Get IRS W-8BEN-E Form
In navigating the complexities of international business dealings, understanding and accurately completing the IRS W-8BEN-E form is crucial for foreign entities engaged with U.S. companies. This form plays a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with U.S. tax laws, specifically for entities that are earning income from U.S. sources. Its primary function is to certify the foreign status of the beneficial owner of the income and, if applicable, assert eligibility for reduced rates or exemption from U.S. withholding tax under the provisions of an income tax treaty. Proper completion of the form not only helps in preventing unnecessary withholding tax but also in avoiding potential penalties for failing to furnish accurate information. With regulations and tax obligations often appearing daunting for foreign entities, a comprehensive understanding of the IRS W-8BEN-E form, its key sections, and the implications of its declarations can significantly smooth the process of international transactions and foster more favorable financial outcomes.
IRS W-8BEN-E Example
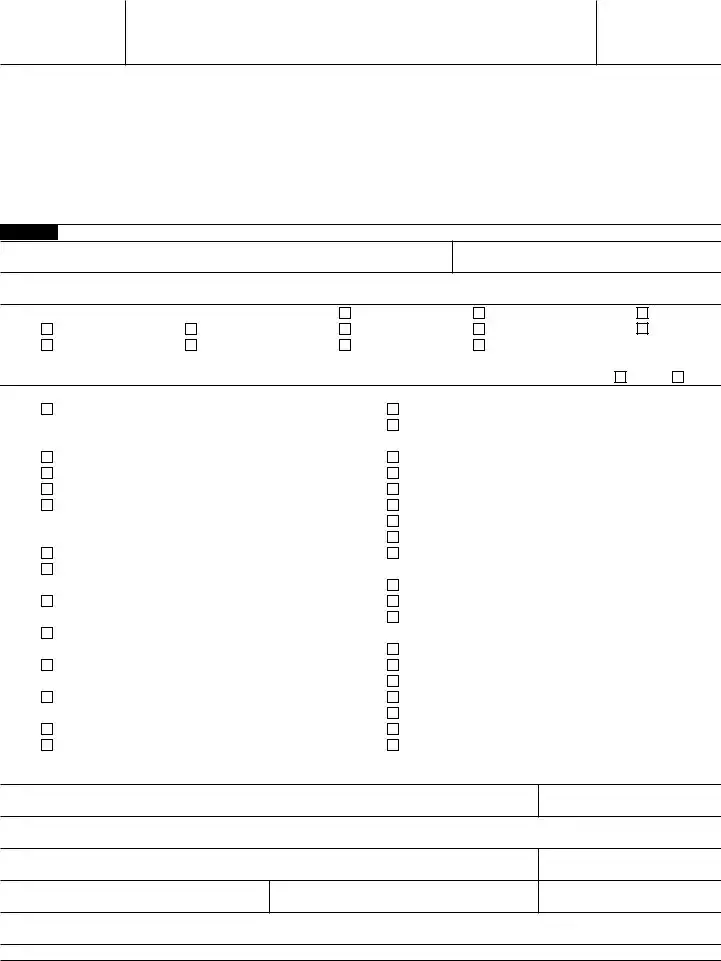
Form
(Rev. October 2021)
Department of the Treasury
Internal Revenue Service
Certificate of Status of Beneficial Owner for
United States Tax Withholding and Reporting (Entities)
▶For use by entities. Individuals must use Form
▶Go to www.irs.gov/FormW8BENE for instructions and the latest information.
▶Give this form to the withholding agent or payer. Do not send to the IRS.
OMB No.
Do NOT use this form for: |
Instead use Form: |
||
• U.S. entity or U.S. citizen or resident . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
. |
• A foreign individual |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
||
• A foreign individual or entity claiming that income is effectively connected with the conduct of trade or business within the United States |
|
|
|
(unless claiming treaty benefits) . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
|
• A foreign partnership, a foreign simple trust, or a foreign grantor trust (unless claiming treaty benefits) (see instructions for exceptions) . |
. |
||
•A foreign government, international organization, foreign central bank of issue, foreign
501(c), 892, 895, or 1443(b) (unless claiming treaty benefits) (see instructions for other exceptions) |
|
• Any person acting as an intermediary (including a qualified intermediary acting as a qualified derivatives dealer) |
. . . . |
Part I Identification of Beneficial Owner
1Name of organization that is the beneficial owner
2Country of incorporation or organization
3Name of disregarded entity receiving the payment (if applicable, see instructions)
4Chapter 3 Status (entity type) (Must check one box only):
Simple trust |
|
Central Bank of Issue |
Private foundation |
Grantor trust |
Disregarded entity |
Corporation Complex trust Estate
International organization
Partnership
Foreign Government - Controlled Entity
Foreign Government - Integral Part
If you entered disregarded entity, partnership, simple trust, or grantor trust above, is the entity a hybrid making a treaty claim? If “Yes,” complete Part III.
Yes
No
5 Chapter 4 Status (FATCA status) (See instructions for details and complete the certification below for the entity's applicable status.)

 Nonparticipating FFI (including an FFI related to a Reporting IGA FFI other than a
Nonparticipating FFI (including an FFI related to a Reporting IGA FFI other than a
Nonreporting IGA FFI. Complete Part XII.

 Foreign government, government of a U.S. possession, or foreign central bank of issue. Complete Part XIII.
Foreign government, government of a U.S. possession, or foreign central bank of issue. Complete Part XIII.
Participating FFI. Reporting Model 1 FFI. Reporting Model 2 FFI.

 Registered
Registered
International organization. Complete Part XIV. Exempt retirement plans. Complete Part XV.
Entity wholly owned by exempt beneficial owners. Complete Part XVI. Territory financial institution. Complete Part XVII.
Excepted nonfinancial group entity. Complete Part XVIII. Excepted nonfinancial
Sponsored FFI. Complete Part IV.

 Certified
Certified

 Certified
Certified

 Certified
Certified

 Certified
Certified

 Certain investment entities that do not maintain financial accounts. Complete Part IX.
Certain investment entities that do not maintain financial accounts. Complete Part IX.

 Excepted nonfinancial entity in liquidation or bankruptcy. Complete Part XX.
Excepted nonfinancial entity in liquidation or bankruptcy. Complete Part XX.
501(c) organization. Complete Part XXI. Nonprofit organization. Complete Part XXII.

