Get IRS 911 Form
For individuals and businesses navigating the complexities of tax issues, the IRS 911 form serves as a critical tool for seeking guidance and resolution. Designed to facilitate access to the Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS), this form acts as a bridge for taxpayers who find themselves facing significant hardships or systemic problems with the Internal Revenue Service. Whether it is a matter of urgency that impedes one's ability to meet basic living expenses or a need for assistance in resolving tax problems that haven't been addressed through normal IRS channels, the IRS 911 form plays a pivotal role. By providing an avenue for direct assistance, the form ensures that individuals and entities can seek help when all other options seem exhausted. The process of filling out and submitting the form is designed to be straightforward, aiming to alleviate rather than add to the taxpayer's burdens. In essence, the IRS 911 form embodies the principle of taxpayer rights and access to support, paving the way for a more streamlined and less stressful resolution of tax-related issues.
IRS 911 Example
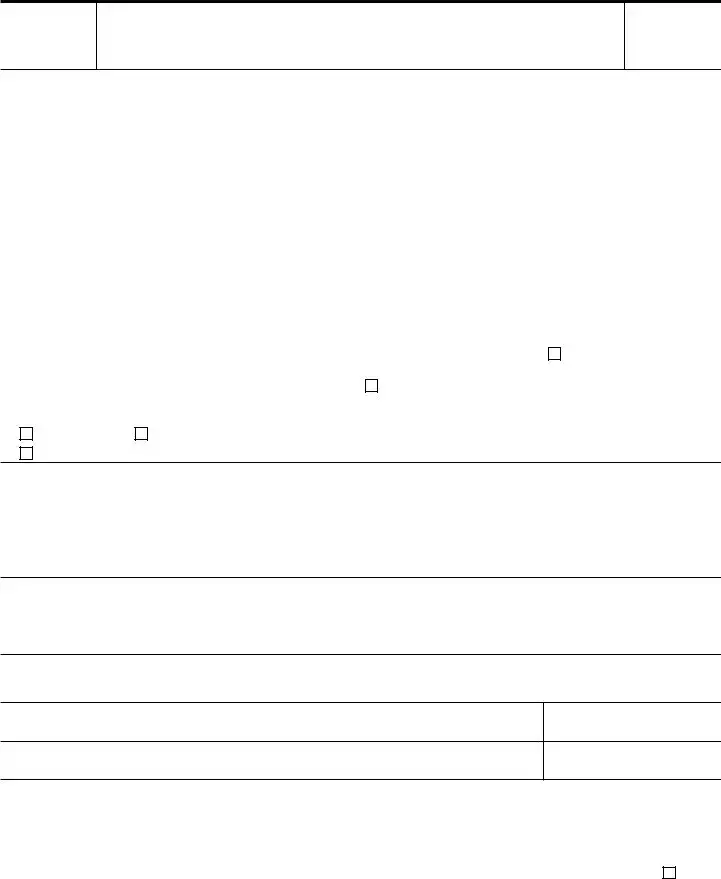
Form 911
(May 2019)
Department of the Treasury - Internal Revenue Service
Request for Taxpayer Advocate Service Assistance
(And Application for Taxpayer Assistance Order)
OMB Number
Section I – Taxpayer Information (See Pages 3 and 4 for Form 911 Filing Requirements and Instructions for Completing this Form.)
1a. |
Your name as shown on tax return |
1b. Taxpayer Identifying Number (SSN, ITIN, EIN) |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2a. |
Spouse's name as shown on tax return (if applicable) |
2b. Spouse's Taxpayer Identifying Number (SSN, ITIN) |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3a. |
Your current street address (Number, Street, & Apt. Number) |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3b. |
City |
|
|
3c. State (or Foreign Country) |
3d. ZIP code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Fax number (if applicable) |
|
5. Email address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
6. Tax form number (1040, 941, 720, etc.) |
7. Tax year(s) or period(s) |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
8. Person to contact if Section II is not being used |
9a. Daytime phone number |
9b. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Check here if you consent to have |
|
|
|
|
|
|
confidential information about your |
|
10. |
Best time to call |
|
|
Check if Cell Phone |
tax issue left on your answering |
|
|
|
|
|
machine or voice message at this |
||
|
|
|
|
|
number. |
|
11. |
Preferred language (if applicable) |
|
|
|
||
|
TTY/TDD Line |
Interpreter needed - Specify language other than English (including sign language) |
||||
|
Other (please specify) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12a. Please describe the tax issue you are experiencing and any difficulties it may be creating
(If more space is needed, attach additional sheets.) (See instructions for completing Lines 12a and 12b)
12b. Please describe the relief/assistance you are requesting (If more space is needed, attach additional sheets.)
