Get IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ Form
Many nonprofit organizations face the annual task of demonstrating their tax-exempt status to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This is where the IRS Schedule A of the Form 990 or 990-EZ comes into play, serving as a critical piece of documentation. This form is meticulously designed to outline the public support percentage, ensuring organizations meet the necessary criteria to maintain their tax-exempt status. Through the form, nonprofits declare their adherence to IRS guidelines, showcasing their sources of income, which must predominantly come from public rather than private sources. Completing this form accurately is pivotal, as it not only affects an organization's tax-exempt status but also its public transparency and trustworthiness. With the IRS scrutinizing these forms to confirm compliance with tax laws, it's essential for nonprofits to understand the nuances of Schedule A, including who must file, the specific information required, and the deadlines for submission. Ultimately, this form represents a key component of a nonprofit's fiscal responsibilities, underlining the importance of clear, accurate, and timely filing.
IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ Example
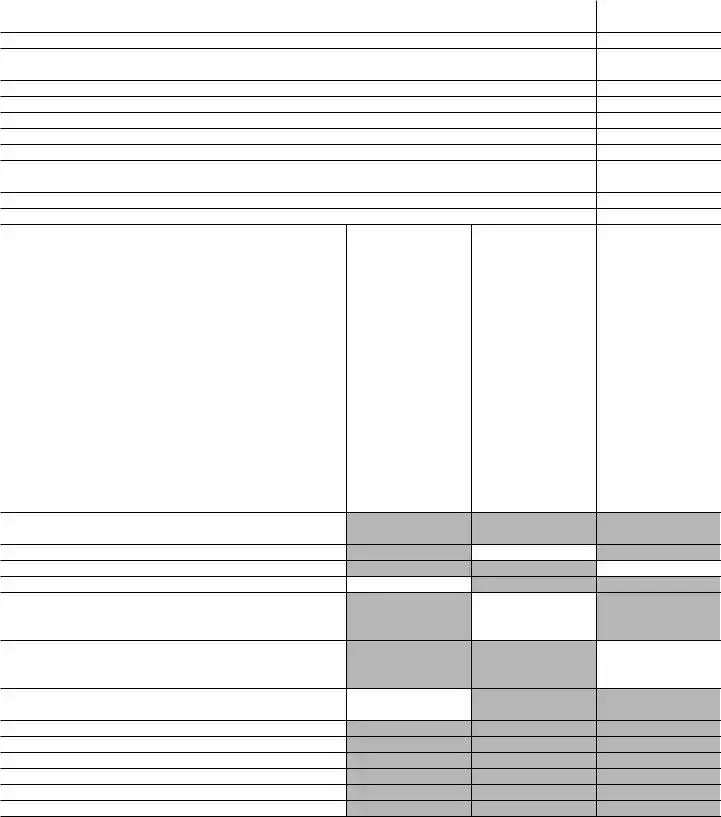
SCHEDULE A |
Public Charity Status and Public Support |
OMB No. |
|
|
|||
2021 |
|||
(Form 990) |
Complete if the organization is a section 501(c)(3) organization or a section 4947(a)(1) nonexempt charitable trust. |
||
|
|||
Department of the Treasury |
▶ Attach to Form 990 or Form |
Open to Public |
|
Internal Revenue Service |
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/Form990 for instructions and the latest information. |
Inspection |
|
Name of the organization |
Employer identification number |
||
Part I Reason for Public Charity Status. (All organizations must complete this part.) See instructions.
The organization is not a private foundation because it is: (For lines 1 through 12, check only one box.)
1 A church, convention of churches, or association of churches described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(i).
A church, convention of churches, or association of churches described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(i).
2 A school described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(ii). (Attach Schedule E (Form 990).)
A school described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(ii). (Attach Schedule E (Form 990).)
3 A hospital or a cooperative hospital service organization described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(iii).
A hospital or a cooperative hospital service organization described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(iii).
4 A medical research organization operated in conjunction with a hospital described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(iii). Enter the hospital’s name, city, and state:
A medical research organization operated in conjunction with a hospital described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(iii). Enter the hospital’s name, city, and state:
5 An organization operated for the benefit of a college or university owned or operated by a governmental unit described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(iv). (Complete Part II.)
An organization operated for the benefit of a college or university owned or operated by a governmental unit described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(iv). (Complete Part II.)
6 A federal, state, or local government or governmental unit described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(v).
A federal, state, or local government or governmental unit described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(v).
7 An organization that normally receives a substantial part of its support from a governmental unit or from the general public described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(vi). (Complete Part II.)
An organization that normally receives a substantial part of its support from a governmental unit or from the general public described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(vi). (Complete Part II.)
8 A community trust described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(vi). (Complete Part II.)
A community trust described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(vi). (Complete Part II.)
9 An agricultural research organization described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(ix) operated in conjunction with a
An agricultural research organization described in section 170(b)(1)(A)(ix) operated in conjunction with a
10
11
12
An organization that normally receives (1) more than 331/3% of its support from contributions, membership fees, and gross receipts from activities related to its exempt functions, subject to certain exceptions; and (2) no more than 331/3% of its support from gross investment income and unrelated business taxable income (less section 511 tax) from businesses acquired by the organization after June 30, 1975. See section 509(a)(2). (Complete Part III.)

 An organization organized and operated exclusively to test for public safety. See section 509(a)(4).
An organization organized and operated exclusively to test for public safety. See section 509(a)(4).

 An organization organized and operated exclusively for the benefit of, to perform the functions of, or to carry out the purposes of one or more publicly supported organizations described in section 509(a)(1) or section 509(a)(2). See section 509(a)(3). Check the box on lines 12a through 12d that describes the type of supporting organization and complete lines 12e, 12f, and 12g.
An organization organized and operated exclusively for the benefit of, to perform the functions of, or to carry out the purposes of one or more publicly supported organizations described in section 509(a)(1) or section 509(a)(2). See section 509(a)(3). Check the box on lines 12a through 12d that describes the type of supporting organization and complete lines 12e, 12f, and 12g.
a
Type I. A supporting organization operated, supervised, or controlled by its supported organization(s), typically by giving the supported organization(s) the power to regularly appoint or elect a majority of the directors or trustees of the supporting organization. You must complete Part IV, Sections A and B.
b
c
d
Type II. A supporting organization supervised or controlled in connection with its supported organization(s), by having control or management of the supporting organization vested in the same persons that control or manage the supported organization(s). You must complete Part IV, Sections A and C.