 Publicly traded NFFE or NFFE affiliate of a publicly traded corporation. Complete Part XXIII.
Publicly traded NFFE or NFFE affiliate of a publicly traded corporation. Complete Part XXIII.
Excepted territory NFFE. Complete Part XXIV.
Active NFFE. Complete Part XXV.
Passive NFFE. Complete Part XXVI.
Excepted
Direct reporting NFFE.
Sponsored direct reporting NFFE. Complete Part XXVIII. Account that is not a financial account.
6Permanent residence address (street, apt. or suite no., or rural route). Do not use a P.O. box or
City or town, state or province. Include postal code where appropriate.
Country
7 Mailing address (if different from above)
City or town, state or province. Include postal code where appropriate. |
|
Country |
|
|
|
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see separate instructions. |
Cat. No. 59689N |
Form |
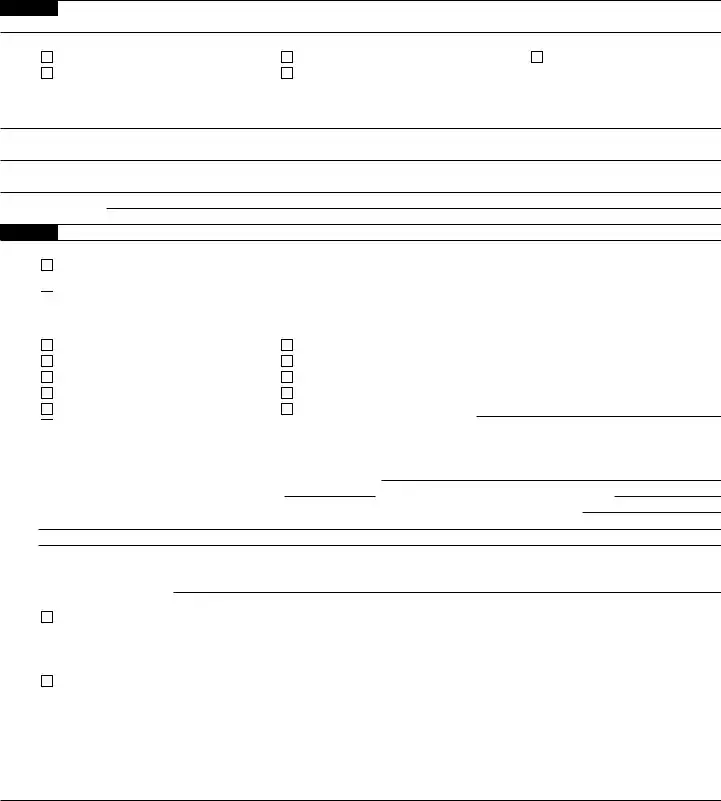
Form |
Page 2 |
|
Part I |
Identification of Beneficial Owner (continued) |
|
8U.S. taxpayer identification number (TIN), if required
9a GIIN
bForeign TIN
c Check if FTIN not legally required . . . . . . ▶ 

10Reference number(s) (see instructions)
Note: Please complete remainder of the form including signing the form in Part XXX.
Part II Disregarded Entity or Branch Receiving Payment. (Complete only if a disregarded entity with a GIIN or a branch of an FFI in a country other than the FFI’s country of residence. See instructions.)
11Chapter 4 Status (FATCA status) of disregarded entity or branch receiving payment
Branch treated as nonparticipating FFI. |
Reporting Model 1 FFI. |
U.S. Branch. |
Participating FFI. |
Reporting Model 2 FFI. |
|
12Address of disregarded entity or branch (street, apt. or suite no., or rural route). Do not use a P.O. box or
City or town, state or province. Include postal code where appropriate. Country
13GIIN (if any)
Part III Claim of Tax Treaty Benefits (if applicable). (For chapter 3 purposes only.)
14
a
b
I certify that (check all that apply): |
|
|
The beneficial owner is a resident of |
|
within the meaning of the income tax |
treaty between the United States and that country. |
|
|

