Get IRS Schedule 8812 1040 Form
For families navigating the complexities of tax returns, understanding the significance of the IRS Schedule 8812 1040 form is a vital step towards maximizing potential benefits. This form, integral for those claiming the Child Tax Credit (CTC), acts as a bridge, enabling taxpayers to calculate and claim additional credits which could substantially lower their tax obligations or enhance their refunds. While it might seem daunting at first, breaking down the Schedule 8812 into its essential components reveals its role in ensuring families receive the financial support they're entitled to. This includes determining eligibility for the credit based not only on income levels but also on residency and relationship tests. Additionally, the form accommodates adjustments for those with three or more qualifying children, making it a crucial tool for households looking to navigate their taxes efficiently. As the landscape of tax legislation continues to evolve, staying informed about the specifics of such forms is more important than ever, offering a clear pathway to leveraging available tax benefits.
IRS Schedule 8812 1040 Example
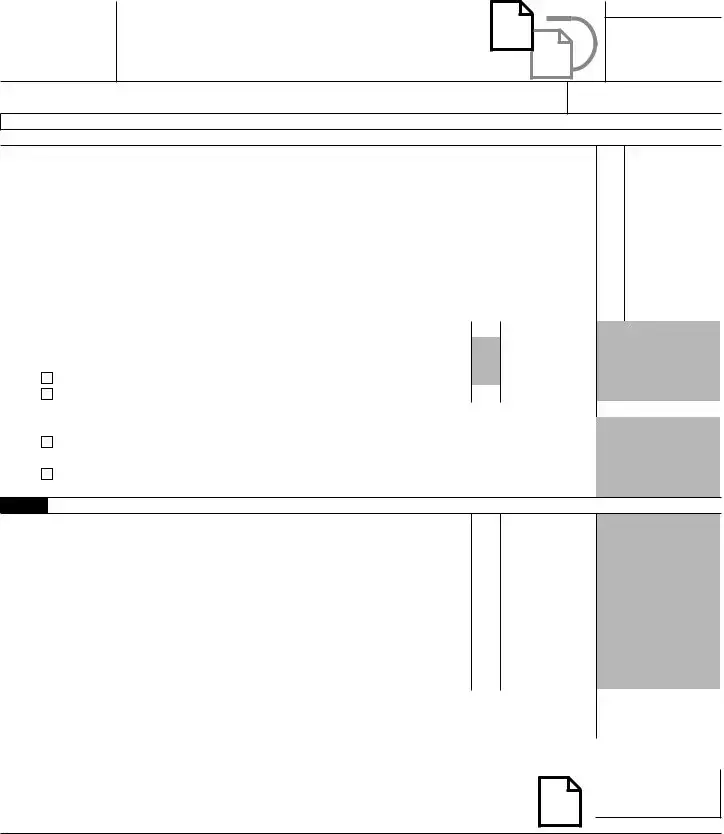
SCHEDULE 8812 |
Additional Child Tax Credit |
1040 |
|
OMB No. |
(Form 1040) |
|
2020 |
||
|
. . . . . . . . . |
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
. . . . . . . . . |
|
|
|
Attach to Form 1040, |
8812 |
||
Department of the Treasury |
Go to www.irs.gov/Schedule8812 for instructions and the latest information. |
Attachment |
||
Internal Revenue Service (99) |
|
|
|
Sequence No. 47 |
Name(s) shown on return |
|
|
|
Your social security number |
Part I |
All Filers |
Caution: If you file Form 2555, stop here; you cannot claim the additional child tax credit.
1If you are required to use the worksheet in Pub. 972, enter the amount from line 10 of the Child Tax Credit
|
and Credit for Other Dependents Worksheet in the publication. Otherwise, enter the amount from line 8 of your |
|
|
|||||||
|
Child Tax Credit and Credit for Other Dependents Worksheet. (See the instructions for Forms 1040 and 1040- |
|
|
|||||||
|
SR, line 19, or the instructions for Form |
. . . . . . . . |
1 |
|||||||
2 |
Enter the amount from line 19 of your Form 1040, Form |
. . . . . . . . |
2 |
|||||||
3 |
Subtract line 2 from line 1. If zero, stop here; you cannot claim this credit . . . . |
. . . . . . . . |
3 |
|||||||
4 |
Number of qualifying children under 17 with the required social security number: |
|
|
|
|
x $1,400. |
|
|
||
|
Enter the result. If zero, stop here; you cannot claim this credit |
. . . . . . . . |
4 |
|||||||
|
TIP: The number of children you use for this line is the same as the number of children you used for line 1 of the |
|
|
|||||||
|
Child Tax Credit and Credit for Other Dependents Worksheet. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
Enter the smaller of line 3 or line 4 |
. . . . . . . . |
5 |
|||||||
6a |
Earned income (see instructions) |
|
|
6a |
|
|
||||
b |
Nontaxable combat pay (see instructions) |
6b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7Is the amount on line 6a more than $2,500?