Type III functionally integrated. A supporting organization operated in connection with, and functionally integrated with, its supported organization(s) (see instructions). You must complete Part IV, Sections A, D, and E.
Type III
e Check this box if the organization received a written determination from the IRS that it is a Type I, Type II, Type III functionally integrated, or Type III
Check this box if the organization received a written determination from the IRS that it is a Type I, Type II, Type III functionally integrated, or Type III
f Enter the number of supported organizations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
gProvide the following information about the supported organization(s).
(i) Name of supported organization |
(ii) EIN |
(iii) Type of organization |
(iv) Is the organization |
(v) Amount of monetary |
(vi) Amount of |
|
|
|
(described on lines |
listed in your governing |
support (see |
other support (see |
|
|
|
above (see instructions)) |
document? |
instructions) |
instructions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(E)
Total
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see the Instructions for Form 990 or |
Cat. No. 11285F |
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021 |
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021 |
Page 2 |
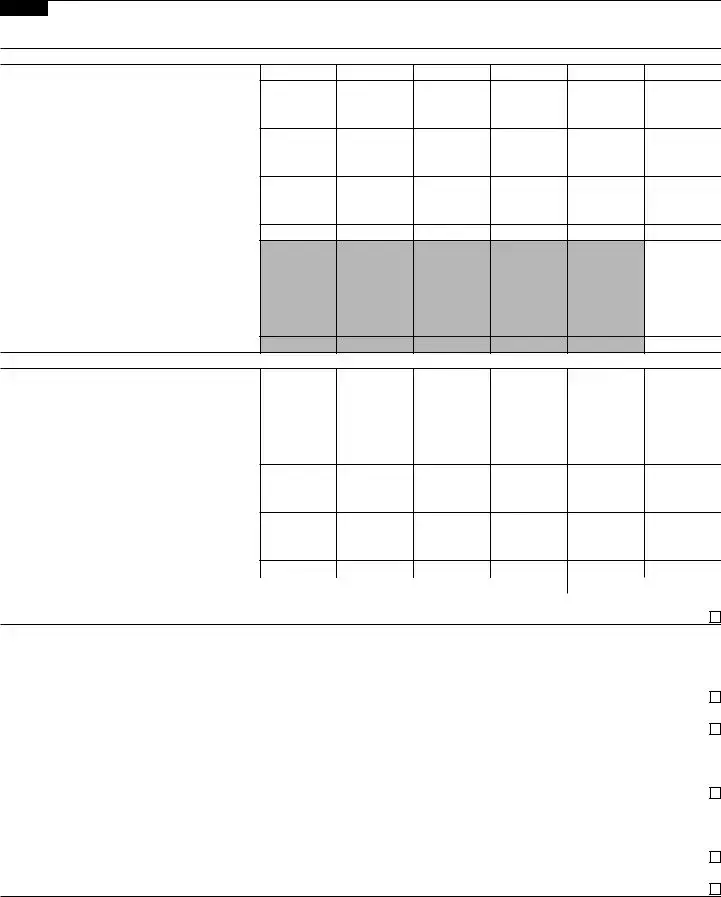
Part II Support Schedule for Organizations Described in Sections 170(b)(1)(A)(iv) and 170(b)(1)(A)(vi) (Complete only if you checked the box on line 5, 7, or 8 of Part I or if the organization failed to qualify under Part III. If the organization fails to qualify under the tests listed below, please complete Part III.)
Section A. Public Support
Calendar year (or fiscal year beginning in) ▶
1Gifts, grants, contributions, and membership fees received. (Do not include any “unusual grants.”) . . .
2Tax revenues levied for the organization’s benefit and either paid to
or expended on its behalf . . . .
3The value of services or facilities furnished by a governmental unit to the organization without charge . . . .
4Total. Add lines 1 through 3 . . . .
5The portion of total contributions by each person (other than a governmental unit or publicly supported organization) included on line 1 that exceeds 2% of the amount shown on line 11, column (f) . . . .
6Public support. Subtract line 5 from line 4
Section B. Total Support
(a)2017
(b)2018
(c)2019
(d)2020
(e)2021
(f)Total
Calendar year (or fiscal year beginning in) ▶ |
(a) 2017 |
(b) 2018 |
(c) 2019 |
(d) 2020 |
(e) 2021 |
(f) Total |
|
7 |
Amounts from line 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
Gross income from interest, dividends, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
payments received on securities loans, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rents, royalties, and income from |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
similar sources |
|
|
|
|
|
|
9Net income from unrelated business activities, whether or not the business is regularly carried on . . . . . .
10Other income. Do not include gain or loss from the sale of capital assets (Explain in Part VI.) . . . . . . .