 The beneficial owner derives the item (or items) of income for which the treaty benefits are claimed, and, if applicable, meets the requirements of the treaty provision dealing with limitation on benefits. The following are types of limitation on benefits provisions that may be included in an applicable tax treaty (check only one; see instructions):
The beneficial owner derives the item (or items) of income for which the treaty benefits are claimed, and, if applicable, meets the requirements of the treaty provision dealing with limitation on benefits. The following are types of limitation on benefits provisions that may be included in an applicable tax treaty (check only one; see instructions):
Government
Company that meets the ownership and base erosion test
Company that meets the derivative benefits test |
|
Other |
Company with an item of income that meets active trade or business test |
Publicly traded corporation |
Favorable discretionary determination by the U.S. competent authority received |
Subsidiary of a publicly traded corporation |
No LOB article in treaty |
|
Other (specify Article and paragraph): |
c The beneficial owner is claiming treaty benefits for U.S. source dividends received from a foreign corporation or interest from a U.S. trade or business of a foreign corporation and meets qualified resident status (see instructions).
The beneficial owner is claiming treaty benefits for U.S. source dividends received from a foreign corporation or interest from a U.S. trade or business of a foreign corporation and meets qualified resident status (see instructions).
15Special rates and conditions (if
The beneficial owner is claiming the provisions of Article and paragraph
of the treaty identified on line 14a above to claim a |
|
|
% rate of withholding on (specify type of income): |
||
Explain the additional conditions in the Article the beneficial owner meets to be eligible for the rate of withholding:
Part IV |
Sponsored FFI |
16Name of sponsoring entity:
17Check whichever box applies.
I certify that the entity identified in Part I:
•Is an investment entity;
•Is not a QI, WP (except to the extent permitted in the withholding foreign partnership agreement), or WT; and
•Has agreed with the entity identified above (that is not a nonparticipating FFI) to act as the sponsoring entity for this entity.
I certify that the entity identified in Part I:
•Is a controlled foreign corporation as defined in section 957(a);
•Is not a QI, WP, or WT;
•Is wholly owned, directly or indirectly, by the U.S. financial institution identified above that agrees to act as the sponsoring entity for this entity; and
•Shares a common electronic account system with the sponsoring entity (identified above) that enables the sponsoring entity to identify all account holders and payees of the entity and to access all account and customer information maintained by the entity including, but not limited to, customer identification information, customer documentation, account balance, and all payments made to account holders or payees.
Form
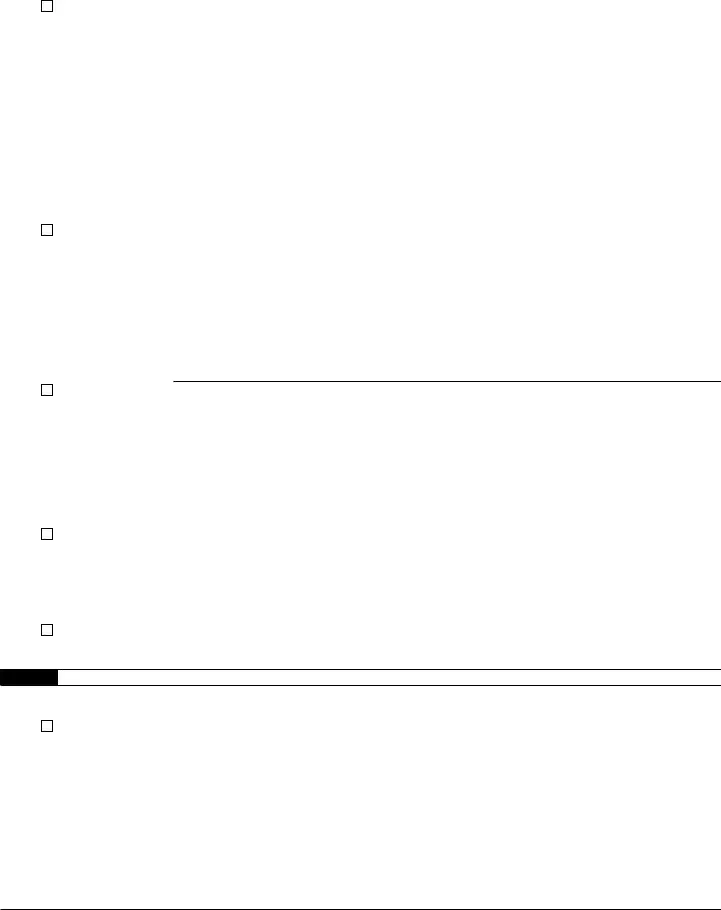
Form |
Page 3 |
|
Part V |
Certified |
|
18 |
I certify that the FFI identified in Part I: |
|
•Operates and is licensed solely as a bank or credit union (or similar cooperative credit organization operated without profit) in its country of incorporation or organization;
•Engages primarily in the business of receiving deposits from and making loans to, with respect to a bank, retail customers unrelated to such bank and, with respect to a credit union or similar cooperative credit organization, members, provided that no member has a greater than 5% interest in such credit union or cooperative credit organization;
•Does not solicit account holders outside its country of organization;
•Has no fixed place of business outside such country (for this purpose, a fixed place of business does not include a location that is not advertised to the public and from which the FFI performs solely administrative support functions);
•Has no more than $175 million in assets on its balance sheet and, if it is a member of an expanded affiliated group, the group has no more than $500 million in total assets on its consolidated or combined balance sheets; and
•Does not have any member of its expanded affiliated group that is a foreign financial institution, other than a foreign financial institution that is incorporated or organized in the same country as the FFI identified in Part I and that meets the requirements set forth in this part.
Part VI |
Certified |
19 |
I certify that the FFI identified in Part I: |
•Is not engaged primarily in the business of investing, reinvesting, or trading in securities, partnership interests, commodities, notional principal contracts, insurance or annuity contracts, or any interest (including a futures or forward contract or option) in such security, partnership interest, commodity, notional principal contract, insurance contract or annuity contract;
•No financial account maintained by the FFI or any member of its expanded affiliated group, if any, has a balance or value in excess of $50,000 (as determined after applying applicable account aggregation rules); and
•Neither the FFI nor the entire expanded affiliated group, if any, of the FFI, have more than $50 million in assets on its consolidated or combined balance sheet as of the end of its most recent accounting year.
Part VII |
Certified |
20Name of sponsoring entity:
21 |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I: |
•Is an FFI solely because it is an investment entity described in Regulations section
•Is not a QI, WP, or WT;
•Will have all of its due diligence, withholding, and reporting responsibilities (determined as if the FFI were a participating FFI) fulfilled by the sponsoring entity identified on line 20; and
•20 or fewer individuals own all of the debt and equity interests in the entity (disregarding debt interests owned by U.S. financial institutions, participating FFIs, registered
Part VIII |
Certified |
22 |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I: |
•Was in existence as of January 17, 2013;
•Issued all classes of its debt or equity interests to investors on or before January 17, 2013, pursuant to a trust indenture or similar agreement; and
•Is certified
Part IX |
Certain Investment Entities that Do Not Maintain Financial Accounts |
23 |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I: |
•Is a financial institution solely because it is an investment entity described in Regulations section
•Does not maintain financial accounts.
Part X
Note: This status only applies if the U.S. financial institution, participating FFI, or reporting Model 1 FFI to which this form is given has agreed that it will treat the FFI as an
24a (All
•Does not act as an intermediary;
•Does not accept deposits in the ordinary course of a banking or similar business;
•Does not hold, as a substantial portion of its business, financial assets for the account of others;
•Is not an insurance company (or the holding company of an insurance company) that issues or is obligated to make payments with respect to a financial account;
•Is not owned by or in an expanded affiliated group with an entity that accepts deposits in the ordinary course of a banking or similar business, holds, as a substantial portion of its business, financial assets for the account of others, or is an insurance company (or the holding company of an insurance company) that issues or is obligated to make payments with respect to a financial account;
•Does not maintain a financial account for any nonparticipating FFI; and
•Does not have any specified U.S. persons that own an equity interest or debt interest (other than a debt interest that is not a financial account or that has a balance or value not exceeding $50,000) in the FFI other than those identified on the FFI owner reporting statement.
Form
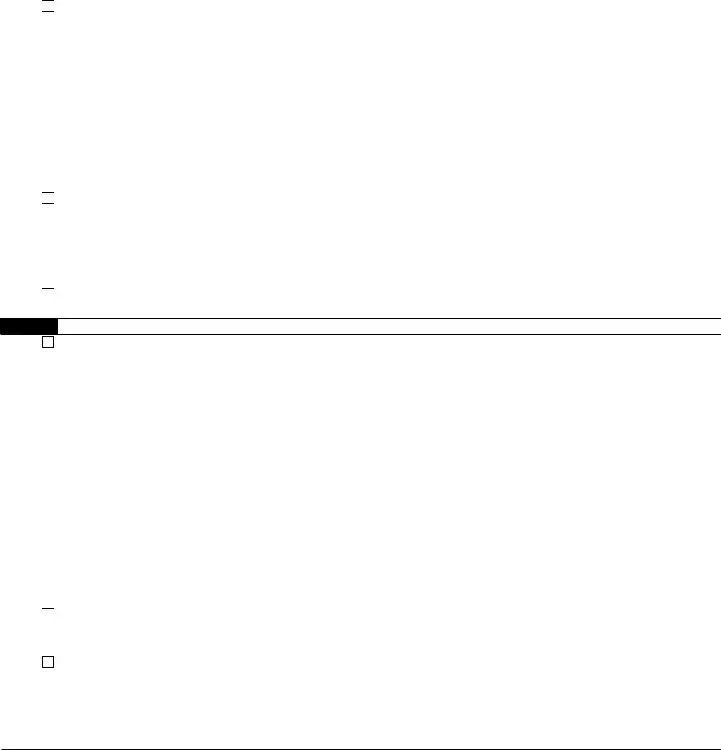
Form |
Page 4 |
|
Part X |
|
|
Check box 24b or 24c, whichever applies. b 

