Get IRS 8853 Form
Navigating the complexities of tax documentation can be a daunting task, yet understanding the specifics of each form is crucial for meeting the Internal Revenue Service’s requirements and maximizing tax benefits. Among these forms, the IRS 8853 form stands out as a key document for individuals participating in Archer Medical Savings Accounts (MSAs) or long-term care insurance contracts. This form is instrumental in reporting contributions to an Archer MSA as well as the distribution of funds from those accounts. Furthermore, it details the tax deductions available for premiums paid on long-term care insurance. The form's sections are designed to provide clarity on how to accurately report these financial activities, which in turn helps taxpayers in making informed decisions regarding their healthcare finances. The proper completion and submission of this form can lead to significant tax advantages, reinforcing its importance in the tax filing process. With its specific focus, IRS 8853 is not applicable to everyone, but for those who do qualify, it serves as a critical tool for managing healthcare-related expenses within the framework of federal taxation.
IRS 8853 Example
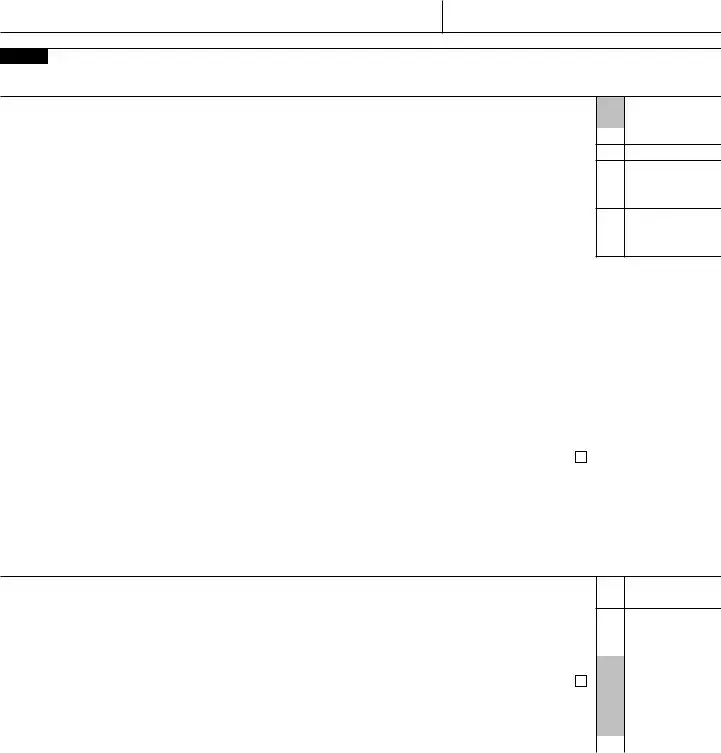
Form 8853 |
|
Archer MSAs and |
|
OMB No. |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
2021 |
||
Department of the Treasury |
|
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/Form8853 for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
|
|
▶ Attach to Form 1040, |
|
Attachment |
Internal Revenue Service (99) |
|
|
Sequence No. 39 |
|
Name(s) shown on return |
|
Social security number of MSA |
|
|
|
|
account holder. If both spouses |
|
|
|
|
have MSAs, see instructions ▶ |
|
|
Section A. Archer MSAs. If you have only a Medicare Advantage MSA, skip Section A and complete Section B.
Part I Archer MSA Contributions and Deductions. See instructions before completing this part. If you are filing jointly and both you and your spouse have high deductible health plans with
1 Total employer contributions to your Archer MSA(s) for 2021 |
1 |
|
2Archer MSA contributions you made for 2021, including those made from January 1, 2022, through
|
April 18, 2022, that were for 2021. Don’t include rollovers. See instructions |
3 |
Limitation from the Line 3 Limitation Chart and Worksheet in the instructions |
4Compensation (see instructions) from the employer maintaining the high deductible health plan. (If
health plan was established.) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5Archer MSA deduction. Enter the smallest of line 2, 3, or 4 here. Also include this amount on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Caution: If line 2 is more than line 5, you may have to pay an additional tax. See instructions.