11 |
Total support. Add lines 7 through 10 |
|
|
|
|
12 |
Gross receipts from related activities, etc. |
|
(see instructions) |
12 |
|
13First 5 years. If the Form 990 is for the organization’s first, second, third, fourth, or fifth tax year as a section 501(c)(3) organization, check this box and stop here . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ▶
Section C. Computation of Public Support Percentage
14 |
Public support percentage for 2021 (line 6, column (f), divided by line 11, column (f)) . . . . |
14 |
|
% |
15 |
Public support percentage from 2020 Schedule A, Part II, line 14 |
15 |
|
% |
16a |
331/3% support |
1/3% or more, check this |
||
|
box and stop here. The organization qualifies as a publicly supported organization |
▶ |
||
b331/3% support
17a
b
organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ▶
18Private foundation. If the organization did not check a box on line 13, 16a, 16b, 17a, or 17b, check this box and see
instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ▶
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021 |
Page 3 |
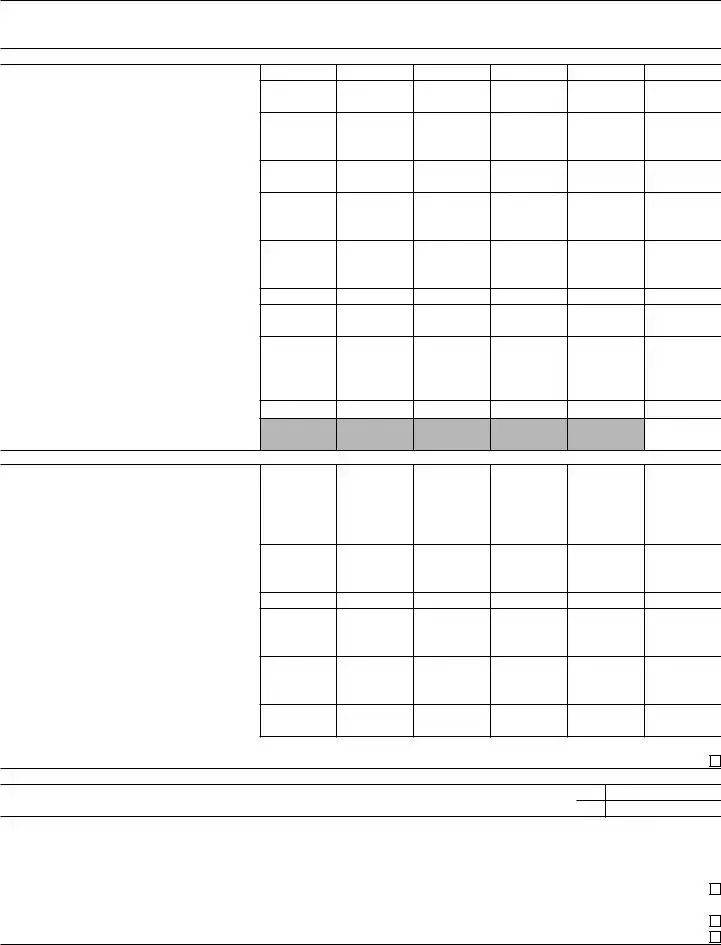
Part III Support Schedule for Organizations Described in Section 509(a)(2)
(Complete only if you checked the box on line 10 of Part I or if the organization failed to qualify under Part II. If the organization fails to qualify under the tests listed below, please complete Part II.)
Section A. Public Support
Calendar year (or fiscal year beginning in) ▶
1Gifts, grants, contributions, and membership fees received. (Do not include any “unusual grants.”)
2Gross receipts from admissions, merchandise sold or services performed, or facilities furnished in any activity that is related to the organization’s
3Gross receipts from activities that are not an unrelated trade or business under section 513
4Tax revenues levied for the
organization’s benefit and either paid to or expended on its behalf . . . .
5The value of services or facilities furnished by a governmental unit to the organization without charge . . . .
6Total. Add lines 1 through 5 . . . .
7a Amounts included on lines 1, 2, and 3
received from disqualified persons .
bAmounts included on lines 2 and 3 received from other than disqualified persons that exceed the greater of $5,000 or 1% of the amount on line 13 for the year
c Add lines 7a and 7b . . . . . .
8Public support. (Subtract line 7c from line 6.) . . . . . . . . . . .
Section B. Total Support
(a)2017
(b)2018
(c)2019
(d)2020
(e)2021
(f)Total
Calendar year (or fiscal year beginning in) ▶ |
(a) 2017 |
(b) 2018 |
(c) 2019 |
(d) 2020 |
(e) 2021 |
(f) Total |
|
9 |
Amounts from line 6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10a |
Gross income from interest, dividends, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
payments received on securities loans, rents, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
royalties, and income from similar sources . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
bUnrelated business taxable income (less section 511 taxes) from businesses acquired after June 30, 1975 . . . .
c Add lines 10a and 10b . . . . .
11Net income from unrelated business activities not included on line 10b, whether or not the business is regularly carried on
12Other income. Do not include gain or loss from the sale of capital assets (Explain in Part VI.) . . . . . . .
13Total support. (Add lines 9, 10c, 11, and 12.) . . . . . . . . . .
14First 5 years. If the Form 990 is for the organization’s first, second, third, fourth, or fifth tax year as a section 501(c)(3) organization, check this box and stop here . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ▶ 

Section C. Computation of Public Support Percentage
15 |
Public support percentage for 2021 (line 8, column (f), divided by line 13, column (f)) |
16 |
Public support percentage from 2020 Schedule A, Part III, line 15 |
Section D. Computation of Investment Income Percentage
15
16
%
%
17 |
Investment income percentage for 2021 (line 10c, column (f), divided by line 13, column (f)) . . . |
17 |
|
% |
18 |
Investment income percentage from 2020 Schedule A, Part III, line 17 |
18 |
|
% |
19a |
331/3% support |
|||
|
17 is not more than 331/3%, check this box and stop here. The organization qualifies as a publicly supported organization . |
▶ |
||
b331/3% support
line 18 is not more than 331/3%, check this box and stop here. The organization qualifies as a publicly supported organization |
▶ |
20 Private foundation. If the organization did not check a box on line 14, 19a, or 19b, check this box and see instructions |
▶ |
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021

Schedule A (Form 990) 2021Page 4
Part IV Supporting Organizations
(Complete only if you checked a box in line 12 on Part I. If you checked box 12a, Part I, complete Sections A and B. If you checked box 12b, Part I, complete Sections A and C. If you checked box 12c, Part I, complete Sections A, D, and E. If you checked box 12d, Part I, complete Sections A and D, and complete Part V.)
Section A. All Supporting Organizations
1Are all of the organization’s supported organizations listed by name in the organization’s governing documents? If “No,” describe in Part VI how the supported organizations are designated. If designated by class or purpose, describe the designation. If historic and continuing relationship, explain.
2Did the organization have any supported organization that does not have an IRS determination of status under section 509(a)(1) or (2)? If “Yes,” explain in Part VI how the organization determined that the supported organization was described in section 509(a)(1) or (2).
3a Did the organization have a supported organization described in section 501(c)(4), (5), or (6)? If “Yes,” answer lines 3b and 3c below.
bDid the organization confirm that each supported organization qualified under section 501(c)(4), (5), or (6) and satisfied the public support tests under section 509(a)(2)? If “Yes,” describe in Part VI when and how the organization made the determination.
cDid the organization ensure that all support to such organizations was used exclusively for section 170(c)(2)(B) purposes? If “Yes,” explain in Part VI what controls the organization put in place to ensure such use.
4a Was any supported organization not organized in the United States (“foreign supported organization”)? If “Yes,” and if you checked box 12a or 12b in Part I, answer lines 4b and 4c below.
bDid the organization have ultimate control and discretion in deciding whether to make grants to the foreign supported organization? If “Yes,” describe in Part VI how the organization had such control and discretion despite being controlled or supervised by or in connection with its supported organizations.
cDid the organization support any foreign supported organization that does not have an IRS determination under sections 501(c)(3) and 509(a)(1) or (2)? If “Yes,” explain in Part VI what controls the organization used to ensure that all support to the foreign supported organization was used exclusively for section 170(c)(2)(B) purposes.
