Get IRS Schedule E 1040 Form
For individuals who earn rental income or are involved in partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in Real Estate Mortgage Investment Conduits (REMICs), understanding and navigating the intricacies of the IRS Schedule E 1040 form is crucial. This form is a key component in the tax filing process, allowing taxpayers to report supplementary income or loss from these ventures. It serves as a conduit for reporting passive income, which is not derived from regular employment, and specifies how this income affects the taxpayer's overall tax liability. The Schedule E 1040 form's complexity necessitates a detailed approach, providing spaces for taxpayers to meticulously document earnings and expenses associated with their property or entities. This ensures that individuals can take full advantage of any applicable deductions or credits, ultimately impacting their tax obligations. Understanding the major aspects of this form not only aids in compliance with tax laws but also enables taxpayers to manage their investments more effectively.
IRS Schedule E 1040 Example
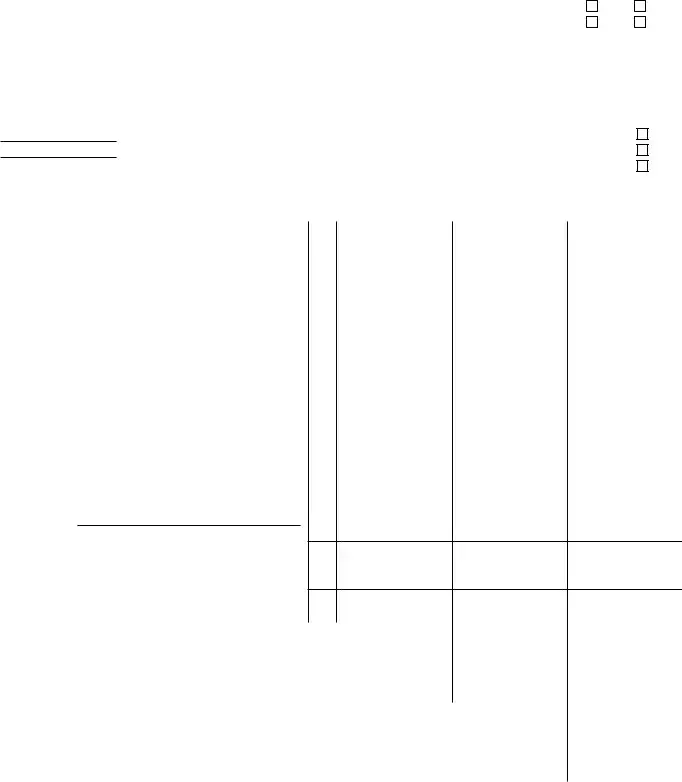
SCHEDULE E |
|
|
|
Supplemental Income and Loss |
|
|
OMB No. |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
(Form 1040) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
(From rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, REMICs, etc.) |
|
2020 |
|||||||||||||||||
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
▶ Attach to Form 1040, |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/ScheduleE for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
Attachment |
|
13 |
||||||||||||||
Internal Revenue Service (99) |
|
|
|
Sequence No. |
||||||||||||||||
Name(s) shown on return |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Your social security number |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
Part I |
Income or Loss From Rental Real Estate and Royalties Note: If you are in the business of renting personal property, use |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Schedule C. See instructions. If you are an individual, report farm rental income or loss from Form 4835 on page 2, line 40. |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
A Did you make any payments in 2020 that would require you to file Form(s) 1099? See instructions . |
. . . . |
Yes |
|
No |
||||||||||||||||
B If “Yes,” did you or will you file required Form(s) 1099? . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
. . . . |
Yes |
|
No |
||||||||||||||
|
1a |
Physical address of each property (street, city, state, ZIP code) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1b |
|
Type of Property |
2 |
For each rental real estate property listed |
|
|
Fair Rental |
|
Personal Use |
|
QJV |
||||||||
|
|
|
(from list below) |
|
above, report the number of fair rental and |
|
|
Days |
|
Days |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
personal use days. Check the |
QJV box only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
if you meet the requirements to file as a |
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
qualified joint venture. See instructions. |
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Type of Property: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
1 |
Single Family Residence |
3 |
5 |
Land |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
2 |
4 |
Commercial |
6 |
Royalties |
8 |
Other (describe) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Income: |
|
|
|
|
Properties: |
|
|
|
A |
B |
|
|
|
C |
|
|
||||
|
3 |
Rents received |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
4 |
Royalties received |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
5 |
Advertising |
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
6 |
Auto and travel (see instructions) |
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
7 |
Cleaning and maintenance |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
8 |
Commissions |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
9 |
Insurance |
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
10 |
Legal and other professional fees |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
11 |
Management fees |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
12 |
Mortgage interest paid to banks, etc. (see instructions) |
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
13 |
Other interest |
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
14 |
Repairs |