I understand that Taxpayer Advocate Service employees may contact third parties in order to respond to this request and I authorize such contacts to be made. Further, by authorizing the Taxpayer Advocate Service to contact third parties, I understand that I will not receive notice, pursuant to section 7602(c) of the Internal Revenue Code, of third parties contacted in connection with this request.
13a. Signature of Taxpayer or Corporate Officer, and title, if applicable
13b. Date signed
14a. Signature of spouse
14b. Date signed
Section II – Representative Information (Attach Form 2848 if not already on file with the IRS.)
1. |
Name of authorized representative |
|
2. |
Centralized Authorization File (CAF) number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
Current mailing address |
|
4. |
Daytime phone number |
Check if |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cell Phone |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
Fax number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. |
Signature of representative |
|
|
|
7. Date signed |
|
|
|
|
||
Catalog Number 16965S |
www.irs.gov |
Form 911 (Rev. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Page 2 |
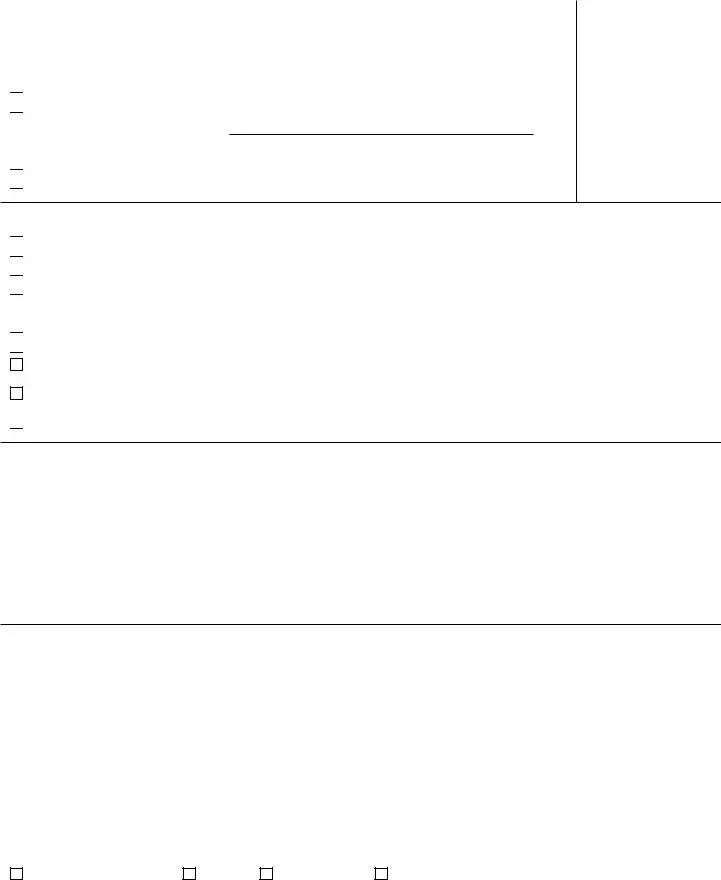
Section III – Initiating Employee Information (Section III is to be completed by the IRS only) |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
Taxpayer name |
|
|
Taxpayer Identifying Number (TIN) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
Name of employee |
2. Phone number |
3a. Function |
3b. Operating division |
4. |
Organization code no. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
How identified and received (Check the appropriate box) |
|
6. |
IRS received date |
||
IRS Function identified issue as meeting Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS) criteria

 (r) Functional referral (Function identified taxpayer issue as meeting TAS criteria)
(r) Functional referral (Function identified taxpayer issue as meeting TAS criteria)

 (x) Congressional correspondence/inquiry not addressed to TAS but referred for TAS handling
(x) Congressional correspondence/inquiry not addressed to TAS but referred for TAS handling
Name of Senator/Representative
Taxpayer or Representative requested TAS assistance

 (n) Taxpayer or representative called into a National Taxpayer Advocate (NTA)
(n) Taxpayer or representative called into a National Taxpayer Advocate (NTA)

 (s) Functional referral (taxpayer or representative specifically requested TAS assistance)
(s) Functional referral (taxpayer or representative specifically requested TAS assistance)
7.TAS criteria (Check the appropriate box. NOTE: Checkbox 9 is for TAS Use Only)

 (1) The taxpayer is experiencing economic harm or is about to suffer economic harm.