5a Did the organization add, substitute, or remove any supported organizations during the tax year? If “Yes,” answer lines 5b and 5c below (if applicable). Also, provide detail in Part VI, including (i) the names and EIN numbers of the supported organizations added, substituted, or removed; (ii) the reasons for each such action;
(iii)the authority under the organization’s organizing document authorizing such action; and (iv) how the action was accomplished (such as by amendment to the organizing document).
bType I or Type II only. Was any added or substituted supported organization part of a class already designated in the organization’s organizing document?
cSubstitutions only. Was the substitution the result of an event beyond the organization’s control?
6Did the organization provide support (whether in the form of grants or the provision of services or facilities) to anyone other than (i) its supported organizations, (ii) individuals that are part of the charitable class benefited by one or more of its supported organizations, or (iii) other supporting organizations that also support or benefit one or more of the filing organization’s supported organizations? If “Yes,” provide detail in Part VI.
7Did the organization provide a grant, loan, compensation, or other similar payment to a substantial contributor (as defined in section 4958(c)(3)(C)), a family member of a substantial contributor, or a 35% controlled entity with regard to a substantial contributor? If “Yes,” complete Part I of Schedule L (Form 990).
8Did the organization make a loan to a disqualified person (as defined in section 4958) not described on line 7? If “Yes,” complete Part I of Schedule L (Form 990).
9a Was the organization controlled directly or indirectly at any time during the tax year by one or more disqualified persons, as defined in section 4946 (other than foundation managers and organizations described in section 509(a)(1) or (2))? If “Yes,” provide detail in Part VI.
bDid one or more disqualified persons (as defined on line 9a) hold a controlling interest in any entity in which the supporting organization had an interest? If “Yes,” provide detail in Part VI.
cDid a disqualified person (as defined on line 9a) have an ownership interest in, or derive any personal benefit from, assets in which the supporting organization also had an interest? If “Yes,” provide detail in Part VI.
10a Was the organization subject to the excess business holdings rules of section 4943 because of section 4943(f) (regarding certain Type II supporting organizations, and all Type III
bDid the organization have any excess business holdings in the tax year? (Use Schedule C, Form 4720, to determine whether the organization had excess business holdings.)
Yes No
1 |
2 |
3a
3b
3c
4a
4b
4c
5a
5b
5c
6
7
8
9a
9b
9c
10a
10b
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021 |
Page 5 |
|
Part IV |
Supporting Organizations (continued) |
|
11Has the organization accepted a gift or contribution from any of the following persons?
aA person who directly or indirectly controls, either alone or together with persons described on lines 11b and 11c below, the governing body of a supported organization?
bA family member of a person described on line 11a above?
cA 35% controlled entity of a person described on line 11a or 11b above? If “Yes” to line 11a, 11b, or 11c, provide detail in Part VI.
Section B. Type I Supporting Organizations
Yes No
11a
11b
11c
1Did the governing body, members of the governing body, officers acting in their official capacity, or membership of one or more supported organizations have the power to regularly appoint or elect at least a majority of the organization’s officers, directors, or trustees at all times during the tax year? If “No,” describe in Part VI how the supported organization(s) effectively operated, supervised, or controlled the organization’s activities. If the organization had more than one supported organization, describe how the powers to appoint and/or remove officers, directors, or trustees were allocated among the supported organizations and what conditions or restrictions, if any, applied to such powers during the tax year.
2Did the organization operate for the benefit of any supported organization other than the supported organization(s) that operated, supervised, or controlled the supporting organization? If “Yes,” explain in Part VI how providing such benefit carried out the purposes of the supported organization(s) that operated, supervised, or controlled the supporting organization.
Section C. Type II Supporting Organizations
Yes No
1
2
1Were a majority of the organization’s directors or trustees during the tax year also a majority of the directors or trustees of each of the organization’s supported organization(s)? If “No,” describe in Part VI how control or management of the supporting organization was vested in the same persons that controlled or managed the supported organization(s).
Section D. All Type III Supporting Organizations
Yes No
1
1Did the organization provide to each of its supported organizations, by the last day of the fifth month of the organization’s tax year, (i) a written notice describing the type and amount of support provided during the prior tax year, (ii) a copy of the Form 990 that was most recently filed as of the date of notification, and (iii) copies of the organization’s governing documents in effect on the date of notification, to the extent not previously provided?
2Were any of the organization’s officers, directors, or trustees either (i) appointed or elected by the supported organization(s) or (ii) serving on the governing body of a supported organization? If “No,” explain in Part VI how the organization maintained a close and continuous working relationship with the supported organization(s).
3By reason of the relationship described on line 2, above, did the organization’s supported organizations have a significant voice in the organization’s investment policies and in directing the use of the organization’s income or assets at all times during the tax year? If “Yes,” describe in Part VI the role the organization’s supported organizations played in this regard.
Section E. Type III Functionally Integrated Supporting Organizations
Yes No
1
2
3
1Check the box next to the method that the organization used to satisfy the Integral Part Test during the year (see instructions).
a The organization satisfied the Activities Test. Complete line 2 below.
The organization satisfied the Activities Test. Complete line 2 below.
b The organization is the parent of each of its supported organizations. Complete line 3 below.
The organization is the parent of each of its supported organizations. Complete line 3 below.
c The organization supported a governmental entity. Describe in Part VI how you supported a governmental entity (see instructions).
The organization supported a governmental entity. Describe in Part VI how you supported a governmental entity (see instructions).
2 Activities Test. Answer lines 2a and 2b below. |
Yes No |
aDid substantially all of the organization’s activities during the tax year directly further the exempt purposes of the supported organization(s) to which the organization was responsive? If “Yes,” then in Part VI identify those supported organizations and explain how these activities directly furthered their exempt purposes, how the organization was responsive to those supported organizations, and how the organization determined
that these activities constituted substantially all of its activities.
bDid the activities described on line 2a, above, constitute activities that, but for the organization’s involvement, one or more of the organization’s supported organization(s) would have been engaged in? If “Yes,” explain in Part VI the reasons for the organization’s position that its supported organization(s) would
have engaged in these activities but for the organization’s involvement.