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
15 |
Supplies |
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
16 |
Taxes |
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
17 |
Utilities |
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
18 |
Depreciation expense or depletion |
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
19 |
Other (list) |
▶ |
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
20 |
Total expenses. Add lines 5 through 19 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
21Subtract line 20 from line 3 (rents) and/or 4 (royalties). If result is a (loss), see instructions to find out if you must
file Form 6198 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
22Deductible rental real estate loss after limitation, if any,
|
on Form 8582 (see instructions) |
22 ( |
) ( |
|
) ( |
) |
23a |
Total of all amounts reported on line 3 for all rental properties . . . . |
23a |
|
|
|
|
b |
Total of all amounts reported on line 4 for all royalty properties . . . . |
23b |
|
|
|
|
c |
Total of all amounts reported on line 12 for all properties |
23c |
|
|
|
|
d |
Total of all amounts reported on line 18 for all properties |
23d |
|
|
|
|
e |
Total of all amounts reported on line 20 for all properties |
23e |
|
|
|
|
24 |
Income. Add positive amounts shown on line 21. Do not include any losses |
. . . . . . . |
24 |
|
|
|
25 |
Losses. Add royalty losses from line 21 and rental real estate losses from line 22. Enter total losses here . |
25 |
( |
) |
||
26 |
Total rental real estate and royalty income or (loss). Combine lines 24 and 25. Enter the result |
|
|
|
||
|
here. If Parts II, III, IV, and line 40 on page 2 do not apply to you, also enter this amount on |
|
|
|
||
|
Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 5. Otherwise, include this amount in the total on line 41 on page 2 . |
26 |
|
|
||
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see the separate instructions. |
Cat. No. 11344L |
Schedule E (Form 1040) 2020 |
||||

Schedule E (Form 1040) 2020 |
Attachment Sequence No. 13 |
Page 2 |
Name(s) shown on return. Do not enter name and social security number if shown on other side.
Your social security number
Caution: The IRS compares amounts reported on your tax return with amounts shown on Schedule(s)
Part II Income or Loss From Partnerships and S Corporations — Note: If you report a loss, receive a distribution, dispose of stock, or receive a loan repayment from an S corporation, you must check the box in column (e) on line 28 and attach the required basis computation. If you report a loss from an
27Are you reporting any loss not allowed in a prior year due to the
|
|
|
see instructions before completing this section |
. . . . . . . . |
. |
. |
|
Yes |
No |
|||||||||||||||||
28 |
|
|
|
(a) Name |
|
|
|
|
(b) |
Enter P for |
(c) Check if |
|
|
(d) Employer |
|
(e) |
Check if |
|
|
(f) Check if |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
partnership; S |
foreign |
|
|
identification |
|
basis computation |
|
any amount is |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for S corporation |
partnership |
|
|
number |
|
is required |
|
|
|
not at risk |
||||||
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Passive Income and Loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nonpassive Income |
and Loss |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
(g) Passive loss allowed |
|
(h) Passive income |
|
(i) Nonpassive loss allowed |
(j) Section 179 expense |
|
(k) |
Nonpassive income |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
(attach Form 8582 if required) |
|
from Schedule |
|
(see Schedule |
|
deduction from Form 4562 |
|
from Schedule |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29a |
Totals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
b |
Totals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
Add columns (h) and (k) of line 29a |
. . . . . . . |
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
31 |
|
Add columns (g), (i), and (j) of line 29b |
. . . . . . . |
|
31 |
|
( |
|
|
|
) |
|||||||||||||||
32 |
|
Total partnership and S corporation income or (loss). Combine lines 30 and 31 . . . . |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
Part III |
Income or Loss From Estates and Trusts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
Name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b) Employer |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