|
No. Leave line 7 blank and enter |
|
|
|
|
|
Yes. Subtract $2,500 from the amount on line 6a. Enter the result |
|
7 |
|
|
8 |
Multiply the amount on line 7 by 15% (0.15) and enter the result |
. . . . . . . . |
8 |
|
|
Next. On line 4, is the amount $4,200 or more?
No. If line 8 is zero, stop here; you cannot claim this credit. Otherwise, skip Part II and enter the smaller of line 5 or line 8 on line 15.
Yes. If line 8 is equal to or more than line 5, skip Part II and enter the amount from line 5 on line 15.
Otherwise, go to line 9.
Part II Certain Filers Who Have Three or More Qualifying Children
9Withheld social security, Medicare, and Additional Medicare taxes from Form(s)
|
instructions |
|
9 |
|
|
||
10 |
Enter the total of the amounts from Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 14, and Schedule 2 |
|
|
|
|||
|
(Form 1040), line 5, plus any taxes that you identified using code “UT” and entered on |
|
|
|
|||
|
Schedule 2 (Form 1040), line 8 |
|
10 |
|
|
||
11 |
Add lines 9 and 10 |
} |
11 |
|
|
||
12 |
1040 and |
Enter the total of the amounts from Form 1040 or |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
12 |
|
|
||||
13 |
Subtract line 12 from line 11. If zero or less, enter |
. . . . . . . |
13 |
|
|||
14 |
Enter the larger of line 8 or line 13 |
. . . . . . . |
14 |
|
|||
|
Next, enter the smaller of line 5 or line 14 on line 15. |
|
|
|
|
||
Part III |
Additional Child Tax Credit |
|
|
|
|
||
15 |
This is your additional child tax credit |
. . . . . . . |
15 |
|
|||
1040 |
. . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . |
Enter this amount on Form 1040, line 28; Form
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see your tax return instructions. |
Cat. No. 59761M |
Schedule 8812 (Form 1040) 2020 |
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The IRS Schedule 8812 form is used with Form 1040 to calculate the additional child tax credit that may be available to taxpayers. |
| Eligibility | Eligibility for the credit on Schedule 8812 depends on the taxpayer's income, the number of qualifying children, and whether the taxpayer has already claimed the full amount of the Child Tax Credit on Form 1040. |
| Requirements | Taxpayers must have one or more qualifying children and meet certain income thresholds to use Schedule 8812. |
| Governing Law | Federal tax law as covered under the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) governs the requirements and processes related to Schedule 8812, which does not vary by state. |
Guide to Writing IRS Schedule 8812 1040
To ensure you're taking full advantage of tax credits related to dependents, the IRS Schedule 8812 form is your go-to document. This form is crucial for individuals looking to claim the Child Tax Credit (CTC) or the Additional Child Tax Credit (ACTC). The process involves a series of steps designed to verify your eligibility and calculate the amount you can claim. Following these steps carefully will help streamline your tax filing experience, making sure you don't miss out on valuable tax benefits.
Steps for Filling out the IRS Schedule 8812 1040 Form
- Start by reading the instructions provided by the IRS for Schedule 8812 carefully. These instructions are key to understanding eligibility requirements and how to accurately complete the form.
- Gather your financial documents, including your income statements and information regarding all qualifying children. This will make the process smoother and more accurate.
- Proceed to Part I if your child has a Social Security Number (SSN) that allows them to be claimed for the Child Tax Credit. Fill in the child’s name, SSN, and the credit amount as per the instructions.
- If your child does not have an SSN, move to Part II. Here, you'll calculate the Additional Child Tax Credit using earned income. Input the necessary information as directed by the form instructions.
- Use Part III to calculate the total amount of your credits. This section helps determine the refundable portion of the Child Tax Credit.