3Parent of Supported Organizations. Answer lines 3a and 3b below.
aDid the organization have the power to regularly appoint or elect a majority of the officers, directors, or
trustees of each of the supported organizations? If “Yes” or “No,” provide details in Part VI. |
3a |
|
b Did the organization exercise a substantial degree of direction over the policies, programs, and activities of each |
|
|
of its supported organizations? If “Yes,” describe in Part VI the role played by the organization in this regard. |
3b |
|
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021 |
Page 6 |
|
Part V |
Type III |
|
1 Check here if the organization satisfied the Integral Part Test as a qualifying trust on Nov. 20, 1970 (explain in Part VI). See instructions. All other Type III
Check here if the organization satisfied the Integral Part Test as a qualifying trust on Nov. 20, 1970 (explain in Part VI). See instructions. All other Type III
Section |
(A) Prior Year |
(B) Current Year |
||
(optional) |
||||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Net |
1 |
|
|
2 |
Recoveries of |
2 |
|
|
3 |
Other gross income (see instructions) |
3 |
|
|
4 |
Add lines 1 through 3. |
4 |
|
|
5 |
Depreciation and depletion |
5 |
|
|
6Portion of operating expenses paid or incurred for production or collection of gross income or for management, conservation, or maintenance of
|
property held for production of income (see instructions) |
6 |
|
|
7 |
Other expenses (see instructions) |
7 |
|
|
8 |
Adjusted Net Income (subtract lines 5, 6, and 7 from line 4) |
8 |
|
|
Section |
(A) Prior Year |
(B) Current Year |
||
(optional) |
||||
|
|
|
||
1Aggregate fair market value of all
a |
Average monthly value of securities |
1a |
b Average monthly cash balances |
1b |
|
c |
Fair market value of other |
1c |
d Total (add lines 1a, 1b, and 1c) |
1d |
|
eDiscount claimed for blockage or other factors (explain in detail in Part VI):
2 |
Acquisition indebtedness applicable to |
2 |
3 |
Subtract line 2 from line 1d. |
3 |
4Cash deemed held for exempt use. Enter 0.015 of line 3 (for greater amount,
|
see instructions). |
4 |
|
|
5 |
Net value of |
5 |
|
|
6 |
Multiply line 5 by 0.035. |
6 |
|
|
7 |
Recoveries of |
7 |
|
|
8 |
Minimum Asset Amount (add line 7 to line 6) |
8 |
|
|
Section |
|
|
Current Year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Adjusted net income for prior year (from Section A, line 8, column A) |
1 |
|
|
2 |
Enter 0.85 of line 1. |
2 |
|
|
3 |
Minimum asset amount for prior year (from Section B, line 8, column A) |
3 |
|
|
4 |
Enter greater of line 2 or line 3. |
4 |
|
|
5 |
Income tax imposed in prior year |
5 |
|
|
6Distributable Amount. Subtract line 5 from line 4, unless subject to
emergency temporary reduction (see instructions). |
6 |
7 Check here if the current year is the organization’s first as a
Check here if the current year is the organization’s first as a
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021 |
|
|
|
|
Page 7 |
|||
Part V |
Type III |
|
||||||
Section |
|
|
|
|
Current Year |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
1 |
Amounts paid to supported organizations to accomplish exempt purposes |
|
1 |
|
||||
2 |
Amounts paid to perform activity that directly furthers exempt purposes of supported |
|
|
|||||
|
organizations, in excess of income from activity |
|
|
2 |
|
|||
3 |
Administrative expenses paid to accomplish exempt purposes of supported organizations |
3 |
|
|||||
4 |
Amounts paid to acquire |
|
|
4 |
|
|||
5 |
Qualified |
5 |
|
|||||
6 |
Other distributions (describe in Part VI). See instructions. |
|
|
6 |
|
|||
7 |
Total annual distributions. Add lines 1 through 6. |
|
|
7 |
|
|||
8 |
Distributions to attentive supported organizations to which the organization is responsive |
|
|
|||||
|
(provide details in Part VI). See instructions. |
|
|
8 |
|
|||
9 |
Distributable amount for 2021 from Section C, line 6 |
|
|
9 |
|
|||
10 |
Line 8 amount divided by line 9 amount |
|
|
10 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
(i) |
(ii) |
|
(iii) |
|
Section |
(see instructions) |
Underdistributions |
Distributable |
|||||
Excess Distributions |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amount for 2021 |
||
1 |
Distributable amount for 2021 from Section C, line 6 |
|
|
|
|
|||
2 |
Underdistributions, if any, for years prior to 2021 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
(reasonable cause |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
instructions. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
3 |
Excess distributions carryover, if any, to 2021 |
|
|
|
|
|||
a |
From 2016 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
b |
From 2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
c |
From 2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
d |
From 2019 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
e |
From 2020 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
f |
Total of lines 3a through 3e |
|
|
|
|
|
||
g |
Applied to underdistributions of prior years |
|
|
|
|
|||
h |
Applied to 2021 distributable amount |
|
|
|
|
|||
i |
Carryover from 2016 not applied (see instructions) |
|
|
|
|
|||
j |
Remainder. Subtract lines 3g, 3h, and 3i from line 3f. |
|
|
|
|
|||
4 |
Distributions for 2021 from |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Section D, line 7: |
$ |
|
|
|
|
||
a |
Applied to underdistributions of prior years |
|
|
|
|
|||
b |
Applied to 2021 distributable amount |
|
|
|
|
|||
c |
Remainder. Subtract lines 4a and 4b from line 4. |
|
|
|
|
|||
5 |
Remaining underdistributions for years prior to 2021, if |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
any. Subtract lines 3g and 4a from line 2. For result |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
greater than zero, explain in Part VI. See instructions. |
|
|
|
|
|||
6 |
Remaining underdistributions for 2021. Subtract lines 3h |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
and 4b from line 1. For result greater than zero, explain in |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Part VI. See instructions. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
7 |
Excess distributions carryover to 2022. Add lines 3j |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
and 4c. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
8 |
Breakdown of line 7: |
|
|
|
|
|
||
a |
Excess from 2017 . . . |
|
|
|
|
|
||
b |
Excess from 2018 . . . |
|
|
|
|
|
||
c |
Excess from 2019 . . . |
|
|
|
|
|
||
d |
Excess from 2020 . . . |
|
|
|
|
|
||
e |
Excess from 2021 . . . |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021

Schedule A (Form 990) 2021 |
Page 8 |
|
Part VI |
Supplemental Information. Provide the explanations required by Part II, line 10; Part II, line 17a or 17b; Part |
|
|
III, line 12; Part IV, Section A, lines 1, 2, 3b, 3c, 4b, 4c, 5a, 6, 9a, 9b, 9c, 11a, 11b, and 11c; Part IV, Section |
|
|
B, lines 1 and 2; Part IV, Section C, line 1; Part IV, Section D, lines 2 and 3; Part IV, Section E, lines 1c, 2a, 2b, |
|
|
3a, and 3b; Part V, line 1; Part V, Section B, line 1e; Part V, Section D, lines 5, 6, and 8; and Part V, Section E, |
|
|
lines 2, 5, and 6. Also complete this part for any additional information. (See instructions.) |
|
|
|
|
Schedule A (Form 990) 2021
Document Specifics
| Fact Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Schedule A (Form 990 or 990-EZ) is primarily used by public charities to provide the IRS with the necessary information to verify that they meet public support requirements. |
| 2 | This schedule is attached to and forms part of the Form 990 or 990-EZ filed annually by organizations. |
| 3 | It categorizes organizations as public charities or as private foundations, impacting their qualification for tax-exempt status. |
| 4 | Organizations must provide detailed information about their sources of income to demonstrate compliance with public support thresholds over a five-year period. |