2
3
4
5
Part II |
Archer MSA Distributions |
|
|
|
|
|
6a |
Total distributions you and your spouse received in 2021 from all Archer MSAs (see instructions) |
. . |
6a |
|
||
b Distributions included on line 6a that you rolled over to another Archer MSA or a health savings |
|
|
||||
|
account. Also include any excess contributions (and the earnings on those excess contributions) |
|
|
|||
|
included on line 6a that were withdrawn by the due date of your return. See instructions . . |
. |
. . |
6b |
|
|
c |
Subtract line 6b from line 6a |
. |
. . |
6c |
|
|
7 |
Unreimbursed qualified medical expenses (see instructions) |
. |
. . |
7 |
|
|
8 |
Taxable Archer MSA distributions. Subtract line 7 from line 6c. If zero or less, enter |
include |
|
|
||
|
this amount in the total on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 8e. On the dotted line next to Schedule 1 |
|
|
|||
|
(Form 1040), line 8e, enter “MSA” and the amount |
. |
. . |
8 |
|
|
9a |
If any of the distributions included on line 8 meet any of the Exceptions to the Additional 20% Tax |
|
|
|||
|
(see instructions), check here |
. |
▶ |
|
|
|
b Additional 20% tax (see instructions). Enter 20% (0.20) of the distributions included on line 8 that are |
|
|
||||
|
subject to the additional 20% tax. Also include this amount in the total on Schedule 2 (Form 1040), |
|
|
|||
|
line 17e |
. |
. . |
9b |
|
|
Section B. Medicare Advantage MSA Distributions. If you are filing jointly and both you and your spouse received distributions in 2021 from a Medicare Advantage MSA, complete a separate Section B for each spouse. See instructions.
10 |
Total distributions you received in 2021 from all Medicare Advantage MSAs (see instructions) . |
. . |
10 |
|
|
11 |
Unreimbursed qualified medical expenses (see instructions) |
. . |
11 |
|
|
12 |
Taxable Medicare Advantage MSA distributions. Subtract line 11 from line 10. If zero or less, enter |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|||
|
Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 8z, enter “Med MSA” and the amount |
. . |
12 |
|
|
13a |
If any of the distributions included on line 12 meet any of the Exceptions to the Additional 50% Tax |
|
|
||
|
(see instructions), check here |
▶ |
|
|
|
b Additional 50% tax. Enter 50% (0.50) of the distributions included on line 12 that are subject to the |
|
|
|||
|
additional 50% tax. See instructions for the amount to enter if you had a Medicare Advantage MSA |
|
|
||
|
at the end of 2020. Also include this amount in the total on Schedule 2 (Form 1040), line 17f . |
. . |
13b |
|
|
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see your tax return instructions. |
Cat. No. 24091H |
|
|
Form 8853 (2021) |
|
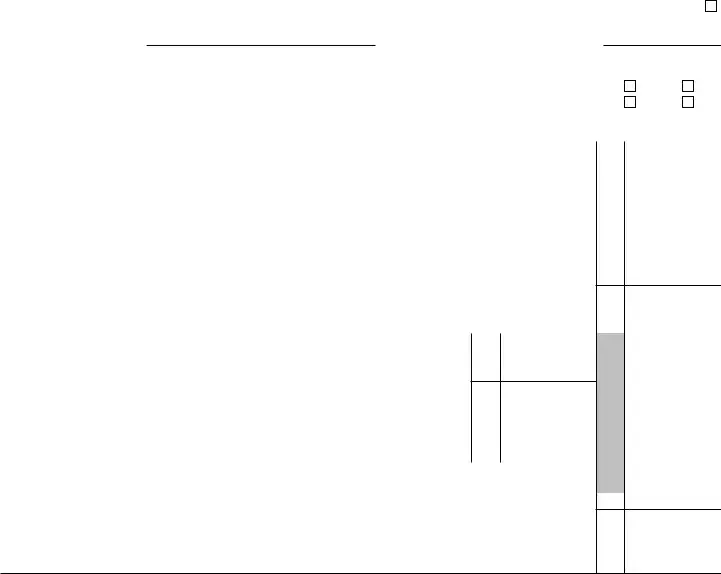
Form 8853 (2021) |
|
Attachment Sequence No. 39 |
Page 2 |
Name of policyholder (as shown on return) |
|
Social security number of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
policyholder ▶ |
|
|
|
||
Section C. |
|||
before completing this section. |
|
|
|
If more than one Section C is attached, check here . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. ▶ |
|
14a Name of insured ▶ |
b Social security number of insured ▶ |
|
|
15In 2021, did anyone other than you receive payments on a per diem or other periodic basis under a qualified LTC insurance contract covering the insured or receive accelerated death benefits under a life
insurance policy covering the insured? |
Yes |
No |
16 Was the insured a terminally ill individual? |
Yes |
No |
Note: If “Yes” and the only payments you received in 2021 were accelerated death benefits that were |
|
|
paid to you because the insured was terminally ill, skip lines 17 through 25 and enter |