(1) The taxpayer is experiencing economic harm or is about to suffer economic harm.

 (2) The taxpayer is facing an immediate threat of adverse action.
(2) The taxpayer is facing an immediate threat of adverse action.

 (3) The taxpayer will incur significant costs if relief is not granted (including fees for professional representation).
(3) The taxpayer will incur significant costs if relief is not granted (including fees for professional representation).

 (4) The taxpayer will suffer irreparable injury or
(4) The taxpayer will suffer irreparable injury or
(if any items

 (5) The taxpayer has experienced a delay of more than 30 days to resolve a tax account problem.
(5) The taxpayer has experienced a delay of more than 30 days to resolve a tax account problem.

 (6) The taxpayer did not receive a response or resolution to their problem or inquiry by the date promised.
(6) The taxpayer did not receive a response or resolution to their problem or inquiry by the date promised.
(7)A system or procedure has either failed to operate as intended, or failed to resolve the taxpayer's problem or dispute within the IRS.
(8)The manner in which the tax laws are being administered raise considerations of equity, or have impaired or will impair the taxpayer's rights.

 (9) The NTA determines compelling public policy warrants assistance to an individual or group of taxpayers (TAS Use Only)
(9) The NTA determines compelling public policy warrants assistance to an individual or group of taxpayers (TAS Use Only)
8.What action(s) did you take to help resolve the issue? (This block MUST be completed by the initiating employee)
If you were unable to resolve the issue, state the reason why (if applicable)
9.Provide a description of the Taxpayer's situation, and where appropriate, explain the circumstances that are creating the economic burden and how the Taxpayer could be adversely affected if the requested assistance is not provided
(This block MUST be completed by the initiating employee)
10. How did the taxpayer learn about the Taxpayer Advocate Service |
|
|
||
IRS Forms or Publications |
Media |
IRS Employee |
Other (please specify) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Catalog Number 16965S |
|
www.irs.gov |
|
Form 911 (Rev. |

Page 3
Instructions for completing Form 911
Form 911 Filing Requirements
The Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS) is an independent organization within the IRS that helps taxpayers and protects taxpayer rights. We can help you resolve problems you can’t resolve with the IRS. And our service is free. TAS can help you if:
•Your problem is causing financial difficulty for you, your family, or your business.
•You face (or your business is facing) an immediate threat of adverse action.
•You’ve tried repeatedly to contact the IRS but no one has responded, or the IRS hasn’t responded by the date promised.
TAS will generally ask the IRS to stop certain activities while your request for assistance is pending (for example, lien filings, levies, and
seizures).
Where to Send this Form:
•The quickest method is Fax. TAS has at least one office in every state, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico. Submit this request to the TAS office in your state or city. You can find the fax number in the government listings in your local telephone directory, on our website at www.taxpayeradvocate.irs.gov, or in Publication 1546, Taxpayer Advocate Service - Your Voice at the IRS.
•You also can mail this form. You can find the mailing address and phone number (voice) of your local Taxpayer Advocate office in your phone book, on our website, and in Pub. 1546, or get this information by calling our
•Are you sending the form from overseas? Fax it to
•Please be sure to fill out the form completely and submit it to the TAS office nearest you so we can work your issue as soon as possible.
What Happens Next?
If you don't hear from us within one week of submitting Form 911, please call the TAS office where you sent your request. You can find
the number at www.taxpayeradvocate.irs.gov.
Important Notes: Please be aware that by submitting this form, you are authorizing TAS to contact third parties as necessary to respond to your request, and you may not receive further notice about these contacts. For more information see IRC 7602(c).
Caution: TAS will not consider frivolous arguments raised on this form. You can find examples of frivolous arguments in Publication 2105, Why do I have to Pay Taxes? If you use this form to raise frivolous arguments, you may be subject to a penalty of $5,000.
Paperwork Reduction Act Notice: We ask for the information on this form to carry out the Internal Revenue laws of the United States. Your response is voluntary. You are not required to provide the information requested on a form that is subject to the Paperwork Reduction Act unless the form displays a valid OMB control number. Books or records relating to a form or its instructions must be retained as long as their contents may become material in the administration of any Internal Revenue law. Generally, tax returns and return information are confidential, as required by Code section 6103. Although the time needed to complete this form may vary depending on individual circumstances, the estimated average time is 30 minutes.
Should you have comments concerning the accuracy of this time estimate or suggestions for making this form simpler, please write to: Internal Revenue Service, Tax Products Coordinating Committee, Room 6406, 1111 Constitution Ave. NW, Washington, DC 20224.