identification number |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Passive Income and Loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nonpassive Income and Loss |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
(c) Passive deduction or loss allowed |
|
(d) Passive income |
|
(e) Deduction or loss |
|
|
(f) Other income from |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
(attach Form 8582 if required) |
|
from Schedule |
|
from Schedule |
|
|
Schedule |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34a |
Totals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
b |
Totals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
Add columns (d) and (f) of line 34a |
. . . . . . . |
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
36 |
|
Add columns (c) and (e) of line 34b |
. . . . . . . |
|
36 |
|
( |
|
|
|
) |
|||||||||||||||
37 |
|
Total estate and trust income or (loss). Combine lines 35 and 36 . . . |
. . . . . . . |
|
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Part IV |
Income or Loss From Real Estate Mortgage Investment Conduits |
Holder |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
38 |
|
|
(a) Name |
|
(b) Employer identification |
|
|
(c) Excess inclusion from |
(d) Taxable income (net loss) |
|
|
(e) Income from |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Schedules Q, line 2c |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
number |
|
|
|
(see instructions) |
from Schedules Q, line 1b |
|
|
Schedules Q, line 3b |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
|
Combine columns (d) and (e) only. Enter the result here and include in the total on line 41 below |
39 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
Part V |
Summary |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
40 |
|
Net farm rental income or (loss) from Form 4835. Also, complete line 42 below |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
41 |
|
Total income or (loss). Combine lines 26, 32, 37, 39, and 40. Enter the result here and on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 5 ▶ |
41 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42Reconciliation of farming and fishing income. Enter your gross farming and fishing income reported on Form 4835, line 7; Schedule
43Reconciliation for real estate professionals. If you were a real estate professional
(see instructions), enter the net income or (loss) you reported |
anywhere on Form |
|
|
|
|
1040, Form |
in which |
|
|
|
|
you materially participated under the passive activity loss rules |
. . . |
. . . |
43 |
|
|
Schedule E (Form 1040) 2020
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Form Purpose | Schedule E (Form 1040) is used by taxpayers to report income and losses from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs. |
| Who Must File | Individuals, estates, and trusts who have income or loss from any rental real estate, royalties, or pass-through entities as defined by the IRS must file Schedule E with their Form 1040. |
| Supplemental Income | Schedule E is specifically designed for reporting supplemental income and loss. It is not used for reporting regular wages or salary income. |
| Passive Activity Limits | Certain losses reported on Schedule E are subject to passive activity loss rules, which may limit the amount of loss taxpayers can deduct. |
| Reporting Rents | Taxpayers report income and expenses related to rental real estate on Schedule E, including amounts received as rent, expenses paid for maintenance, repairs, and improvements. |
| State-Specific Forms | Some states require a separate state-specific form similar to Schedule E for state income tax purposes. These forms are governed by state tax law. |
| Filing Deadline | The filing deadline for Schedule E coincides with the IRS deadline for Form 1040, typically April 15th of each year, unless an extension is applied for and granted. |
Guide to Writing IRS Schedule E 1040
Filling out the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) is a crucial step for individuals who need to report income or losses from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs. The steps outlined below will guide you through the process, ensuring accuracy and compliance. Before embarking on this task, gather all necessary documentation, such as rental income statements, mortgage interest statements, and partnership income reports. This preparation will streamline the process, making it more efficient and less prone to errors.
- Begin by entering your name and Social Security Number at the top of the form to ensure it matches the information on your Form 1040.