- Once all parts are accurately completed, attach Schedule 8812 to your Form 1040 or Form 1040-SR. Ensure all information is correct and matches the information on your other tax documents.
- Review the form for any errors. Double-check your calculations and the information provided to avoid processing delays or audits.
- File your tax return with Schedule 8812 attached by the tax filing deadline to ensure you receive any credits you're eligible for without delay.
Completing and submitting the IRS Schedule 8812 form is essential for claiming certain tax credits. By carefully following the steps above, you can confidently navigate this process. Remember, accurate and timely filing is crucial to maximizing your tax benefits and minimizing potential issues with the IRS.
Understanding IRS Schedule 8812 1040
-
What is the IRS Schedule 8812 form used for?
The IRS Schedule 8812 form is used by taxpayers to calculate and claim the Additional Child Tax Credit (ACTC). This credit is available to individuals who have dependents that qualify them for the Child Tax Credit (CTC) but who receive less than the full amount of the CTC because their tax liability is less than the credit. The Schedule 8812 form helps determine the refundable portion of the credit that could be received as a refund.
-
Who needs to file Schedule 8812 with their 1040 form?
Any taxpayer who wants to claim the Additional Child Tax Credit and has earned income must file Schedule 8812 along with their Form 1040 or Form 1040-SR. This typically includes families with children who have Social Security numbers and meet the other eligibility requirements for the Child Tax Credit, who may not have owed enough tax to claim the full non-refundable Child Tax Credit.
-
What information do I need to complete Schedule 8812?
To complete Schedule 8812, you will need:
- Your Social Security Number (SSN) or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN).
- The SSN or ITIN of each qualifying child.
- Your earned income amount for the tax year.
- Details of any credits or deductions that apply to your situation.
-
How does Schedule 8812 work with the Child Tax Credit?
Schedule 8812 is an extension of the Child Tax Credit designed to benefit those who have a lower tax liability than the credit amount for which they are eligible. Essentially, while the Child Tax Credit is a primary benefit for reducing tax liability, Schedule 8812 enables taxpayers to receive a refund for the portion of the Child Tax Credit that exceeds their tax owed, making the Additional Child Tax Credit refundable to them.
-
Can I file Schedule 8812 electronically?
Yes, you can file Schedule 8812 and your Form 1040 electronically through IRS authorized e-filing systems. Many taxpayers find electronic filing more convenient and efficient, and it can speed up the processing time of your tax return and any refund due.
-
What is the deadline for filing Schedule 8812?
Schedule 8812 should be filed alongside your Form 1040 or 1040-SR by the annual tax filing deadline, typically April 15 unless the date falls on a weekend or holiday, in which case the deadline is the next business day. If you request an extension for filing your tax return, the same extension applies to Schedule 8812.
-
Are there any common mistakes to avoid when filling out Schedule 8812?
Common mistakes include:
- Entering the wrong Social Security Numbers for you or your dependents.
- Incorrectly calculating earned income.
- Overlooking other credits or deductions that affect your eligibility or the amount of the ACTC.
-
How do I know if my child qualifies for the Additional Child Tax Credit?
To qualify for the Additional Child Tax Credit, your child must first qualify for the Child Tax Credit. This generally means that the child must be under 17 at the end of the tax year, live with you for more than half the year, and meet certain relationship and support tests. Additionally, the child must have a Social Security Number that is valid for employment in the U.S.
-
What if I received a letter from the IRS regarding Schedule 8812?
If the IRS sends you a letter or notice regarding Schedule 8812, it's essential to read it carefully and respond by the deadline given. The IRS may request additional information to verify your eligibility for the credit or to correct errors. Failure to respond can result in delays or adjustments to your refund. If you're uncertain about how to respond, consider consulting a tax professional.
-
Where can I get help with filing Schedule 8812?
Help with filing Schedule 8812 can be found through several resources:
- The IRS website offers instructions and resources for filling out the form.
- Tax preparation software often includes guidance for completing Schedule 8812.
- Professional tax preparers and accountants can provide personal assistance.
- Free tax assistance programs, such as VITA (Volunteer Income Tax Assistance) and TCE (Tax Counseling for the Elderly), are available for qualifying individuals.
