efficiency.
Penalty and interest rates are negotiable: The form outlines specific rates for late filing and payments, such as a 5% late filing fee per month and a 10% late payment fee. These rates are set by ordinance and are not subject to negotiation or alteration by individual taxpayers or city staff.
The "Enter Total Amount Paid" section is for the exact amount due only: This section can lead to confusion, with some believing it should only reflect the bottom-line amount owed after all calculations. It should, however, include the total payment submitted with the return, which might also account for pre-payments or additional amounts paid in anticipation of future liabilities.
Correcting these misconceptions can streamline the tax return process, ensuring businesses remain compliant and reduce the risk of unnecessary penalties. Always refer to the official City of Phoenix website or consult with a tax professional for the most accurate and personalized advice.
Key takeaways
Filing the Phoenix Tax Return form correctly is crucial for businesses to comply with city tax regulations. Here are some key takeaways to remember:
- Use black or blue ink only when filling out the form to ensure that your information is legible and accurately processed.
- It's important to indicate any changes to your mailing address on the form to guarantee that you receive all correspondence from the City Treasurer.
- The form is due on the 20th of the month following the tax period you are reporting for. Late submissions may incur penalties and interest charges.
- Businesses without an account with the City of Phoenix must establish one by completing an application available at the city’s official website before filing this return.
- Detailed deductions must be outlined on the back of the form, ensuring that you accurately calculate your net taxable amount and applicable taxes.
- If intending to cancel your license, you must check the appropriate box, note the reason and effective date for cancellation, and sign at the bottom of the form.
- Ensure that the correct tax amount is entered, including calculating any penalty and interest owed for late filings or payments as per the specifications on the form.
- To avoid errors, check all calculations for total deductions, tax liabilities, credit balances, and the net amount due to ensure accuracy before submitting.
- The declaration signed under penalty of perjury requires that all schedules and statements accompanying the return are true, correct, and complete to the best of your knowledge.
The Phoenix Tax Return form is a critical document for business operations within the city. For assistance, businesses can call the City of Phoenix, use TTY services for the hearing impaired, or visit the official website. Remembering these key points will aid in the successful and compliant submission of your tax return.
Popular PDF Documents
1065 Vs 1120 - Crucial for determining a shareholder's eligibility for certain tax benefits, such as the Qualified Business Income deduction.
Transfer Taxes Illinois - It serves as a vital document for county and state revenue departments, facilitating proper assessment and taxation.