- Under Part I, concerning rental real estate and royalties, list each property individually. Include information such as the property’s address, type (single-family, multi-family, vacation home, land, etc.), and your total rental income received.
- For each property listed in Part I, calculate the expenses incurred, such as mortgage interest, property taxes, insurance, repairs and maintenance, and any professional fees. Enter these in the corresponding columns.
- If you're reporting income or losses from royalties, fill in the relevant details in the section provided below the rental real estate portion. Include gross receipts and the various expenses associated with generating this royalty income.
- In Part II, input information related to partnership and S corporations. Here, you'll need to specify the name and employer identification number (EIN) of the entities through which you're reporting income or losses. Clearly state the amount of income or losses from these entities as specified in the Schedule K-1 forms you received.
- For those reporting income from estates and trusts in Part III, detail the name of the estate or trust, its EIN, and the amount of income or loss as reported on your Schedule K-1.
- In Part IV, if applicable, provide information on income or losses from real estate mortgage investment conduits (REMICs). This involves detailing the name and EIN of the REMIC and the residual interest amounts, again based on Schedule K-1 received.
- Sum up all income and losses reported in the previous sections to arrive at the total amount. This figure will be reported on your Form 1040, affecting your taxable income.
- Throughout the form, ensure accuracy by double-checking the figures against your documents. Inaccurate reporting can lead to audits, penalties, or interest charges from the IRS.
- Finally, review the entire form for completeness and accuracy. Sign and date it if required before attaching it to your Form 1040. Submit the completed package to the IRS by the appropriate deadline, typically April 15, unless an extension has been granted.
After submitting the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040), the next steps involve waiting for the IRS to process your information. Monitoring your mail or email for any correspondence from the IRS is essential, as they may request additional information or clarification. Stay organized and retain copies of all submitted documents along with their respective confirmation receipts (if applicable). This precaution ensures you're prepared to address any potential issues that may arise during the processing of your tax return.
Understanding IRS Schedule E 1040
-
What is the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) and who needs to file it?
The IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) is a supplemental form used by taxpayers to report income and expenses from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs. Individuals need to file this form if they have income or losses from any of these sources. It's essential for reporting passive income or losses that aren't related to regular employment.
-
Can I file Schedule E electronically?
Yes, the IRS accepts electronic filing of Schedule E as part of your overall Form 1040 submission. Most tax software platforms support the electronic preparation and submission of this schedule. This can simplify the process, reduce errors, and expedite your filing and any potential refund.
-
What information do I need to complete Schedule E?
- Rental property addresses and dates of acquisition.
- Income received from rental properties, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, or trusts.
- Expenses associated with these income sources, including maintenance, mortgage interest, insurance, and management fees.
- Details of any partnership or S corporation interests.
- Information on estates or trusts from which you receive income.
Gathering these details before you begin will help streamline the filing process.
-
How does Schedule E affect my tax liabilities?
The income or losses you report on Schedule E impact your total taxable income on your Form 1040. If you report profits from your rental or other passive activities, this could increase your tax liability. Conversely, reporting losses may decrease it. It's important to accurately report all income and expenses to correctly calculate your tax obligations.
-
What are common mistakes to avoid when filling out Schedule E?
- Not reporting all income received from rental properties or other sources.
- Misclassifying personal expenses as rental expenses.
- Failing to keep accurate records throughout the year.
- Overlooking deductions you're entitled to claim.
Careful attention to detail and good recordkeeping can help avoid these and other mistakes.
-
Can losses reported on Schedule E be deducted?
Yes, losses reported on Schedule E can often be deducted. However, there are rules and limitations. For example, passive activity loss limitations may restrict how much you can deduct each year. It's also important to distinguish between rental activities and other passive activities, as different rules may apply. Consulting a tax professional can help you navigate these complexities.
-
What happens if I make a mistake on Schedule E?