Common mistakes
Filling out the IRS Schedule 8812 for the 1040 form is an essential task to claim the child tax credit. It's a straightforward process, but errors can occur that might delay your refund or result in unexpected tax liabilities. Here are six common mistakes to be aware of:
Not verifying eligibility criteria: Before you start, ensure that the child meets the age, relationship, support, dependent, citizenship, and residence tests to qualify for the credit. Failing to do so may lead to claiming the credit inaccurately.
Incorrect Social Security Numbers (SSNs): It's crucial to double-check the SSNs for both the taxpayer and the qualifying child. Any discrepancies or input errors can result in the rejection of the credit.
Omitting required information: Every field that applies to your situation needs to be filled out completely. Skipping parts of the form can lead to processing delays or a denial of the credit.
Miscalculating the credit: The amount of child tax credit you're eligible for depends on your income, the number of qualifying children, and other factors. Incorrect calculations can either result in claiming less than you're entitled to or owing back to the IRS if you claim too much.
Not attaching Schedule 8812 to the 1040 form: For paper filers, it's a common mistake to forget to attach the completed Schedule 8812 to your tax return. This oversight can delay processing your return and the credit.
Ignoring IRS notices: If the IRS needs more information or finds a discrepancy in your Schedule 8812, they will contact you. Not responding in a timely manner can lead to delays in your refund or adjustments to the credit.
Avoiding these mistakes requires attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the tax laws regarding the child tax credit. If you're uncertain about your eligibility or how to fill out the form, consulting with a tax professional can provide clarity and peace of mind. Remember, accurate and complete tax filings ensure that you receive the correct credit amount without unnecessary delays.
Documents used along the form
When dealing with the IRS Schedule 8812 (Form 1040), it's typically to claim the Child Tax Credit or the Additional Child Tax Credit. This form is an essential tool for taxpayers who want to make sure they're seizing every possible tax advantage available for parents or guardians. However, filling out this form is rarely done in isolation. To complete it accurately and to bolster your tax return, several other documents are often necessary. Understanding these documents can make the process smoother and could potentially maximize your tax benefits.
- Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return: This is the backbone of your tax documentation, serving as the primary form for individuals reporting their income, deducting expenses, and claiming tax credits. Schedule 8812 is actually a part of Form 1040, supplementing it when you're claiming certain credits related to dependents.
- Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement: Almost everyone employed will receive a Form W-2 from their employer. This form reports your annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld from your paycheck. It provides crucial information needed to fill out both Form 1040 and Schedule 8812 accurately.
- Form 1099: If you're self-employed, an independent contractor, or have other types of income (like interest, dividends, or government payments), you'll likely receive a Form 1099. This form shows income that hasn’t had taxes withheld, which must be reported on your Form 1040 and might affect the credits you claim on Schedule 8812.
- Schedule C, Profit or Loss from Business (Sole Proprietorship): For those who are self-employed or run a business as a sole proprietor, this schedule reports how much money the business made or lost. It helps determine the amount of taxable income you have, potentially affecting the amount of credit you can claim for your dependents on Schedule 8812.
- Schedule EIC, Earned Income Credit: This is used alongside Form 1040 to claim the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), aimed at benefiting working people with low to moderate income. Eligibility for the EITC can depend on your income level and family size, which might also influence the child tax credit calculations on Schedule 8812.
In conclusion, while IRS Schedule 8812 (Form 1040) plays a critical role in claiming credits for dependents, it’s only part of the larger tax return process. Each of these additional documents serves its unique purpose in ensuring that your tax return is comprehensive and that you're taking full advantage of available tax benefits. Collecting and accurately completing these forms can significantly influence the outcome of your tax responsibilities and benefits for the year.
Similar forms
The IRS Schedule 8812 1040 form is closely related to the main Form 1040, which is the U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. This foundational document is the starting point for most taxpayers, detailing income, deductions, and credits to determine the amount of tax owed or refund due. Schedule 8812 supplements Form 1040, providing specific calculations for the Child Tax Credit, indicating its relationship as a detailed exploration of a particular section of the broader tax landscape covered by Form 1040.
Similar to Schedule 8812, Form W-2, provided by employers, plays a crucial role in completing tax returns. It reports an employee's annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld from their paycheck. While W-2 forms directly feed into the information required for Form 1040, Schedule 8812 delineates the eligibility and credit amount for qualifying children, showcasing how various forms combine to provide a comprehensive view of an individual’s tax responsibilities and benefits.