•Has provided, or will provide, an FFI owner reporting statement that contains:
(i)The name, address, TIN (if any), chapter 4 status, and type of documentation provided (if required) of every individual and specified U.S. person that owns a direct or indirect equity interest in the
(ii)The name, address, TIN (if any), and chapter 4 status of every individual and specified U.S. person that owns a debt interest in the
(iii)Any additional information the withholding agent requests in order to fulfill its obligations with respect to the entity.
•Has provided, or will provide, valid documentation meeting the requirements of Regulations section
c 
 I certify that the FFI identified in Part I has provided, or will provide, an auditor's letter, signed within 4 years of the date of payment,
I certify that the FFI identified in Part I has provided, or will provide, an auditor's letter, signed within 4 years of the date of payment,
from an independent accounting firm or legal representative with a location in the United States stating that the firm or representative has reviewed the FFI’s documentation with respect to all of its owners and debt holders identified in Regulations section
Check box 24d if applicable (optional, see instructions).
d
 I certify that the entity identified on line 1 is a trust that does not have any contingent beneficiaries or designated classes with unidentified beneficiaries.
I certify that the entity identified on line 1 is a trust that does not have any contingent beneficiaries or designated classes with unidentified beneficiaries.
Part XI
25a
•Operates as a distributor with respect to debt or equity interests of the restricted fund with respect to which this form is furnished;
•Provides investment services to at least 30 customers unrelated to each other and less than half of its customers are related to each other;
•Is required to perform AML due diligence procedures under the
•Operates solely in its country of incorporation or organization, has no fixed place of business outside of that country, and has the same country of incorporation or organization as all members of its affiliated group, if any;
•Does not solicit customers outside its country of incorporation or organization;
•Has no more than $175 million in total assets under management and no more than $7 million in gross revenue on its income statement for the most recent accounting year;
•Is not a member of an expanded affiliated group that has more than $500 million in total assets under management or more than $20 million in gross revenue for its most recent accounting year on a combined or consolidated income statement; and
•Does not distribute any debt or securities of the restricted fund to specified U.S. persons, passive NFFEs with one or more substantial U.S. owners, or nonparticipating FFIs.
Check box 25b or 25c, whichever applies.
I further certify that with respect to all sales of debt or equity interests in the restricted fund with respect to which this form is furnished that are made after December 31, 2011, the entity identified in Part I:
b Has been bound by a distribution agreement that contained a general prohibition on the sale of debt or securities to U.S. entities and U.S. resident individuals and is currently bound by a distribution agreement that contains a prohibition of the sale of debt or securities to any specified U.S. person, passive NFFE with one or more substantial U.S. owners, or nonparticipating FFI.
Has been bound by a distribution agreement that contained a general prohibition on the sale of debt or securities to U.S. entities and U.S. resident individuals and is currently bound by a distribution agreement that contains a prohibition of the sale of debt or securities to any specified U.S. person, passive NFFE with one or more substantial U.S. owners, or nonparticipating FFI.
c
Is currently bound by a distribution agreement that contains a prohibition on the sale of debt or securities to any specified U.S. person, passive NFFE with one or more substantial U.S. owners, or nonparticipating FFI and, for all sales made prior to the time that such a restriction was included in its distribution agreement, has reviewed all accounts related to such sales in accordance with the procedures identified in Regulations section
Form

Form |
Page 5 |
|
Part XII |
Nonreporting IGA FFI |
|
26 |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I: |
|
• Meets the requirements to be considered a nonreporting financial institution pursuant to an applicable IGA between the United States and
. The applicable IGA is a
Model 1 IGA or a
Model 2 IGA; and
is treated as a |
|
under the provisions of the applicable IGA or Treasury regulations |
||
(if applicable, see instructions); |
|
|
|
|
• If you are a trustee documented trust or a sponsored entity, provide the name of the trustee or sponsor |
|
. |
||
The trustee is:
U.S.
Foreign
Part XIII Foreign Government, Government of a U.S. Possession, or Foreign Central Bank of Issue
27
I certify that the entity identified in Part I is the beneficial owner of the payment, and is not engaged in commercial financial activities of a type engaged in by an insurance company, custodial institution, or depository institution with respect to the payments, accounts, or obligations for which this form is submitted (except as permitted in Regulations section
Part XIV |
International Organization |
Check box 28a or 28b, whichever applies.
28a |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I is an international organization described in section 7701(a)(18). |
b |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I: |
•Is comprised primarily of foreign governments;
•Is recognized as an intergovernmental or supranational organization under a foreign law similar to the International Organizations Immunities Act or that has in effect a headquarters agreement with a foreign government;
•The benefit of the entity’s income does not inure to any private person; and
•Is the beneficial owner of the payment and is not engaged in commercial financial activities of a type engaged in by an insurance company, custodial institution, or depository institution with respect to the payments, accounts, or obligations for which this form is submitted (except as permitted in Regulations section
Part XV |
Exempt Retirement Plans |
Check box 29a, b, c, d, e, or f, whichever applies. 29a 

•Is established in a country with which the United States has an income tax treaty in force (see Part III if claiming treaty benefits);
•Is operated principally to administer or provide pension or retirement benefits; and
•Is entitled to treaty benefits on income that the fund derives from U.S. sources (or would be entitled to benefits if it derived any such income) as a resident of the other country which satisfies any applicable limitation on benefits requirement.
b
•Is organized for the provision of retirement, disability, or death benefits (or any combination thereof) to beneficiaries that are former employees of one or more employers in consideration for services rendered;
•No single beneficiary has a right to more than 5% of the FFI’s assets;
•Is subject to government regulation and provides annual information reporting about its beneficiaries to the relevant tax authorities in the country in which the fund is established or operated; and
(i)Is generally exempt from tax on investment income under the laws of the country in which it is established or operates due to its status as a retirement or pension plan;
(ii)Receives at least 50% of its total contributions from sponsoring employers (disregarding transfers of assets from other plans described in this part, retirement and pension accounts described in an applicable Model 1 or Model 2 IGA, other retirement funds described in an applicable Model 1 or Model 2 IGA, or accounts described in Regulations section
(iii)Either does not permit or penalizes distributions or withdrawals made before the occurrence of specified events related to retirement, disability, or death (except rollover distributions to accounts described in Regulations section
(iv)Limits contributions by employees to the fund by reference to earned income of the employee or may not exceed $50,000 annually.
c |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I: |
•Is organized for the provision of retirement, disability, or death benefits (or any combination thereof) to beneficiaries that are former employees of one or more employers in consideration for services rendered;
•Has fewer than 50 participants;
•Is sponsored by one or more employers each of which is not an investment entity or passive NFFE;
•Employee and employer contributions to the fund (disregarding transfers of assets from other plans described in this part, retirement and pension accounts described in an applicable Model 1 or Model 2 IGA, or accounts described in Regulations section
•Participants that are not residents of the country in which the fund is established or operated are not entitled to more than 20% of the fund’s assets; and
•Is subject to government regulation and provides annual information reporting about its beneficiaries to the relevant tax authorities in the country in which the fund is established or operates.
Form