If you discover a mistake on your filed Schedule E, you should amend it as soon as possible by filing Form 1040-X along with an amended Schedule E. This can correct income, deductions, or credits and potentially avoid penalties for underreporting. It's advisable to address corrections promptly to stay in compliance with IRS regulations.
-
Where can I find more help with Schedule E?
For more help with Schedule E, you can refer to the instructions provided by the IRS with the form. Additionally, the IRS website offers resources and guides. Tax professionals and IRS-authorized e-file providers can also assist with more personalized advice and filing assistance.
Common mistakes
Filling out the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) can be a complicated process that requires attention to detail. Mistakes on this form can be costly, leading to audits, fines, or missed deductions. Below are ten common mistakes people often make when completing this form:
-
Not reporting all income - People sometimes forget to include all rental income or mistakenly omit it, which can trigger IRS notices and penalties.
-
Incorrectly separating expenses - It's essential to correctly distinguish between improvements and repairs, as they are deducted differently over time.
-
Failing to claim the correct depreciation - This can significantly impact the income reported and the taxes owed. Calculating depreciation requires understanding the specifics of IRS rules.
-
Mixing personal and rental expenses - Only expenses strictly related to the rental activity should be reported, not personal expenses.
-
Overlooking pass-through deduction qualifications - Certain rental activities may qualify for a 20% business income deduction, which is often missed.
-
Not properly reporting partnership or S Corporation information - Income from these sources must be reported accurately to avoid discrepancies.
-
Misunderstanding active participation rules - Knowing whether you qualify for active participation impacts how losses are deducted.
-
Forgetting to report foreign real estate - Owning and earning from foreign properties requires specific disclosures and reporting.
-
Using the wrong form or tax year version - Each tax year can have updates or changes to the Schedule E form that must be adhered to.
-
Miscalculating expenses or income due to lack of records - Maintaining thorough records throughout the year is critical to accurate reporting.
Avoiding these common mistakes requires diligence, thorough record-keeping, and a good understanding of the tax laws applicable to rental property and passive income. When in doubt, consulting with a tax professional can provide clarity and ensure that your Schedule E is accurately filled out, maximizing your benefits and minimizing any negative impacts.
Documents used along the form
When taxpayers need to report income or losses from rentals, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs, they turn to the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040). This form is a critical part of the tax filing process for those who have these types of investments. However, the complexity of tax situations means that Schedule E is rarely filed alone. Several other documents and forms often accompany it to provide a comprehensive view of the taxpayer's financial situation. Understanding these associated documents can help ensure accurate and complete tax reporting.
- Form 4562: Depreciation and Amortization - This form is essential for reporting the depreciation and amortization of properties listed on Schedule E. It captures information on the purchase date, type of property, cost, and method of depreciation or amortization, providing a basis for expense deductions on the property reported.
- Form 8825: Rental Real Estate Income and Expenses of a Partnership or an S Corporation - Specifically designed for entities such as partnerships and S corporations, this form reports income and expenses from rental real estate activities. It complements Schedule E by detailing the entity's property operations, which are necessary for individual partners or shareholders to accurately report their share of income or loss.
- Schedule K-1 (Form 1065): Partner's Share of Income, Deductions, Credits, etc. - This form provides detailed information about a partner's share of partnership income, deductions, and credits. Schedule K-1 is essential for partners to complete their Schedule E accurately, as it includes the necessary details to report their share of the partnership's financial activities.
- Schedule K-1 (Form 1120S): Shareholder's Share of Income, Deductions, Credits, etc. - Similar to the Schedule K-1 for partnerships, this form is for shareholders of an S corporation. It outlines the shareholder's proportion of income, deductions, and credits from the corporation, informing their entries on Schedule E.
- Form 1099-MISC: Miscellaneous Income - Often, taxpayers receive this form for rental income, royalties, or other types of income that need to be reported on Schedule E. It provides details about the source and amount of income, ensuring taxpayers do not overlook any taxable income or necessary deductions and adjustments.