| 5 | Failure to adequately complete and submit Schedule A can result in penalties or loss of tax-exempt status for the organization. |
| 6 | Sections include details on public support, total support, and supporting materials that validate the organization's adherence to the requirements. |
| 7 | Governing laws for Schedule A and its submission requirements include the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) sections applicable to non-profit and tax-exempt organizations. |
Guide to Writing IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ
Filling out the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form is a critical step for many tax-exempt organizations. This document is essential for maintaining their tax-exempt status with the IRS, demonstrating their commitment to public financial accountability. The process requires careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the organization's financial activities over the past fiscal year. By following a step-by-step approach, organizations can ensure they complete this form accurately and effectively.
- Gather the necessary information. Before starting, ensure you have the organization's financial statements, donor lists, and details about any significant activities or changes in the past year. This information will support the answers provided on the form.
- Identify which sections of the form apply to your organization. The IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ includes different sections for various types of organizations, such as museums, hospitals, schools, and other public charities. Selecting the correct sections is crucial for accurately representing your organization's activities and financial situation.
- Complete Part I, which focuses on the Reason for Public Charity Status. Here, you will classify your organization based on the nature of its activities, funding sources, and relationship with other entities. Choose the category that best fits your organization's operations.
- Fill out Part II if your organization is a public charity under sections 509(a)(1) and 170(b)(1)(A)(vi). This part requires detailed information about gifts, grants, and contributions received, which will help determine if the organization meets the public support test.
- If applicable, complete Part III, which pertains to organizations qualifying under section 509(a)(2). Similar to Part II, this section requires input on revenue, but with a focus on categorizing different types of income to calculate public support percentages.
- For organizations that operate as a supporting organization under sections 509(a)(3) and 4942(j)(3) or (5), fill in Part IV. This section asks for detailed information about the supported organizations and the relationship between them.
- Complete Part V if your organization benefits from excess business holdings as defined in section 4943. This part is less commonly applicable but crucial for those it affects.
- Go over the form to ensure all applicable fields are accurately completed and that the form aligns with the organization's financial documents and records. Accuracy here is vital to avoid issues with the IRS.
- Have an authorized representative or officer of the organization review and sign the form. Their signature attests to the accuracy of the information provided.
- Finally, submit the form to the IRS by the appropriate deadline, which is typically the 15th day of the 5th month after the organization's fiscal year ends. Depending on the IRS's current filing requirements, you may need to file electronically or by mail.
Filling out the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form meticulously is an investment in your organization's future. Completing this form not only complies with federal regulations but also reaffirms your organization's commitment to transparency and accountability. By following these steps, organizations can navigate the process more smoothly and efficiently.
Understanding IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ
-
What is the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form?
The IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form is a supplemental document that tax-exempt organizations attach to their Form 990 or 990-EZ. This form is used to provide the IRS with information on the public charity status and public support of the organization. It helps to ensure that the organization meets the tax-exemption qualifications under Section 501(c)(3).
-
Who is required to file Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ?
All organizations that have obtained tax-exempt status under Section 501(c)(3) must file Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ along with their Form 990 or 990-EZ. This includes public charities, private foundations, and other non-profit entities recognized as exempt by the IRS.
-
What information do I need to complete Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ?
To complete Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ, organizations need to provide comprehensive details about their public charity status. This includes information on:
- Public support test calculations
- Revenue sources
- Activities and operational information
- Relationships with non-charitable entities
Documentation supporting the provided information may also be required.
-
How does an organization determine its public charity status on Schedule A?
Public charity status is determined based on the support and revenue an organization receives. The IRS provides tests, such as the public support test, to assess whether an organization qualifies as a public charity. If an organization receives a significant part of its funding from the general public, government grants, or other public sources, it typically qualifies as a public charity.
-
What happens if an organization fails to file Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ?
If an organization fails to file Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ, it may face penalties. This could include fines for each day the form is late. The organization's tax-exempt status may also be at risk if the failure to file is part of a pattern of non-compliance. It's crucial for organizations to file all required forms accurately and on time to maintain their tax-exempt status.
-
Can Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ be filed electronically?
Yes, organizations can file Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ electronically, along with their main Form 990 or 990-EZ. The IRS encourages electronic filing as it is faster, more secure, and ensures better accuracy of the information submitted. Most tax preparation software supports electronic filing of these forms.
-
Are there exceptions to who must file Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ?
While most 501(c)(3) organizations must file Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ, there are exceptions. For example, religious institutions such as churches, and certain affiliates, are not required to file. It's important for each organization to review the IRS guidelines to determine if they are exempt from filing this schedule.
-
Where can I find help to fill out Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ?
There are several resources available to help organizations fill out Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ. The IRS provides instructions for the schedule on its website. Additionally, tax professionals and organizations that specialize in non-profit accounting can provide assistance. Educating staff on the requirements and seeking knowledgeable help ensures accurate and timely filing.
Common mistakes
Filing the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form is a critical aspect of maintaining a nonprofit organization’s tax-exempt status. However, it's not uncommon for people to make mistakes in this process. Recognizing these errors can help ensure accurate reporting and compliance with IRS regulations.