|
|
17Gross LTC payments received on a per diem or other periodic basis. Enter the total of the amounts from box 1 of all Forms
box in box 3 is checked |
|
17 |
|
Caution: Don’t use lines 18 through 26 to figure the taxable amount of benefits paid under an LTC |
|
|
|
insurance contract that isn’t a qualified LTC insurance contract. Instead, if the benefits aren’t |
|
|
|
excludable from your income (for example, if the benefits aren’t paid for personal injuries or sickness |
|
|
|
through accident or health insurance), report the amount not excludable as income on Schedule 1 |
|
|
|
(Form 1040), line 8z or, for taxpayers filing Form |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 Enter the part of the amount on line 17 that is from qualified LTC insurance contracts |
18 |
19Accelerated death benefits received on a per diem or other periodic basis. Don’t include any amounts
|
you received because the insured was terminally ill. See instructions . . . . |
. . . . . . . |
19 |
|
20 |
Add lines 18 and 19 |
. . . . . . . |
20 |
|
|
Note: If you checked “Yes” on line 15 above, see Multiple Payees in the |
|
|
|
|
instructions before completing lines 21 through 25. |
|
|
|
21 |
Multiply $400 by the number of days in the LTC period |
21 |
|
|
22Costs incurred for qualified LTC services provided for the insured during the
|
LTC period (see instructions) |
22 |
|
23 |
Enter the larger of line 21 or line 22 |
23 |
|
24 |
Reimbursements for qualified LTC services provided for the insured during the |
|
|
|
LTC period |
24 |
|
|
Caution: If you received any reimbursements from LTC contracts issued |
|
|
|
before August 1, 1996, see instructions. |
|
|
25 |
Per diem limitation. Subtract line 24 from line 23 |
. . . . . . . |
25 |
26Taxable payments. Subtract line 25 from line 20. If zero or less, enter
Schedule NEC, line 12. On the dotted line next to Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 8z or, for taxpayers |
|
filing Form |
26 |
Form 8853 (2021)
Document Specifics
| Fact Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | The IRS 8853 form is officially titled "Archer MSAs and Long-Term Care Insurance Contracts". |
| 2 | This form is used to report contributions to an Archer MSA as well as to figure the deduction for Archer MSA contributions. |
| 3 | It also serves to report distributions from Archer MSAs or Medicare Advantage MSAs. |
| 4 | Additionally, the IRS 8853 form is used for reporting taxable payments from long-term care insurance contracts. |
| 5 | Filers must complete and attach this form to their Form 1040 or Form 1040-SR tax return. |
| 6 | The form requires detailed information about the insurance contract or MSA provider, including the name, address, and taxpayer identification number (TIN). |
| 7 | For distributions from an Archer MSA or Medicare Advantage MSA, the form helps determine if the amounts are taxable or not. |
| 8 | There are no state-specific versions of IRS Form 8853; it is a federal form processed by the Internal Revenue Service. |
| 9 | Instructions for completing and filing Form 8853 can be found on the official IRS website. |
Guide to Writing IRS 8853
Filling out the IRS 8853 form is a straightforward process, requiring careful attention to detail to ensure accuracy. After completion, this document plays a crucial role in the processing of specific tax situations related to health savings accounts and long-term care insurance contracts, among other things. Documenting these details accurately is pivotal for maintaining compliance and optimizing potential benefits. To guide through the procedure, follow the steps below, taking note to review each section thoroughly before proceeding to the next.