In the complex landscape of tax preparation, these forms and documents play vital roles in ensuring the transparency and completeness of a taxpayer's financial disclosure. By accurately completing and attaching these related documents to Schedule E, taxpayers can navigate their tax responsibilities with confidence, knowing they have provided a thorough account of their investment income and expenses. Such diligence not only aids in compliance with tax laws but also optimizes the taxpayer's position regarding allowable deductions and credits.
Similar forms
The IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) is primarily used for reporting income or loss from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs. This form serves as a critical tool for taxpayers to report passive income or losses that are not subject to self-employment taxes. Similar documents in various respects include Schedule C, Form 4562, Schedule D, Form 8825, Form 1120-S, Schedule K-1, and Form 1041. Each has its own purpose but shares commonalities in how they capture and report income, expenses, and losses.
Schedule C (Form 1040) is similar to Schedule E in that it's used by individuals to report income or loss from a business they operated or a profession they practiced as a sole proprietor. Both forms require detailed income statements and allow for the deduction of expenses incurred in the process of generating income, albeit for different types of activities—Schedule C for business operations and Schedule E for passive income endeavors.
Form 4562, Depreciation and Amortization, parallels Schedule E through its function of reporting depreciation, which is a common expense on properties reported on Schedule E. Landlords and real estate investors use Form 4562 to calculate and report the depreciation of rental property, which is then often transferred to Schedule E to adjust the income or loss from rental activities.
Schedule D (Form 1040), which is used for reporting capital gains and losses from the sale or exchange of capital assets, shares a relationship with Schedule E in the landscape of tax reporting. Both forms involve the reporting of financial movements—Schedule D focusing on capital events and Schedule E on passive income activities—but each influences the taxpayer's overall financial picture and tax liability.
Form 8825, Rental Real Estate Income and Expenses of a Partnership or an S Corporation, is specifically related to Schedule E as it captures similar information but from entities rather than individuals. It is essentially the partnership or S corporation equivalent of Schedule E, used when these entities report income and expenses from rental real estate operations, which are then passed through to the individual partners or shareholders on Schedule K-1.
Form 1120-S, U.S. Income Tax Return for an S Corporation, includes a Schedule K-1 component that reports each shareholder's share of the corporation's income, deductions, credits, etc. This mirrors the function of Schedule E where an individual reports their share of income or loss from partnerships, S corporations, estates, and trusts, highlighting a conduit approach to taxing entity-level activities at the individual level.
Schedule K-1 is directly complementary to Schedule E, serving as the document that reports an individual's share of income, deductions, and credits from partnerships, S corporations, trusts, and estates. Recipients of a K-1 use the information to complete their Schedule E, making these documents inherently linked in the process of reporting pass-through income.
Finally, Form 1041, U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts, is akin to Schedule E in its objective to report income, deductions, and credits of trusts and decedent's estates. When beneficiaries receive distributions of income from these entities, the information affects their reporting on Schedule E, illustrating how these forms work together within the broader framework of income tax reporting.
Dos and Don'ts
Filling out the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) for reporting supplemental income and loss from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs requires careful attention to detail. Here are some dos and don'ts to consider during this process:
- Do review all the instructions provided by the IRS for Schedule E carefully to ensure you understand the requirements and the information you need to provide.
- Do gather all necessary documentation related to your rental real estate, royalties, and other supplemental income before you begin filling out the form.
- Do use the correct tax year version of Schedule E to ensure that your filing adheres to the most current tax laws and regulations.
- Do double-check your figures for income and expenses to avoid any mathematical errors.
- Do report all income from rental properties, royalties, partnerships, and other sources accurately to avoid potential legal and financial penalties.
- Don't forget to include all necessary attachments when submitting Schedule E, such as statements from partnerships or S corporations.
- Don't overlook passive activity loss limits which can affect how much of a loss you can deduct.
- Don't hesitate to seek professional help if you’re uncertain about how to complete the form or if you have complex rental property or partnership issues.
- Don't incorrectly categorize personal expenses as rental expenses as this can lead to inaccuracies and potential scrutiny from the IRS.