Form |
Page 6 |
|
Part XV |
Exempt Retirement Plans (continued) |
|
d |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I is formed pursuant to a pension plan that would meet the requirements of section 401(a), other |
|
than the requirement that the plan be funded by a trust created or organized in the United States.
e
I certify that the entity identified in Part I is established exclusively to earn income for the benefit of one or more retirement funds
|
described in this part or in an applicable Model 1 or Model 2 IGA, or accounts described in Regulations section |
|
retirement and pension accounts), or retirement and pension accounts described in an applicable Model 1 or Model 2 IGA. |
f |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I: |
• Is established and sponsored by a foreign government, international organization, central bank of issue, or government of a U.S. possession (each as defined in Regulations section
• Is established and sponsored by a foreign government, international organization, central bank of issue, or government of a U.S. possession (each as defined in Regulations section
Part XVI |
Entity Wholly Owned by Exempt Beneficial Owners |
30 |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I: |
•Is an FFI solely because it is an investment entity;
•Each direct holder of an equity interest in the investment entity is an exempt beneficial owner described in Regulations section
•Each direct holder of a debt interest in the investment entity is either a depository institution (with respect to a loan made to such entity) or an exempt beneficial owner described in Regulations section
•Has provided an owner reporting statement that contains the name, address, TIN (if any), chapter 4 status, and a description of the type of documentation provided to the withholding agent for every person that owns a debt interest constituting a financial account or direct equity interest in the entity; and
•Has provided documentation establishing that every owner of the entity is an entity described in Regulations section
(f)and/or (g) without regard to whether such owners are beneficial owners.
Part XVII |
Territory Financial Institution |
31
I certify that the entity identified in Part I is a financial institution (other than an investment entity) that is incorporated or organized under the laws of a possession of the United States.
Part XVIII |
Excepted Nonfinancial Group Entity |
32 |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I: |
•Is a holding company, treasury center, or captive finance company and substantially all of the entity’s activities are functions described in Regulations section
•Is a member of a nonfinancial group described in Regulations section
•Is not a depository or custodial institution (other than for members of the entity’s expanded affiliated group); and
•Does not function (or hold itself out) as an investment fund, such as a private equity fund, venture capital fund, leveraged buyout fund, or any investment vehicle with an investment strategy to acquire or fund companies and then hold interests in those companies as capital assets for investment purposes.
Part XIX |
Excepted Nonfinancial |
33 |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I: |
•Was formed on (or, in the case of a new line of business, the date of board resolution approving the new line of business) (date must be less than 24 months prior to date of payment);
•Is not yet operating a business and has no prior operating history or is investing capital in assets with the intent to operate a new line of business other than that of a financial institution or passive NFFE;
•Is investing capital into assets with the intent to operate a business other than that of a financial institution; and
•Does not function (or hold itself out) as an investment fund, such as a private equity fund, venture capital fund, leveraged buyout fund, or any investment vehicle whose purpose is to acquire or fund companies and then hold interests in those companies as capital assets for investment purposes.
Part XX Excepted Nonfinancial Entity in Liquidation or Bankruptcy
34 |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I: |
|
|
|
• Filed a plan of liquidation, filed a plan of reorganization, or filed for bankruptcy on |
|
; |
• During the past 5 years has not been engaged in business as a financial institution or acted as a passive NFFE;
• Is either liquidating or emerging from a reorganization or bankruptcy with the intent to continue or recommence operations as a nonfinancial entity; and
• Has, or will provide, documentary evidence such as a bankruptcy filing or other public documentation that supports its claim if it remains in bankruptcy or liquidation for more than 3 years.
Form
Form |
Page 7 |
||
Part XXI |
|
501(c) Organization |
|
35 |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I is a 501(c) organization that: |
||
• Has been issued a determination letter from the IRS that is currently in effect concluding that the payee is a section 501(c) organization that is |
|||
dated |
|
; or |
|
•Has provided a copy of an opinion from U.S. counsel certifying that the payee is a section 501(c) organization (without regard to whether the payee is a foreign private foundation).
Part XXII |
Nonprofit Organization |
36 |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I is a nonprofit organization that meets the following requirements. |
•The entity is established and maintained in its country of residence exclusively for religious, charitable, scientific, artistic, cultural or educational purposes;
•The entity is exempt from income tax in its country of residence;
•The entity has no shareholders or members who have a proprietary or beneficial interest in its income or assets;
•Neither the applicable laws of the entity’s country of residence nor the entity’s formation documents permit any income or assets of the entity to be distributed to, or applied for the benefit of, a private person or noncharitable entity other than pursuant to the conduct of the entity’s charitable activities or as payment of reasonable compensation for services rendered or payment representing the fair market value of property which the entity has purchased; and
•The applicable laws of the entity’s country of residence or the entity’s formation documents require that, upon the entity’s liquidation or dissolution, all of its assets be distributed to an entity that is a foreign government, an integral part of a foreign government, a controlled entity of a foreign government, or another organization that is described in this part or escheats to the government of the entity’s country of residence or any political subdivision thereof.
Part XXIII Publicly Traded NFFE or NFFE Affiliate of a Publicly Traded Corporation
Check box 37a or 37b, whichever applies.
37a |
I certify that: |
•The entity identified in Part I is a foreign corporation that is not a financial institution; and
•The stock of such corporation is regularly traded on one or more established securities markets, including (name one securities exchange upon which the stock is regularly traded).
b
 I certify that:
I certify that:
•The entity identified in Part I is a foreign corporation that is not a financial institution;
•The entity identified in Part I is a member of the same expanded affiliated group as an entity the stock of which is regularly traded on an established securities market;
• The name of the entity, the stock of which is regularly traded on an established securities market, is |
|
; and |
|||
• The name of the securities market on which the stock is regularly traded is |
|
|
. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Part XXIV |
Excepted Territory NFFE |
|
|
|
|
38
 I certify that:
I certify that:
•The entity identified in Part I is an entity that is organized in a possession of the United States;
•The entity identified in Part I:
(i)Does not accept deposits in the ordinary course of a banking or similar business;
(ii)Does not hold, as a substantial portion of its business, financial assets for the account of others; or
(iii)Is not an insurance company (or the holding company of an insurance company) that issues or is obligated to make payments with respect to a financial account; and
•All of the owners of the entity identified in Part I are bona fide residents of the possession in which the NFFE is organized or incorporated.
Part XXV Active NFFE
39
 I certify that:
I certify that:
•The entity identified in Part I is a foreign entity that is not a financial institution;
•Less than 50% of such entity’s gross income for the preceding calendar year is passive income; and