Instructions for Section I
1a. Enter your name as shown on the tax return that relates to this request for assistance.
1b. Enter your Taxpayer Identifying Number. If you're an individual this will be either a Social Security Number (SSN) or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN). If you're a business entity this will be your Employer Identification Number (EIN) (e.g. a
partnership, corporation, trust or
2a. Enter your spouse's name (if applicable) if this request relates to a jointly filed return.
2b. Enter your spouse's Taxpayer Identifying Number (SSN or ITIN) if this request relates to a jointly filed return.
4.Enter your fax number, including the area code.
5.Enter your email address. We'll only contact you by email if we can't reach you by phone and your issue appears to be time- sensitive. We will not, however, use your email address to discuss the specifics of your case.
6.Enter the number of the Federal tax return or form that relates to this request. For example, an individual taxpayer with an income tax issue would enter Form 1040.
7.Enter the quarterly, annual, or other tax year or period that relates to this request. For example, if this request involves an income tax issue, enter the calendar or fiscal year, if an employment tax issue, enter the calendar quarter.
Instructions for Section I ► continue on the next page
Catalog Number 16965S |
www.irs.gov |
Form 911 (Rev. |

Page 4
Instructions for Section I - (Continued from Page 3)
8.Enter the name of the individual we should contact if Section II is not being used. For partnerships, corporations, trusts, etc., enter the name of the individual authorized to act on the entity's behalf. If the contact person is not the taxpayer or other authorized individual, please see the Instructions for Section II.
9a. Enter your daytime telephone number, including the area code. If this is a cell phone number, please check the box.
9b. If you have an answering machine or voice mail at this number and you consent to TAS leaving confidential information about your tax issue at this number, please check the box. You are not obligated to have information about your tax issue left at this number. If other individuals have access to the answering machine or the voice mail and you do not wish for them to receive any confidential information about your tax issue, please do not check the box.
10.Indicate the best time to call you. Please specify A.M. or P.M. hours.
11.Indicate any special communication needs (such as sign language). Specify any language other than English.
12a. Please describe the tax issue you are experiencing and any difficulties it may be creating. Specify the actions that the IRS has taken (or not taken) to resolve the issue. If the issue involves an IRS delay of more than 30 days in resolving your issue, indicate the date you first contacted the IRS for assistance. See Section III for a specific list of TAS criteria.
12b. Please describe the relief/assistance you are requesting. Specify the action you want taken and believe necessary to resolve the issue. Furnish any documentation you believe would assist us in resolving the issue.
Note: The signing of this request allows the IRS by law to suspend any applicable statutory periods of limitation relating to the assessment or collection of taxes. However, it does not suspend any applicable periods for you to perform acts related to assessment or collection, such as petitioning the Tax Court for redetermination of a deficiency or requesting a Collection Due Process hearing.
Instructions for Section II
Taxpayers: If you wish to have a representative act on your behalf, you must give him/her power of attorney or tax information authorization for the tax return(s) and period(s) involved. For additional information see Form 2848, Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative, or Form 8821, Tax Information Authorization, and the accompanying instructions.
Representatives: If you are an authorized representative submitting this request on behalf of the taxpayer identified in Section I, complete Blocks 1 through 7 of Section II. Attach a copy of Form 2848, Form 8821, or other power of attorney. Enter your Centralized Authorization File (CAF) number in Block 2 of Section II. The CAF number is the unique number that the IRS assigns to a representative after Form 2848 or Form 8821 is filed with an IRS office.
Note: Form 8821 does not authorize your appointee to advocate your position with respect to the Federal tax laws; to execute waivers, consents, or closing agreements; or to otherwise represent you before the IRS. Form 8821 does authorize anyone you designate to inspect and/or receive your confidential tax information in any office of the IRS, for the type of tax and tax periods you list on
Form 8821.
Instructions for Section III (For IRS Use Only) Please complete this section in its entirety.
Enter the taxpayer's name and taxpayer identification number from the first page of this form.
1.Enter your name.
2.Enter your phone number.
3a. Enter your Function (e.g., ACS, Collection, Examination, Customer Service, etc.).
3b. Enter your Operating Division (W&I, SB/SE, LB&I, or TE/GE).
4.Enter the Organization code number for your office (e.g., 18 for AUSC, 95 for Los Angeles).
5.Check the appropriate box that best reflects how the need for TAS assistance was identified. For example, did taxpayer or representative call or write to an IRS function or TAS.