Schedule EIC (Earned Income Credit) is another document that complements the purpose of Schedule 8812 by focusing on a specific tax credit. While Schedule 8812 deals with tax credits for those with qualifying children, Schedule EIC is designed for low- to moderate-income workers and families, particularly those with children, to reduce their tax liability or increase their refund. Both schedules serve to navigate the complex pathways of tax credits, yet they target different aspects of taxpayer support.
Form 8863, Education Credits (American Opportunity and Lifetime Learning Credits), is akin to Schedule 8812 in that it pertains to a specific tax benefit, in this case, education-related. Taxpayers use Form 8863 to calculate and claim credits for education expenses paid for themselves, a spouse, or dependents. This mirrors the structured approach of Schedule 8812, which focuses on outlining the child tax credit rather than educational expenses, highlighting the tailored nature of various tax documents to specific financial scenarios.
The Child and Dependent Care Expenses Form, or Form 2441, also shares similarities with Schedule 8812. Both forms are designed to assist taxpayers in claiming credits related to the care of qualifying individuals. However, while Schedule 8812 is focused on the Child Tax Credit, Form 2441 helps taxpayers calculate the credit for child and dependent care expenses necessary for employment. This delineation between the forms underlines the IRS's segmentation of tax benefits based on the nature of the expenses and the beneficiaries involved.
Form 8962, the Premium Tax Credit (PTC) form, is used to calculate the premium tax credit and reconcile any advance payments of the credit. Like Schedule 8812, Form 8962 caters to a specific group of taxpayers—those who have purchased health insurance through the marketplace. Both documents serve to ensure that eligible taxpayers receive the proper tax credits, be it for health insurance through Form 8962 or child-related expenses through Schedule 8812, emphasizing the targeted approach of the IRS in administering tax benefits.
Lastly, the Adoption Credit Form 8839 bears resemblance to Schedule 8812 by offering tax relief to families with specific circumstances. This time, the focus is on providing financial relief for those who have incurred adoption expenses. Similar to how Schedule 8812 assists taxpayers in claiming credits for dependent children, Form 8839 aids in recouping some of the substantial costs associated with adoption. Both forms underscore the IRS’s efforts to support families through tax relief mechanisms tailored to their unique life events.
Dos and Don'ts
Filling out the IRS Schedule 8812 1040 form, also known as the form for the Additional Child Tax Credit, requires careful attention to detail and adherence to IRS guidelines. To ensure accuracy and compliance, here are key dos and don'ts to consider:
Do:
- Ensure you meet eligibility requirements before filling out Schedule 8812. Review the criteria for the Child Tax Credit to confirm your eligibility, including age, relationship, support, dependent status, citizenship, and residence tests.
- Use the correct tax year's form. Tax laws and forms can change annually, so it's crucial to use the most up-to-date version of Schedule 8812 to ensure compliance with current tax codes.
- Gather all necessary documentation such as your child’s Social Security number and proof of residency. This documentation is essential for verifying the child’s eligibility for the credit.
- Seek guidance if needed. If you're unsure about any part of the form or your eligibility, consult a tax professional or utilize IRS resources. Accurate completion of the form can help avoid processing delays or potential audits.
Don't:
- Overlook the importance of accurately reporting your income. The amount of the Additional Child Tax Credit you can claim may be affected by your adjusted gross income. Reporting inaccurate income figures can lead to errors in your credit calculation.
- Forget to include the Social Security numbers for all qualifying children. Each child you claim must have a valid Social Security number that you must report on Schedule 8812.
- Misinterpret eligibility rules. Ensure you understand the criteria for qualifying children, including age limits and residency requirements, to avoid mistakenly claiming ineligible dependents.
- Delay filing due to confusion or uncertainty. Procrastination can lead to rushed submissions, which can increase the risk of errors. Start the process early to give yourself ample time to fill out the form accurately or seek help if necessary.
Misconceptions
The IRS Schedule 8812, often associated with Form 1040, is a document that frequently becomes entangled in myths and misconceptions, leading to confusion and potential errors when taxpayers attempt to claim their deserved credits. Exploring these misunderstandings can shed light on the correct approach to utilizing this form and ensure individuals maximize their eligible tax benefits while remaining compliant with tax laws.
It's only for low-income families: A common misconception is that IRS Schedule 8812 is exclusively designed for low-income families. While it's true that the form is primarily used to calculate the Additional Child Tax Credit, which benefits many lower-income taxpayers, it's important to note that middle-class families can also qualify for this credit, depending on their specific circumstances and income levels.