•Less than 50% of the assets held by such entity are assets that produce or are held for the production of passive income (calculated as a weighted average of the percentage of passive assets measured quarterly) (see instructions for the definition of passive income).
Part XXVI Passive NFFE
40a
I certify that the entity identified in Part I is a foreign entity that is not a financial institution (other than an investment entity organized in a possession of the United States) and is not certifying its status as a publicly traded NFFE (or affiliate), excepted territory NFFE, active NFFE, direct reporting NFFE, or sponsored direct reporting NFFE.
Check box 40b or 40c, whichever applies. b 
c
Form |
Page 8 |
||
Part XXVII |
Excepted |
|
|
41 |
I certify that the entity identified in Part I: |
|
|
•Is a member of an expanded affiliated group;
•Does not maintain financial accounts (other than accounts maintained for members of its expanded affiliated group);
•Does not make withholdable payments to any person other than to members of its expanded affiliated group;
•Does not hold an account (other than depository accounts in the country in which the entity is operating to pay for expenses) with or receive payments from any withholding agent other than a member of its expanded affiliated group; and
•Has not agreed to report under Regulations section
Part XXVIII Sponsored Direct Reporting NFFE (see instructions for when this is permitted)
42Name of sponsoring entity:
43
 I certify that the entity identified in Part I is a direct reporting NFFE that is sponsored by the entity identified on line 42.
I certify that the entity identified in Part I is a direct reporting NFFE that is sponsored by the entity identified on line 42.
Part XXIX Substantial U.S. Owners of Passive NFFE
As required by Part XXVI, provide the name, address, and TIN of each substantial U.S. owner of the NFFE. Please see the instructions for a definition of substantial U.S. owner. If providing the form to an FFI treated as a reporting Model 1 FFI or reporting Model 2 FFI, an NFFE may also use this part for reporting its controlling U.S. persons under an applicable IGA.
Name
Address
TIN
Part XXX Certification
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined the information on this form and to the best of my knowledge and belief it is true, correct, and complete. I further certify under penalties of perjury that:
•The entity identified on line 1 of this form is the beneficial owner of all the income or proceeds to which this form relates, is using this form to certify its status for chapter 4 purposes, or is submitting this form for purposes of section 6050W or 6050Y;
•The entity identified on line 1 of this form is not a U.S. person;
•This form relates to: (a) income not effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business in the United States, (b) income effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business in the United States but is not subject to tax under an income tax treaty, (c) the partner’s share of a partnership’s effectively connected taxable income, or (d) the partner’s amount realized from the transfer of a partnership interest subject to withholding under section 1446(f); and
•For broker transactions or barter exchanges, the beneficial owner is an exempt foreign person as defined in the instructions.
Furthermore, I authorize this form to be provided to any withholding agent that has control, receipt, or custody of the income of which the entity on line 1 is the beneficial owner or any withholding agent that can disburse or make payments of the income of which the entity on line 1 is the beneficial owner.
I agree that I will submit a new form within 30 days if any certification on this form becomes incorrect.
I certify that I have the capacity to sign for the entity identified on line 1 of this form.
Sign Here
▲
Signature of individual authorized to sign for beneficial owner
Print Name |
Date |
Form
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose of Form | The W-8BEN-E form is used by foreign entities to certify their status for purposes of withholding on income received from U.S. sources, ensuring correct tax treatment. |
| Applicable Entities | This form is specifically for entities, not individuals. For individuals, the IRS provides a separate form, the W-8BEN. |
| Key Sections | The form is divided into various sections that collect information on the entity's identification, country of incorporation, type of entity, and FATCA (Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act) classifications. |
| Validity Period | The completed form is valid for the year in which it is signed and the next three calendar years, unless a change in circumstances makes any information on the form incorrect. |
| Governing Law | As a federal form, the W-8BEN-E is governed by the Internal Revenue Code and regulations under the U.S. Department of Treasury, rather than any state-specific laws. |
Guide to Writing IRS W-8BEN-E
The IRS W-8BEN-E form is crucial for foreign entities conducting business in the United States, as it allows them to claim tax treaty benefits, including reduced rates of withholding tax. Proper completion of this document ensures that entities are taxed appropriately on their U.S. source income. The steps to fill out the form are straightforward but require careful attention to detail to ensure all relevant information is accurately provided.
- Identify the beneficial owner: Enter the name of the entity that is the beneficial owner of the income.
- Determine the Entity Type: Check the box that corresponds to the entity's status. This is important for tax treaty benefits.
- Permanent residence address: Provide the address of the entity's permanent residence, not a P.O. box or in-care-of address.
- Mailing address: Fill this out only if it is different from the permanent residence address.
- U.S. taxpayer identification number (TIN): Enter the entity's TIN if it has one. This might not be applicable for all entities.
- Foreign tax identifying number: Provide the entity's tax identifying number as issued by its country of residence.
- Reference number(s): This is optional and may be used for internal tracking purposes.
- Claim of Tax Treaty Benefits: This section is crucial. If the entity is claiming benefits under an income tax treaty between its country of residence and the U.S., specific information including the relevant treaty country and provisions must be accurately detailed.
- Special rates and conditions: If applicable, the entity may need to specify certain conditions under which it is claiming a reduced rate of, or exemption from, withholding. Detailed instructions for this section can be found in the form's official instructions.
Completing the IRS W-8BEN-E form accurately is the first step in ensuring that foreign entities are taxed correctly on their U.S. income. It is essential for entities to review the form thoroughly and consult with a tax professional if they are unsure about any requirements or their tax treaty benefits. Once filled out, the form should be submitted to the withholding agent or payer and not to the IRS, unless specifically requested.
Understanding IRS W-8BEN-E
-
What is the purpose of the IRS W-8BEN-E form?
The IRS W-8BEN-E form is used by entities that are not based in the United States to certify their foreign status. This includes certifying that they are the beneficial owners of the income for which the form is being provided and, if applicable, to claim a reduced rate of, or exemption from, withholding as provided for under an income tax treaty between the United States and the entity's country of residence.
-
Who needs to fill out the IRS W-8BEN-E form?
Entities that are not U.S. persons and are the beneficial owners of an income source from the U.S. need to complete the form. This typically includes foreign corporations, partnerships, trusts, or estates. It does not apply to individuals; individuals would use the IRS W-8BEN form.
-
How often does the IRS W-8BEN-E form need to be updated or renewed?
The validity of the form generally starts from the date the form is signed and ends on the last day of the third succeeding calendar year, unless a change in circumstances makes any information on the form incorrect. For instance, if you complete the form on July 15, 2023, it remains valid through December 31, 2026, unless there are changes affecting the information provided.
-
What information is required to complete the W-8BEN-E form?