- Don't submit Schedule E without reviewing it for completeness and accuracy to ensure that all information is reported correctly and in compliance with IRS guidelines.
Misconceptions
When it comes to filing taxes, the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) can often be misunderstood. This form is used to report income or loss from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs. To clear up some of the confusion, here are six common misconceptions about Schedule E (Form 1040):
- Misconception 1: "Only landlords need to fill it out." Not just landlords, but anyone who receives rental income, royalties, or income through partnerships, S corporations, estates, and trusts needs to use Schedule E. This includes part-owners of rental properties and beneficiaries of estates or trusts.
- Misconception 2: "Personal vacation homes can't be reported on Schedule E." Actually, if you rent out a vacation home for more than 14 days a year, you must report the income on Schedule E. The rules change depending on the number of days rented and used for personal enjoyment.
- Misconception 3: "You can deduct any amount of losses on real estate." The IRS has limitations on the loss amounts that can be deducted. These limitations depend on your role as an active or passive participant in the real estate and your adjusted gross income.
- Misconception 4: "Schedule E is only for reporting annual income." Besides annual income, Schedule E is used to report expenses related to generating income from real estate or other sources listed on the form. This includes advertising, maintenance, and insurance costs.
- Misconception 5: "Repairs and improvements are deducted the same way." The IRS differentiates between repairs and improvements. Repairs can be deducted in the year they are made, while improvements must be depreciated over several years.
- Misconception 6: "Schedule E reporting is optional if you don't make a profit." Even if your activities result in a loss or if you haven't made a profit, you are still required to report all activities on Schedule E. This helps ensure your tax filings are accurate and can also track your losses which may be deductible.
Key takeaways
Understanding the nuances of tax forms is essential for accurately reporting income, deductions, and ultimately determining one's tax liability. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Schedule E (Form 1040) is a critical document for taxpayers who earn rental income, income from partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in Real Estate Mortgage Investment Conduits (REMICs). Here are four key takeaways for effectively filling out and utilizing this form:
- Different Sources of Income: Schedule E is versatile, handling various income types beyond straightforward employment earnings. It’s essential for reporting income or losses from real estate rentals, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and REMICs. Each type of income is reported on a separate part of the form, so understanding the source of one's income is the first step to accurately completing Schedule E.
- Rental Activity Details: For real estate professionals and landlords, Schedule E requests specifics about each rental activity, including the type of property (e.g., single-family residence, multi-unit, etc.), location, and number of days rented versus used personally. Accurately reporting these details is crucial, as they directly impact the allowable deductions and, consequently, the taxable income from these activities.
- Deductions and Expenses: Schedule E allows for the deduction of ordinary and necessary expenses incurred in managing, conserving, or maintaining rental properties. These expenses can significantly reduce taxable income and include advertising, maintenance, utilities, insurance, and property management fees. Documenting and accurately reporting these expenses is vital for maximizing one's deductions while staying compliant with IRS regulations.
- Passive Activity Loss Limitations: The IRS places restrictions on losses from passive activities, including most rental activities, to offset other types of income. The ability to deduct such losses can be limited, making it important for taxpayers to understand the passive activity loss rules. However, there are exceptions, and in certain situations, part or all of these losses may be deductible. Understanding and accurately applying these rules can potentially lower one’s tax liability.
Successfully navigating the complexities of Schedule E is integral for taxpayers with diverse income streams. By comprehensively understanding each section and maintaining meticulous records, individuals can accurately report their earnings and expenses, potentially reducing their tax liability while ensuring compliance with IRS regulations. This form illuminates the importance of detail and precision in the realm of tax preparation and highlights the need for continuous learning in the ever-evolving tax landscape.
Popular PDF Documents
Icbc Bill of Sale - Specifies requirements for identification verification by the Autoplan Agent processing the transaction.
How Do You File an Extension With the Irs - The automatic extension granted with Form 8868 helps organizations avoid the stress of rushing to meet original filing deadlines.