Not substantiating donations properly – Organizations often overlook the requirement to keep detailed records of donations received, including dates, amounts, and donor information. This oversight can lead to inaccuracies on the form.
Failing to report all sources of income – Some nonprofits mistakenly believe that only donations need to be reported, neglecting other sources of income such as sales, services, or investments.
Incorrectly classifying expenses – It’s crucial to correctly categorize expenses between program services, management, and fundraising. Misclassification can affect an organization’s public support calculation and its status.
Overlooking noncash contributions – Items or services donated to the organization, known as in-kind contributions, often go unreported. However, it’s important to assess and disclose their fair market value.
Misunderstanding lobbying activities – Nonprofits must distinguish between direct and grassroots lobbying expenses. Misreporting these can have implications for their tax-exempt status.
Not disclosing related party transactions – Transactions between the organization and its insiders or related entities must be reported to ensure transparency and prevent the misuse of assets.
Omitting foreign activities – Organizations that conduct activities or hold investments outside the United States must provide details of such activities, which are often mistakenly left out.
Ignoring subsequent events – Significant events that occur after the fiscal year-end but before the form is filed should be disclosed if they affect the organization's financial situation or operations.
Improper public inspection disclosure – Nonprofits are required to make certain documents, including their Form 990, available for public inspection. Failure to indicate how these documents can be accessed is a common error.
Lack of detailed program service descriptions – Providing vague or insufficient details about the organization’s mission and the programs conducted can lead to misunderstandings about the nonprofit’s activities and accomplishments.
Avoiding these common missteps when completing Schedule A of the 990 or 990-EZ form is essential for maintaining good standing with the IRS and ensuring continued tax-exempt status. Proper attention to detail, thorough record-keeping, and an understanding of the requirements can significantly impact a nonprofit organization’s compliance and ability to accomplish its mission.
Documents used along the form
When managing the financial affairs and reporting for a non-profit organization, the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form stands as a pivotal document in demonstrating the entity's adherence to tax regulations, particularly those governing public charity status and donor contributions. However, this form does not stand alone in the reporting process. Several other documents and forms are typically prepared and filed in conjunction with Schedule A to provide a full picture of the organization's fiscal health, compliance, and operations. Each of these documents plays a critical role in ensuring that the organization maintains its tax-exempt status and adheres to the regulatory requirements set forth by the IRS.
- Form 990 or 990-EZ: This is the core document that most tax-exempt organizations will file. It provides the IRS with a comprehensive overview of the organization's activities, finances, and governance. While Schedule A is a part of the broader Form 990 or 990-EZ filing, it's important to recognize the distinction and the necessity of the latter to provide general information about the organization.
- Form 990-T: Filed by nonprofit organizations that have generated income from business activities unrelated to their tax-exempt purpose, Form 990-T provides details on taxable income and allows organizations to claim deductions related to conducting their business activities.
- Form 8868: This form is used to apply for an automatic extension of time to file the Form 990 or 990-EZ. Filing this request can be crucial for organizations that need additional time to gather information or navigate complex reporting areas.
- Form 1023 and Form 1023-EZ: These forms are used by organizations seeking to obtain tax-exempt status under IRS Section 501(c)(3). While not annually filed with the Schedule A or Form 990, they are foundational documents that the IRS may reference to ensure the organization's operations remain aligned with its tax-exempt purpose.
- Form 1099-MISC and Form 1099-NEC: These forms are used to report payments made to independent contractors, vendors, and others who are paid for services provided to the nonprofit. These documents help the IRS assess whether the organization is accurately reporting payments and complying with tax withholding requirements.
- State-specific filings: Depending on the state in which the nonprofit operates, there may be additional reporting requirements mirroring the federal Form 990 disclosures but tailored to state regulatory interests. These can include annual reports, charitable solicitation registrations, and state-specific tax exemption forms.
Together, these documents form a comprehensive suite that not only fulfills regulatory reporting requirements but also aids in the strategic management of the organization. By ensuring each document is accurately prepared and timely filed, non-profits can focus on their mission-critical activities with the assurance that their administrative bases are covered. This approach not only facilitates compliance but also enhances the organization’s transparency and accountability to stakeholders.
Similar forms
The IRS Form 1040 Schedule C is similar to the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form, as both are used to report financial details pertaining to the operations of an entity. While the Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form is utilized by non-profit organizations to report contributions, gifts, and grants they receive, Form 1040 Schedule C is used by sole proprietors to report the income, expenses, and overall profit or loss of their business. Both forms play a critical role in ensuring that the entities comply with federal tax obligations by providing a detailed account of their financial activities.
Form 1120, used by corporations to report their income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits, also shares similarities with the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form. Both documents are essential for tax reporting purposes, enabling the respective entities to detail their financial activities over the fiscal year. However, while Form 1120 is for for-profit corporations to calculate their income tax liability, Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ is for non-profits to maintain their tax-exempt status by disclosing their sources of income and expenditures.
Form 1065 is another document resembling the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form, with both serving entities that are not subject to income tax. Form 1065 is used by partnerships to report the income, deductions, gains, and losses from their operations, akin to how non-profit organizations use the Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ to report their financial transactions and compliance with federal regulations. This similarity underscores their roles in ensuring transparent financial reporting to the federal government.
Form 990-PF is similar to the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form as it’s specifically designed for private foundations in the United States. Just like the Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ, which non-profits use to provide information about their financial health and operational efficiency, Form 990-PF allows private foundations to report their assets, grants, contributions, and expenses to the IRS. This ensures both types of entities remain compliant with the IRS’s regulatory requirements and maintain their tax-exempt status.
The IRS Form 990-T is related to the Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form because both are filed by tax-exempt entities. However, Form 990-T is specifically used by these organizations to report and pay income tax on unrelated business income. This form highlights how a non-profit organization can have taxable income, similar to how Schedule A outlines the contributions and grants received which are typical non-taxable sources of income for non-profits.
Form 8282, Donee Information Return, has parallels with the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form due to its use in the non-profit sector, particularly in documenting donations. When non-profit organizations sell or otherwise dispose of donated property within three years after receiving it, they're required to report this on Form 8282. This bears similarity to Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ, as it provides the IRS with information about the sources of a non-profit's income, ensuring transparency and compliance with tax laws.
Form 1023 is akin to the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form because it is an initial step for non-profit organizations seeking federal tax-exempt status under Section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code. In contrast, Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ serves as an ongoing requirement for non-profits to report annually on their finances and operations to maintain their exemption. Both forms are crucial for non-profits to gain and retain the benefits of tax-exempt status.