To complete the form, entities will need to provide their name and country of incorporation or organization, type of entity, their FATCA status, and their GIIN if applicable. Additionally, information regarding the type of income and the claim of treaty benefits for a reduced rate or exemption from withholding may also be necessary, depending on the entity's circumstances.
-
What are the consequences of not submitting a W-8BEN-E form?
Failing to submit a W-8BEN-E form when required can result in a 30% withholding tax on U.S.-source payments to the entity. This tax applies even if the entity might have been eligible for a reduced tax rate under a treaty between the United States and the entity's country of residence.
-
Where can one find a W-8BEN-E form?
The form can be downloaded from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website. Alternatively, the entity may receive the form from the financial institution or other body that is requesting it.
-
Is there a penalty for providing false information on the W-8BEN-E?
Yes. Providing false information on the W-8BEN-E form may lead to penalties, including fines and imprisonment. It's crucial to provide accurate and truthful information to comply with U.S. tax laws.
-
Can the W-8BEN-E form be submitted electronically?
Yes, in many cases, the W-8BEN-E form can be submitted electronically through the financial institution or business that is requesting it. The IRS accepts electronic signatures, making it convenient for foreign entities to comply without needing to mail in the form. However, it's important to verify with the requesting party whether they accept electronic submission and what format they require.
Common mistakes
The IRS W-8BEN-E form is a critical document that foreign entities must fill out to claim exemption from certain U.S. taxes. Errors in filling out this form can lead to issues, including tax liabilities and compliance penalties. Here are eight common mistakes to avoid:
Not using the latest form version: The IRS updates its forms periodically. Filing an outdated version may result in processing delays or rejections.
Incorrect entity classification: Entities often misinterpret their classification under U.S. tax law, leading to incorrect tax treatment. It's vital to understand your entity's classification and select the correct option on the form.
Failing to provide a Tax Identification Number (TIN): For countries that have a tax treaty with the U.S., providing a TIN is necessary to claim treaty benefits. The absence of a TIN might result in withholding at the standard rate rather than the treaty rate.
Incomplete information on beneficial owner(s): Entities must disclose beneficial owners accurately. Incomplete or vague information might lead to compliance issues.
Mismatching name and TIN: The name and TIN provided on the form must match those on file with the IRS. Discrepancies can lead to backup withholding.
Not signing the form: An unsigned form is invalid. Ensure that an authorized individual signs the form before submission.
Selecting the wrong income type: This form differentiates between types of income. Incorrectly identifying the type of income can affect tax withholding rates.
Failure to renew the form: The W-8BEN-E form is valid for three years from the date of signature. Failing to renew it can result in incorrect withholding and potential non-compliance.
When completing the W-8BEN-E form, it is crucial to provide accurate and complete information, understand the implications of each section, and seek guidance if there are any doubts. Doing so helps in ensuring compliance with U.S. tax obligations and in avoiding unnecessary penalties.
Documents used along the form
When international entities engage with U.S. businesses, they often need to handle several legal and financial documents, ensuring compliance and efficient tax handling. One key form in this process is the IRS W-8BEN-E, primarily used by foreign entities to claim exemption from certain U.S. withholding taxes under income tax treaties, among other things. Alongside this form, several other documents are frequently required to complete various compliance and operational needs. Here's a look at some of these essential documents.
- Form SS-4: This document is necessary to obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS. Foreign entities often need an EIN for various reasons, including the facilitation of tax withholding and reporting requirements.
- Form 8233: Exemption From Withholding on Compensation for Independent (and Certain Dependent) Personal Services of a Nonresident Alien Individual. This form is used to claim exemptions from withholding for personal services performed in the U.S., based on tax treaty benefits. It's pertinent for individuals, but in the context of foreign entities, it may apply when they send employees or contractors to work in the U.S.
- Form 1042: Annual Withholding Tax Return for U.S. Source Income of Foreign Persons. It’s filed by U.S. entities that withhold taxes on payments to foreign individuals or entities, detailing the income and withholding amounts. Thus, entities submitting the W-8BEN-E may see this form filed on their behalf, reflecting their U.S.-sourced income and any taxes withheld.
- Form 8802: Application for United States Residency Certification. Used by taxpayers to request a certificate of residency, which helps them claim income tax treaty benefits and reduced withholding rates. While primarily for individuals, entities may also need this for treaty benefits verification.
Each of these documents plays a vital role in the broader context of international taxation and regulatory compliance. By understanding and properly managing these forms, foreign entities can effectively navigate the complexities of U.S. tax obligations, ensuring a smoother operation within the U.S. market. Familiarity with the IRS W-8BEN-E form and its accompanying documents is a cornerstone of this process, offering a foundational step towards compliance and financial efficiency.
Similar forms
The IRS W-8BEN-E form is designed for foreign entities to certify their status for purposes of tax withholding and reporting in the United States. A similar document is the W-8BEN form, which serves an analogous purpose for individuals. Both forms establish the claim that the filer is the beneficial owner of the income and is eligible for reduced rates of, or exemption from, withholding as provided by an income tax treaty. The core difference is the entity type the forms apply to, with the W-8BEN-E tailored for entities and the W-8BEN for individuals.
Another document closely related to the W-8BEN-E is the W-8ECI form. This form is used by foreign entities to declare that all the income associated with the form is effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business within the U.S. Like the W-8BEN-E, it helps determine the correct withholding rate but is specifically for those claiming their income is part of a U.S. business operation, potentially allowing certain deductions and credits.
The Form W-8EXP is tailored for foreign governments, international organizations, foreign central banks of issue, foreign tax-exempt organizations, foreign private foundations, or governments of U.S. possessions. Similar to the W-8BEN-E, the W-8EXP provides a means for these entities to certify their status to claim an exemption from or reduction in U.S. withholding tax. However, it focuses on a narrower group of entities that typically receive income exempt under specific code sections or tax treaties.
Form W-9 is a request for taxpayer identification number and certification. It is used primarily by U.S. persons (including entities). While W-9s and W-8BEN-Es both serve to provide taxpayer identification information to entities that make payments, the W-9 is specifically for U.S. taxpayers, as opposed to the W-8BEN-E’s focus on foreign entities. This document is crucial for entities engaging in financial activities within the U.S. to ensure compliance with U.S. tax laws.
The 1042-S form is another document related to the W-8BEN-E, as it is used to report income paid to foreign persons including individuals, corporations, partnerships, or estates. While the W-8BEN-E is filled out by foreign entities to claim a tax treaty benefit or exempt status, the 1042-S is the document that payors must file and provide to the IRS and the payee, summarizing the income and the associated withholding. It's vital in the operational compliance with U.S. tax law for payments made to foreign entities.