- Begin by gathering all necessary documentation, including Social Security numbers, Archer Medical Savings Account (MSA) contributions, and long-term care insurance contracts. Having these documents at hand will streamline the process.
- Enter the taxpayer's name and Social Security number at the top of the form, ensuring that they match the information on the taxpayer's social security card.
- For Archer MSAs, fill out Part I. This section requires information about contributions and distributions. Start by detailing the total amount contributed to the Archer MSA during the tax year in question.
- In the distributions section of Part I, report all amounts withdrawn from the Archer MSA. It's important to differentiate between used for qualified medical expenses and those that were not.
- Moving to Part II, if applicable, report details regarding long-term care (LTC) insurance contracts. This includes the total premiums paid that qualify for deduction and any benefits received under such contracts.
- For individuals with both an MSA and LTC insurance, ensure that both Part I and Part II are completed accurately, reflecting contributions, distributions, and relevant insurance information.
- Accurately calculate and report any taxable amounts in accordance with IRS instructions. Misreporting can lead to penalties or the need to file amended returns.
- Review the form thoroughly before signing. Errors or omissions could delay processing or affect tax liabilities and refunds.
- Attach the completed IRS 8853 form to the taxpayer's return. Ensure that any other required forms or documentation are also included before submission.
- Finally, submit the tax return with the attached IRS 8853 form to the appropriate IRS address. This will vary depending on the taxpayer's state and whether payments are included with the return.
Once the IRS 8853 form and the associated tax return are submitted, the next steps involve waiting for the IRS to process the submission. During this period, it is wise to keep a copy of the submitted documents for personal records. The IRS may contact individuals for additional information if necessary, so being prepared can expedite any follow-up required. Patience is key, as processing times can vary.
Understanding IRS 8853
-
What is IRS Form 8853?
IRS Form 8853 is a tax document used to report contributions to and distributions from a Medical Savings Account (MSA) or Long-Term Care Insurance contracts. Taxpayers use this form to calculate and report the deductible contributions to their MSA and to report the taxable distributions. It is also utilized to provide information regarding the taxpayer’s long-term care insurance contracts.
-
Who needs to file Form 8853?
Form 8853 must be filed by individuals who have an Archer MSA, Medicare Advantage MSA, or those who are policyholders of a tax-qualified long-term care insurance contract. If you’ve made contributions to, or received distributions from, any of these accounts or policies during the tax year, you’re required to file Form 8853 with your tax return.
-
When is the deadline to file Form 8853?
The deadline to file Form 8853 coincides with your federal income tax return deadline, typically April 15. If you request an extension for your tax return, the same extension applies to Form 8853.
-
How do I obtain Form 8853?
You can download Form 8853 directly from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website. It is available in PDF format and can be filled out electronically or printed and filled out by hand. Additionally, tax software programs commonly include the ability to fill out and file Form 8853 electronically with your tax return.
-
How do I calculate my MSA contribution deduction using Form 8853?
To calculate your MSA contribution deduction, you must fill out the Archer MSA section of Form 8853. Include the total amount of contributions made to your MSA during the year, either by you or on your behalf. The form will guide you through adjustments you may need to make and will calculate the deductible amount to report on your tax return.
-
What happens if I take distributions from my MSA?
If you take distributions from your MSA, you must report these on Form 8853. The form requires details of the amounts used for qualified medical expenses and amounts used for other purposes. Distributions used for qualified medical expenses are tax-free, while those used for other purposes may be taxable and subject to additional penalties.
-
Can I file Form 8853 electronically?
Yes, you can file Form 8853 electronically as part of your federal tax return through IRS e-file. Many tax preparation software programs include the option to complete and file Form 8853 electronically, simplifying the process.