Form 8868, Application for Extension of Time To File an Exempt Organization Return, is similar to the Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form because it directly relates to the filing requirements of non-profit organizations. While Form 8868 provides organizations with additional time to prepare and submit their forms, including the Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ, it underscores the importance of accurate and timely reporting for maintaining tax-exempt status.
The Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) Form 5500 is comparable to the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form, as both entail reporting obligations for organizations. ERISA Form 5500 is required for plan administrators to report information about the operation, funding, assets, and investments of pension and other employee benefit plans, mirroring the transparency and accountability that the Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ demands from non-profits regarding their financial and operational status.
Lastly, the IRS Form 5471, Information Return of U.S. Persons With Respect to Certain Foreign Corporations, resembles the IRS Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ form in its requirement for detailed financial reporting. Form 5471 is used by certain U.S. citizens and residents who are officers, directors, or shareholders in certain foreign corporations, akin to how non-profit organizations use Schedule A 990 or 990-EZ to report financial details to the IRS, demonstrating the federal government's effort to ensure compliance and transparency across different types of entities.
Dos and Don'ts
When completing IRS Schedule A for either the 990 or 990-EZ forms, organizations should take careful steps to ensure accuracy and compliance with tax regulations. Schedule A is particularly important as it relates to public charity status and public support. To assist in this process, here are some advised dos and don'ts:
Do:
Thoroughly review the instructions provided by the IRS for Schedule A to ensure understanding of all requirements. These instructions are integral in providing detailed guidance on how to accurately complete the form.
Keep accurate records of all donations and financial support received over the tax year. Precise record-keeping is essential as it supports the information reported on Schedule A.
Ensure that all parts relevant to your organization's type and status are completed. Schedule A varies depending on whether an organization falls under a public charity or a private foundation, among other classifications.
Seek professional advice if there is any uncertainty about how to report information on Schedule A. Tax professionals or legal advisors who specialize in nonprofit law can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation.
Don't:
Rush through the form without verifying all the data. Errors or inaccuracies can lead to issues with the IRS, including audits or penalties.
Omit required information. If a section of Schedule A applies to your organization, ensure that all requested details are provided. Incomplete forms may be considered incorrectly filed.
Guess or approximate answers. All financial information should be based on actual records and precise calculations to maintain the integrity of your filing.
Ignore the deadlines for filing. Submissions must be made in a timely manner to avoid late filing penalties. Be aware of the specific deadlines that apply to your organization.
Misconceptions
When it comes to charitable organizations and their tax obligations, confusion often surrounds the IRS Schedule A (Form 990 or 990-EZ). Here, we'll debunk some common misconceptions to help you better understand these forms.
Only large nonprofits must file: There's a belief that Schedule A is only for big organizations. However, most public charities, regardless of size, are required to file it as part of their Form 990 or 990-EZ, provided they meet the filing threshold.
It’s just about financial information: While financial data is crucial, Schedule A also requires details about public support, which helps the IRS determine your organization's public charity status each year.
If you file Form 990, Schedule A is optional: This is not true. If an organization files Form 990 or 990-EZ, Schedule A is generally required as well. It’s an essential part of demonstrating your public charity status.
Schedule A is filed separately: Some believe Schedule A must be filed independently of Form 990 or 990-EZ. Actually, it is submitted together with the main form as a part of the complete tax return for the organization.
The same information every year will suffice: The information on Schedule A can change significantly from year to year, based on varying public support and financial details. It’s not a “fill once, file forever” form.
Only monetary donations are reported: In addition to cash donations, Schedule A also requires reporting of other types of support, such as securities, real estate, and in-kind donations. This broader view helps calculate public support percentage.
There's no need to explain unusual grants: Actually, if a large, unexpected grant skews your public support test, you’re expected to provide an explanation on Schedule A. This keeps your public charity status intact despite abnormal funding years.
Public support test is a one-time calculation: The public support test is not a one-off. Organizations must calculate it every year to demonstrate that they receive a substantial portion of their support from the public and not merely a few major donors.
Filing late has no serious consequences: Filing Schedule A late can have significant repercussions, including penalties or loss of tax-exempt status. It’s crucial to file on time to maintain your standing as a public charity.
Understanding the real requirements behind Schedule A for Form 990 or 990-EZ can guide your organization through the complexities of tax compliance, helping to maintain its integrity and focus on its mission.
Key takeaways
When it comes to handling Form 990 or 990-EZ, specifically the Schedule A, it’s vital for non-profit organizations to accurately report and provide details on their public charity status and public support. Let’s explore some key takeaways to ensure your organization handles this form correctly:
- Determine Your Eligibility: Before filling out Schedule A, ensure your organization is actually required to do so. Generally, public charities and certain non-profits must complete it as part of their Form 990 or 990-EZ.
- Understand Public Charity Status: Schedule A is used to report the organization’s status as a public charity. Different sections of Schedule A apply based on how your organization qualifies as a public charity.
- Annual Filing is Required: This schedule must be filed every year together with the Form 990 or 990-EZ to maintain your organization’s public charity status.
- Review Instructions Carefully: The IRS instructions for Schedule A provide guidance on which sections to complete and how to accurately report information. Misinterpretation or skipping sections can lead to inaccuracies or IRS inquiries.
- Public Support Calculation: Sections of Schedule A require organizations to calculate and report the amount of public support received. Understanding how to correctly calculate this figure is crucial for determining your qualifying status.
- Document and Keep Records: Supporting documentation for all reported figures should be meticulously kept. This is essential not only for internal records but also in case of an IRS audit.
- Be Aware of Changes in Status: If your organization experiences changes in its public charity status or public support calculations, these changes must be reflected in Schedule A filings.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: Given the complexity of tax laws and reporting requirements, seeking advice from a tax professional or attorney specializing in non-profit law can prevent errors and ensure compliance.
Completing Schedule A accurately is crucial for demonstrating your organization's compliance with IRS requirements and maintaining its public charity status. Paying close attention to detail, keeping abreast of legal changes, and consulting with professionals when in doubt are key strategies for successful compliance.
Popular PDF Documents
IRS 2210 - Form 2210 is especially relevant for those with non-wage income, assisting in calculating necessary tax payments.
Wisconsin Department of Revenue Forms - It serves as a legal agreement, providing security and peace of mind for individuals delegating their tax-related tasks.