Form 8288-B, Application for Withholding Certificate for Dispositions by Foreign Persons of U.S. Real Property Interests, is pertinent in the context of real estate transactions. While its focus is more specific than the broad purview of the W-8BEN-E, both forms play crucial roles in how foreign entities interact with U.S. tax obligations. The 8288-B allows foreign sellers of U.S. property to apply for a reduced withholding tax rate or exemption, reflecting the W-8BEN-E’s function of establishing status for tax withholding purposes.
The SS-4, Application for Employer Identification Number (EIN), is used by entities to obtain an EIN from the IRS. While it is not directly related to tax withholding like the W-8BEN-E, it is essential for foreign entities engaged in trade or business in the U.S. since they need an EIN for tax reporting purposes. Having an EIN is often a prerequisite for completing the W-8BEN-E, making the SS-4 a complementary document in the administrative process.
Form 8233, Exemption From Withholding on Compensation for Independent (and Certain Dependent) Personal Services of a Nonresident Alien Individual, is somewhat akin to the W-8BEN-E, as it allows individuals, rather than entities, to claim exemptions from withholding on income earned in the U.S. The parallels between them illustrate the breadth of documentation available for a variety of filers seeking to navigate U.S. tax laws, each tailored to specific circumstances and types of income.
Finally, the Certificate of Status of Beneficial Owner for United States Tax Withholding and Reporting (Entities) is a document that complements the purpose of the W-8BEN-E. Meant for entities to prove their status for tax withholding purposes, this certificate can be used in lieu of the W-8BEN-E in certain situations. It’s another tool in the regulatory framework, allowing foreign entities to establish their bona fides in dealings with the U.S. tax system.
In summary, the IRS W-8BEN-E form operates within a complex ecosystem of tax documents, each with its own focus but together facilitating the proper reporting and withholding of taxes for foreign entities and individuals engaged with the U.S. financial system. Understanding these forms and their interconnections is essential for navigating U.S. tax compliance for foreign participants in the U.S. economy.
Dos and Don'ts
Filling out the IRS W-8BEN-E form can seem daunting, but careful attention to detail can make the process smoother. Below are key do's and don'ts to consider.
Do's:
- Review the form thoroughly before beginning to ensure understanding of all required information.
- Use the official instructions provided by the IRS to guide you through each part of the form accurately.
- Double-check the information for precision, including the legal name of the entity and tax identification numbers.
- Seek advice from a tax professional if there are any uncertainties or complicated scenarios.
Don'ts:
- Avoid using outdated versions of the form; always download the latest version from the IRS website.
- Do not leave required fields blank. If a section does not apply, enter "N/A" or the appropriate indication as directed by the instructions.
- Refrain from guessing on any information. Incorrect information can lead to processing delays or errors in tax withholding and reporting.
- Do not delay in submitting the form if requested by a financial institution or other entity. Late submission may impact financial transactions.
Misconceptions
The IRS W-8BEN-E form is often misunderstood, which can lead to confusion and potential compliance issues for foreign entities doing business with US companies. Below are nine common misconceptions about the W-8BEN-E form, each explained to clarify the accurate requirements and purposes of this important document.
Only applicable to large foreign entities: The W-8BEN-E form is required for all foreign entities that receive certain types of income from US sources, regardless of their size. This includes small businesses, partnerships, and corporations.
It's a one-time submission: The validity of the W-8BEN-E form generally lasts for three years from the date of signing. Entities must resubmit the form to the withholding agent if any information changes or to renew it before it expires.
Only used for tax reporting purposes: While tax reporting is a significant purpose of the W-8BEN-E form, it's also used to claim benefits under tax treaties between the United States and the entity's country of residence, potentially reducing withholding taxes.
It grants exemption from all US taxes: Submitting a W-8BEN-E form does not automatically exempt an entity from all US taxes. It may qualify the entity for reduced rates or exemptions on certain types of income under applicable tax treaties.
Personal information isn't necessary: Accurate and complete information about the entity, including the Entity Classification, Tax Identification Number (TIN), and country of citizenship, is crucial for correct processing and compliance with IRS regulations.
It's only relevant for entities in certain industries: Any foreign entity that earns income from US sources that is subject to withholding tax must complete the W-8BEN-E form, irrespective of the industry in which it operates.
The form is too complex to complete without professional help: Although the W-8BEN-E can appear daunting due to its detailed instructions and multiple sections, many entities can complete it accurately by closely following the IRS's instructions or seeking minimal guidance from a tax professional.
US-based entities need to complete the W-8BEN-E form: US entities should not complete the W-8BEN-E form. Instead, they may be required to fill out Form W-9. The W-8BEN-E is strictly for foreign entities.
The IRS directly receives all W-8BEN-E forms: Typically, the foreign entity submits the W-8BEN-E form to the withholding agent or financial institution that requested it, not directly to the IRS. However, these entities may be required to provide the forms to the IRS upon request.
Understanding the W-8BEN-E form is crucial for foreign entities engaging in financial activities involving US sources of income. Dispelling these misconceptions is an important step towards ensuring compliance and taking full advantage of available tax benefits.
Key takeaways
The IRS W-8BEN-E form is an essential document for foreign entities receiving income from U.S. sources. Understanding its purpose, requirements, and proper completion methods can significantly impact tax obligations and compliance with U.S. tax law. Here are six key takeaways to ensure accurate and effective use of the form:
- Identification of Beneficial Owner: The primary purpose of the W-8BEN-E form is to correctly identify the beneficial owner of the income. This ensures that income paid to foreign entities is appropriately taxed according to treaties and agreements between the U.S. and the country where the beneficial owner resides.
- Claiming Tax Treaty Benefits: Foreign entities can use the W-8BEN-E to claim benefits under an income tax treaty between their country and the United States. Accurately completing the form allows entities to reduce the withholding tax rate on their U.S.-source income, in accordance with the relevant treaty.
- Updated Information is Crucial: The form needs to reflect current information. If there are any changes to the beneficial owner’s status, structure, or country of residence, a new W-8BEN-E must be submitted to reflect these changes. Outdated or incorrect information can lead to improper withholding and potential penalties.
- Understanding The Different Parts: The W-8BEN-E form is detailed and contains multiple parts, requiring specific information depending on the entity's status as per U.S. tax law definitions. Understanding which sections apply is critical for accurately completing the form and avoiding common mistakes.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: Entities must retain a copy of the completed W-8BEN-E form and be prepared to present it upon request by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or the withholding agent. This ensures evidence of compliance with U.S. tax law and can be vital during audits.
- Professional Guidance Recommended: Given the complexity of international tax laws and regulations, consulting with a tax professional or legal expert when completing the W-8BEN-E is highly recommended. Professional advice can help in navigating the nuances of the form and ensuring compliance with U.S. tax obligations.
Popular PDF Documents
IRS Schedule 2 1040 or 1040-SR - Completing Schedule 2 properly is essential for accurately reflecting tax responsibilities and avoiding potential penalties.
IRS Schedule O 990 or 990-EZ - This form is crucial for documenting the board of directors' oversight and involvement in key decisions and policies of the organization.