6.Enter the date the taxpayer or representative called or visited an IRS office to request TAS assistance. Or enter the date when the IRS received the Congressional correspondence/inquiry or a written request for TAS assistance from the taxpayer or representative. If the IRS identified the taxpayer's issue as meeting TAS criteria, enter the date this determination was made.
7.Check the box that best describes the reason TAS assistance is requested. Box 9 is for TAS Use Only.
8.State the action(s) you took to help resolve the taxpayer's issue. State the reason(s) that prevented you from resolving the taxpayer's issue. For example, levy proceeds cannot be returned because they were already applied to a valid liability; an overpayment cannot be refunded because the statutory period for issuing a refund expired; or current law precludes a specific interest abatement.
9.Provide a description of the taxpayer's situation, and where appropriate, explain the circumstances that are creating the economic burden and how the taxpayer could be adversely affected if the requested assistance is not provided.
10.Ask the taxpayer how he or she learned about the TAS and indicate the response here.
Catalog Number 16965S |
www.irs.gov |
Form 911 (Rev. |
Document Specifics
| Fact Number | Detail |
|---|---|
| 1 | The IRS Form 911 is officially titled "Request for Taxpayer Advocate Service Assistance (And Application for Taxpayer Assistance Order)." |
| 2 | This form is used by taxpayers to request help from the Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS) when they are experiencing financial difficulties, or when the IRS's system is not functioning as it should. |
| 3 | Upon submission, the taxpayer's issue is assigned to an advocate who will work with them directly to address and resolve their concerns. |
| 4 | Filing this form does not guarantee immediate resolution but ensures that the taxpayer's issue is formally recognized and addressed by the TAS. |
| 5 | TAS services are free for taxpayers, designed as a last-resort option for those who have tried using normal IRS channels without success. |
| 6 | There are no geographical restrictions for using the IRS Form 911, meaning it can be filed by taxpayers living anywhere in the United States. |
| 7 | The form can be submitted either by mail, fax, or in person at a local TAS office, providing flexibility for how taxpayers can seek assistance. |
Guide to Writing IRS 911
When a taxpayer is experiencing significant hardship or issues with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and standard channels have not been effective in resolving the matter, filing Form 911, Request for Taxpayer Advocate Service Assistance (And Application for Taxpayer Assistance Order), can be a critical step. This form serves as a request for assistance from the Taxpayer Advocate Service, an independent organization within the IRS, aimed at helping taxpayers resolve their problems. Properly completing the form is essential for the request to be considered. Follow the steps below carefully to ensure your submission is accurate and complete.
- Download the latest version of Form 911 directly from the IRS website to ensure you have the most up-to-date form.
- Begin by providing your personal information in the sections provided, including your name, social security number or taxpayer identification number, and your current address.
- Indicate your preferred method of contact by filling in your telephone number(s) and the best time to reach you.
- Provide a detailed explanation of your tax issue and the hardship it is causing. Be as specific as possible to help the Taxpayer Advocate Service understand your situation and how they can assist you.
- List the tax years or periods involved. This information helps in identifying and reviewing your case accurately.
- Describe the actions you have already taken to try and resolve the issue with the IRS, including any previous attempts to contact them or solutions you have attempted.
- Specify the type of assistance you are seeking. Detail what resolution you believe would be fair, such as an expedited process, abatement of penalties, or a payment plan.
- Sign and date the form. If a representative is filling out the form on your behalf, make sure they provide their information and signature as well.
Once you have completed and reviewed the form for accuracy and completeness, submit it following the instructions provided on the form itself. The IRS provides several submission options, including mail and fax. After submission, the Taxpayer Advocate Service will review your request and contact you for further information or to discuss the next steps. Remember, the goal of the Taxpayer Advocate Service is to assist taxpayers in resolving their problems with the IRS, and providing thorough and accurate information on Form 911 can facilitate this process.
Understanding IRS 911
-
What is the IRS 911 Form?
The IRS 911 Form, known as the Request for Taxpayer Advocate Service Assistance (And Application for Taxpayer Assistance Order), is a document taxpayers use to seek help from the Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS). The TAS is an independent organization within the IRS designed to help taxpayers resolve problems they have been unable to resolve through regular IRS channels.
-
Who is eligible to use the IRS 911 Form?
Any taxpayer facing significant hardship, confusion, or difficulty with their taxes may use Form 911. This includes individuals, businesses, and organizations that have been unable to resolve their issues through traditional IRS customer service avenues.
-
When should you file an IRS 911 Form?