You must owe taxes to benefit from it: Contrary to what some may believe, you do not need to owe taxes to benefit from the Additional Child Tax Credit facilitated through Schedule 8812. If the amount of the Child Tax Credit exceeds the amount of tax you owe, the excess amount may be refundable via the Additional Child Tax Credit, thus potentially offering a refund even if you do not owe taxes.
Only biological parents can file it: Another common myth is that only biological parents are eligible to file Schedule 8812. However, stepparents, grandparents, foster parents, or siblings who provide more than half of a child's support and meet other IRS criteria may also be eligible to claim the credit, provided the child lived with them for more than half of the tax year.
Filing is the same for every taxpayer: The process and benefit of filing Schedule 8812 can vary significantly among taxpayers depending on numerous factors, including their income, filing status, number of qualifying children, and other tax credits claimed. It's a personalized calculation that reflects an individual's or family's unique tax situation.
There's no limit on the number of children you can claim: While it might seem that the more qualifying children you have, the greater the credit you can claim, the IRS imposes limits on the number of children for whom the credit can be claimed. The credit amount begins to phase out at certain income thresholds, which are updated annually for inflation.
It's a one-size-fits-all form: Schedule 8812 is not a universal form that applies uniformly to all who attempt to claim the Additional Child Tax Credit. Taxpayers must meet specific eligibility requirements, complete several calculations, and may need to provide additional supporting documentation to claim the credit accurately.
Filing it guarantees a larger refund: While filing Schedule 8812 can indeed increase a taxpayer's refund if they are eligible for the Additional Child Tax Credit, it does not guarantee a larger refund in every case. The actual impact on a taxpayer’s refund amount depends on their overall tax situation, including total income, deductions, and credits claimed.
Understanding the truths behind these misconceptions about IRS Schedule 8812 can empower taxpayers to navigate their tax obligations more confidently and accurately, potentially unlocking benefits they might otherwise have overlooked.
Key takeaways
The IRS Schedule 8812 form, associated with the 1040 individual income tax return, is essential for taxpayers who wish to claim the Additional Child Tax Credit (ACTC). Here are seven key takeaways to understand when filling out and using this form:
- Eligibility Requirements: To use Schedule 8812, taxpayers must first establish their eligibility. This form is specifically designed for those who have dependents and are eligible to claim the Child Tax Credit (CTC) or the Additional Child Tax Credit.
- Understanding the Child Tax Credit: The Child Tax Credit is a vital element for taxpayers with dependent children. Schedule 8812 is used to calculate the ACTC, which may be available to families who do not owe any taxes and, therefore, cannot benefit fully from the non-refundable CTC.
- Information Gathering: Before filling out the form, gather all necessary information related to your dependents. This includes Social Security numbers, the amount of income earned, and any child care expenses. This step is crucial for accurately completing your tax return.
- Filling Out the Form: Schedule 8812 consists of parts that must be filled out, depending on individual circumstances. Taxpayers should carefully read each section and provide the required information to determine their eligibility for the ACTC.
- Calculating the Credit: The form comes with detailed instructions that guide taxpayers through the process of calculating their potential credit. It is important to follow these instructions precisely to ensure an accurate calculation of the ACTC.
- Impact on Your Refund: Claiming the ACTC can significantly increase a taxpayer's refund. This highlights the importance of accurately completing Schedule 8812 and understanding how it affects the overall tax situation.
- Professional Advice: Considering the complexities associated with tax forms and credits, seeking advice from a tax professional is recommended. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation, ensuring that you maximize your benefits while remaining compliant with tax laws.
Correctly filling out and understanding the implications of the IRS Schedule 8812 can have a significant impact on a taxpayer's financial situation. By following these key takeaways, taxpayers can confidently navigate their way through the process of claiming the Additional Child Tax Credit.
Popular PDF Documents
Total Ordinary Dividends Vs Qualified Dividends - Clarifications on the instructions for line 11a to ensure accurate completion of the worksheet.
Addendum Meaning in Real Estate - The document is designed to be attached and form part of an existing purchase and sale contract, clearly stating the terms related to personal property transfer.
What Is 990 Tax Form - By allowing for the detailed description of governance structures and routines, the form supports a narrative of effective and responsible management.