You should file a Form 911 when you believe you are experiencing economic harm or significant systemic delays, or if you feel the IRS procedures have not resolved your tax issue. It is particularly applicable when you need immediate action to avoid detrimental consequences.
-
How do you file an IRS 911 Form?
You can file Form 911 by faxing or mailing it to your local Taxpayer Advocate Service office. Additionally, you can call the TAS, and a representative may complete the form on your behalf during the call. It's important to provide as much detail as possible about your situation to expedite the process.
-
What information is needed to complete Form 911?
To complete Form 911, you will need your personal information, including your name, address, and Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN). You also need to describe your tax issue and the efforts you've made to resolve it with the IRS. Furthermore, detailing the type of assistance you're seeking from the TAS is necessary.
-
Is there a fee to file Form 911?
There is no fee to file Form 911. The services provided by the Taxpayer Advocate Service are free to taxpayers.
-
What happens after you file Form 911?
After filing Form 911, a case advocate from the Taxpayer Advocate Service will review your situation. They may contact you for additional information. The advocate will then work with you and the IRS to resolve your tax issue, keeping you updated on the progress.
-
Can Form 911 be filed on behalf of someone else?
Yes, Form 911 can be filed on behalf of another person if you have a valid Power of Attorney (Form 2848) or if you are a legally designated representative. You will need to attach the appropriate documentation establishing your authority to act on behalf of the taxpayer.
-
How long does it take for the Taxpayer Advocate Service to respond to a Form 911 request?
The response time for a Form 911 request can vary based on the complexity of the case and the current workload of the Taxpayer Advocate Service. However, the TAS aims to contact taxpayers within a few days of receiving the form to begin addressing their concerns.
Common mistakes
Filling out the IRS 911 form, a request for Taxpayer Advocate Service Assistance (And Application for Taxpayer Assistance Order), is an important step for taxpayers seeking help with resolving tax issues. However, several common mistakes can hinder the process, leading to delays or unsatisfactory resolutions. Understanding and avoiding these errors can significantly improve the chances of a favorable outcome.
Not providing complete information: One of the most frequent errors is leaving parts of the form blank. Each question is designed to gather necessary details about your situation. Incomplete forms can lead to delays as the IRS seeks additional information.
Failing to clearly describe the tax issue: A vague or incomplete description of your problem can make it difficult for the Taxpayer Advocate Service to understand what you need. Be as detailed and clear as possible to avoid misunderstandings.
Incorrectly identifying the tax years involved: Ensure the tax years in question are accurately stated. Mixing up dates or omitting relevant years can complicate the resolution process.
Omitting contact information: Your phone number, email address, and mailing address are crucial for communication. Missing or incorrect contact details can prevent the Taxpayer Advocate Service from reaching you with questions or updates.
Not signing the form: An unsigned IRS 911 form is considered incomplete and will not be processed. Ensure you sign the form before submission to validate your request.
Using outdated forms: The IRS periodically updates its forms. Submitting an outdated version of IRS 911 can result in your request being rejected. Always check the IRS website for the most current form.
To avoid these mistakes:
Review the form thoroughly before and after filling it out to ensure all fields are completed.
Provide a detailed explanation of your tax issue, including specific dates and figures, if applicable.
Double-check the tax years you mention to ensure they are accurate.
Confirm your contact information is correct and up-to-date.
Remember to sign the form. If you're filing jointly, both parties must sign.
Always use the latest version of the form, which you can find on the IRS website.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can streamline the process of getting the help you need from the Taxpayer Advocate Service.
Documents used along the form
When individuals face significant challenges or hardships that prevent them from resolving tax issues, the IRS Form 911, Request for Taxpayer Advocate Service Assistance (And Application for Taxpayer Assistance Order), becomes a crucial tool. This form is a plea for special help from the IRS's Taxpayer Advocate Service, aimed at those who need immediate assistance. However, this form doesn't stand alone. Several other documents often accompany it to provide a clearer picture of the taxpayer's situation, ensuring the IRS has all the necessary information to assist effectively.
- Form 2848, Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative: This document is essential if you're having a representative act on your behalf in matters with the IRS. It grants them the authority to receive your confidential tax information and to perform acts like signing agreements with the IRS on your behalf.
- Form 8821, Tax Information Authorization: Similar to Form 2848, this form allows someone else to access your tax records from the IRS. However, unlike the power of attorney, it doesn't allow the individual to represent you before the IRS. It's commonly used by taxpayers who need someone to gather information for them but don't require representation.
- Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return: Often, issues requiring the help of the Taxpayer Advocate Service stem from problems with a taxpayer's income tax return. Including the most recent Form 1040 can help clarify these issues, providing a foundation for the taxpayer's case.
- Form 433-A, Collection Information Statement for Wage Earners and Self-Employed Individuals: For cases involving payment plans or offers in compromise, this detailed financial statement is vital. It gives the IRS a snapshot of the taxpayer's financial situation, including income, expenses, and assets.
- Form 4506, Request for Copy of Tax Return: This form is useful if you need to provide a previous year's tax return but don't have a copy. It's particularly relevant when resolving tax issues that span multiple years, allowing both the taxpayer and the IRS to review what was reported in prior years.
Accompanying the IRS Form 911 with these documents can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the Taxpayer Advocate Service's assistance. It's a proactive approach, supplying the information needed to understand your situation better and act on your behalf. Remember, each situation is unique, so it might be helpful to consult with a tax professional to determine exactly which documents will support your case most effectively.
Similar forms
The IRS 911 form is a request for Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS) Assistance (And Application for Taxpayer Assistance Order), designed to help taxpayers who are experiencing significant hardships. A similar document is the Form 843, "Claim for Refund and Request for Abatement." This form allows taxpayers to claim refunds or request the abatement of certain taxes, penalties, fees, and interest. Both forms are used to seek relief from financial difficulties, though the Form 843 is specifically used for seeking refunds or abatements, indicating a focused approach compared to the broad assistance requested through Form 911.
Another counterpart is the Form 9465, "Installment Agreement Request," through which taxpayers can request to make monthly installment payments if they cannot pay the full amount of taxes they owe. Like the IRS 911 form, Form 9465 is used by individuals facing financial strain, offering a structured solution to manage their tax liabilities over time, rather than immediate relief or direct intervention by the Taxpayer Advocate Service.
The Offer in Compromise (Form 656) is an agreement between the taxpayer and the IRS that settles a taxpayer’s tax liabilities for less than the full amount owed. It shares similarities with the IRS 911 form in that it provides a means for taxpayers to address overwhelming tax debts. However, while the Form 911 facilitates assistance and potential intervention by the TAS for a wide range of tax issues, the Form 656 specifically targets the reduction of the tax burden itself through negotiation, reflecting a more singular focus.
Form 2848, "Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative," allows taxpayers to authorize an individual, such as a lawyer or accountant, to represent them before the IRS. This form is similar to the IRS 911 form because it centers on the taxpayer's need for assistance in dealing with the IRS. However, Form 2848 deals specifically with representation rights, enabling the delegated individual to perform actions such as receiving confidential tax information or negotiating with the IRS on the taxpayer's behalf, unlike the broader help sought through Form 911.
Last, the Form 4506-T, "Request for Transcript of Tax Return," enables taxpayers to request past tax returns and tax account information. Though primarily a tool for obtaining records, it shares an underlying similarity with the IRS 911 form: both are utilized in situations where the taxpayer needs to ascertain or rectify their tax status. The Form 4506-T assists by providing access to factual tax return information, which can be critical for resolving disputes or issues that might lead to a taxpayer needing TAS assistance through Form 911.
Dos and Don'ts
Filling out IRS Form 911, which is the request for Taxpayer Advocate Service Assistance (And Application for Taxpayer Assistance Order), can be a pivotal step in resolving tax issues. Properly completing this form can ease the process considerably. Here are some dos and don’ts to keep in mind:
Do:- Provide complete and accurate information: Every section should be filled out with current and correct data to avoid delays.
- Explain the hardship clearly: Describe the financial hardship or the immediate need compelling you to seek assistance. Clarity and detail will help the IRS understand your situation better.
- Include necessary documentation: Attach any relevant documents that support your case. This could include notices from the IRS, prior correspondence, or proof of hardship.
- Review for errors: Before submitting, double-check your form for mistakes or omissions. This can prevent processing delays.
- Use the most current form: Ensure you're using the latest version of Form 911. The IRS occasionally updates forms, and using an outdated version can lead to your request being denied.
- Contact the Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS) for help: If you’re unsure about any part of the form or if your situation is complex, don’t hesitate to reach out for guidance.
- Leave sections blank: If a section does not apply, fill it with a “N/A” instead of leaving it empty. This shows you acknowledged every part of the form.
- Use the form for general tax help: Form 911 is specifically for individuals experiencing significant hardship or financial difficulties. It is not a general tax assistance form.
- Forget to sign and date: An unsigned or undated form will not be processed. Ensure you sign and date Form 911 before submitting.
- Ignore IRS notices: Continue to address any IRS notices you may receive even after submitting Form 911. Ignoring them can complicate your situation.
- Submit incomplete documentation: Failing to attach all necessary documents can delay the review process or lead to a denial of your request.
- Underestimate the importance of timely submission: Don’t wait until it’s too late. If you’re facing a deadline or immediate action is necessary, submit Form 911 as soon as possible.
Misconceptions
The IRS Form 911, officially known as the Request for Taxpayer Advocate Service Assistance (And Application for Taxpayer Assistance Order), often elicits confusion among taxpayers. This form plays a crucial role in resolving tax issues. However, several misconceptions surround its use and purpose. By dispelling these myths, taxpayers can better navigate their interactions with the IRS and make informed decisions about their tax situations.
- Misconception 1: The IRS Form 911 is only for emergencies.
While the form's number might suggest it's for urgent issues, it's actually designed to request assistance from the Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS) for a wide range of tax problems. Individuals and businesses can use this form when they face significant hardship, are dealing with IRS system issues, or need help in resolving tax problems that haven't been fixed through normal channels.
- Misconception 2: Filing Form 911 will lead to IRS audits.
Another common fear is that requesting help from the TAS by submitting Form 911 may flag the taxpayer for audits. This is not the case. The TAS's mission is to assist taxpayers in resolving their tax issues and to advocate for them within the IRS. Seeking help from the TAS will not increase the odds of an audit or result in retaliatory actions from the IRS.
- Misconception 3: Form 911 is a complicated process that requires a tax professional.
While dealing with tax issues can be daunting, the process of completing and submitting Form 911 is straightforward. The form asks for basic information about the taxpayer and a description of the tax problem and any hardship it's causing. Taxpayers can complete this form on their own, but they are also free to seek help from a tax professional if they prefer.
- Misconception 4: The Taxpayer Advocate Service charges fees for its services.
Some taxpayers hesitate to file Form 911 due to a belief that the TAS's services come with a cost. However, the TAS is an independent organization within the IRS designed to help taxpayers navigate and resolve issues at no charge. Its services include help with resolving tax problems, providing information about taxpayer rights, and helping to ensure that taxpayers are treated fairly under the law.
Key takeaways
The IRS Form 911, Request for Taxpayer Advocate Service Assistance (And Application for Taxpayer Assistance Order), is an important document for taxpayers seeking help with IRS-related issues that haven't been resolved through standard channels. Understanding how to fill out and use this form effectively is crucial for timely assistance. Below are seven key takeaways that taxpayers should keep in mind.
- Eligibility criteria: Taxpayers who are experiencing economic harm or significant system delays, or who need assistance in resolving tax problems that haven't been resolved through normal IRS channels, may qualify for assistance.
- Personal information is crucial: It's important to fill out all personal information accurately on the form, including your name, social security number or taxpayer identification number, and contact information. This ensures the Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS) can reach you without delay.
- Describe your issue clearly: Providing a clear and detailed description of your tax issue on the form is vital. Include specific details and any steps already taken to try to resolve the issue with the IRS. This helps the TAS understand the nature of your problem quickly.
- Indicate the relief sought: Be specific about the type of help you're seeking. Whether it's a resolution to a billing issue, penalty relief, or assistance in dealing with a tax lien, clearly stating your needs helps the TAS advocate on your behalf more effectively.
- Include relevant documentation: Submitting any relevant documentation along with your Form 911 can expedite the process. This may include notices from the IRS, previous correspondence, tax returns related to the issue, and any other documents that support your case.
- Understand TAS limitations: While the Taxpayer Advocate Service can assist with many issues, there are limitations. TAS typically doesn't handle cases that are already in litigation, under criminal investigation, or those that have been decided by the IRS Appeals Office. Knowing these limitations helps set realistic expectations.
- Submitting your form: You can submit your completed Form 911 directly to the Taxpayer Advocate Service either by mail or fax, or by calling your local TAS office to request assistance. Find your local TAS office's contact information on the IRS website to ensure your form is received by the correct office.
Utilizing the IRS Form 911 effectively can provide taxpayers with much needed assistance during challenging times. It's a vital tool for those who feel overwhelmed by IRS processes or who haven't found resolution through standard procedures.
Popular PDF Documents
U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return - Penalties can be imposed for late filing or failing to report full and accurate income and deductions on the form.
How to File Power of Attorney in California - The authorized representative on a 3520-PIT must be someone the taxpayer fully trusts, as they will have access to sensitive financial information.