-
Where can I find more information about Form 8853?
For more detailed information about Form 8853, including instructions for completing the form, visit the IRS website at www.irs.gov. The site provides a comprehensive set of resources, including the form itself, detailed instructions, and frequently asked questions about MSAs and long-term care insurance contracts.
Common mistakes
Filling out IRS Form 8853, associated with Archer MSAs and Long-Term Care Insurance Contracts, can sometimes be tricky. Mistakes in this area can lead to unnecessary audits, penalties, or a delay in processing. Here are some of the common errors individuals make when completing this form:
- Not checking the correct tax year at the top of the form. It is crucial to ensure that the form corresponds to the correct tax year to prevent processing delays or wrongful accounting of contributions and distributions.
- Incorrectly reporting Archer MSA contributions. Individuals often mistake personal contributions for employer contributions or vice versa. This discrepancy can impact the deductibility of the contributions and the taxable income report.
- Forgetting to include required information about the HDHP (High Deductible Health Plan). The form requires specifics about the health plan that qualifies the individual for an Archer MSA, including the name of the health plan provider and the period of coverage.
- Overlooking the need to calculate and report taxable distributions. Distributions from the Archer MSA that are not used for qualified medical expenses must be reported as taxable income. Many individuals fail to accurately calculate or report these amounts.
- Misreporting or not reporting long-term care insurance contracts. If a portion of the Archer MSA is used to pay premiums for a long-term care insurance contract, it has to be reported correctly. Failing to do so can lead to audits or penalties.
- Omitting signatures and dates. One of the simplest yet most frequently encountered mistakes is not signing the form or dating it at the bottom. An unsigned form is considered incomplete and will not be processed.
When filled out correctly, Form 8853 provides essential information to the IRS about Archer MSAs and long-term care insurance contracts. By avoiding these common mistakes, individuals can ensure smoother processing of their tax information.
Documents used along the form
The IRS Form 8853 is a critical document for taxpayers who wish to report medical savings account (MSA) contributions, distributions, and to note the health savings account (HSA) or Medicare Advantage MSA. However, filling out the IRS Form 8853 accurately often necessitates gathering and consulting various other forms and documents to ensure the completeness and accuracy of the information reported. Here is a list of documents commonly used alongside IRS Form 8853, each serving a distinct purpose in the preparation process:
- Form 1040 or 1040-SR: These forms are the U.S. individual income tax return documents. Taxpayers need them to attach the IRS Form 8853 and report their overall income, deductions, and tax credits.
- Form 1099-SA: This document details distributions from HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA accounts. It is vital for accurately reporting received distributions on the IRS Form 8853.
- Form 5498-SA: This form reports contributions to an Archer MSA, HSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA, and it is necessary for confirming the contributions made during the tax year.
- Schedule A (Form 1040): This form is used for itemized deductions, including medical and dental expenses, which can be relevant when detailing MSA contributions on the IRS Form 8853.
- Form 8889: This form is specifically for Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and must be filed alongside Form 8853 if the taxpayer has contributions to or distributions from an HSA.
- Insurance Plan Statements: Documents detailing the insurance plan contributions, coverage, and qualified medical expenses are critical for verifying the information submitted on IRS Form 8853.
- Medical Expense Receipts: Receipts for qualified medical expenses paid out-of-pocket are essential for taxpayers looking to detail these expenses accurately on their IRS Form 8853.
- MSA Provider Statements: Statements from the MSA provider detail the account contributions, earnings, and distributions, serving as a reference for the IRS Form 8853.
- Employer Contribution Statements: Documents or statements from employers that detail contributions to an employee's MSA or HSA are important for accurate reporting on the IRS Form 8853.
Preparing to complete the IRS Form 8853 requires careful attention to detail and thorough documentation. By gathering and utilizing these associated forms and documents, taxpayers can ensure the accuracy of their medical savings accounts reporting and comply with IRS requirements. This preparation not only leads to a smoother filing process but also helps in maximizing potential tax advantages available through MSAs and HSAs.
Similar forms
The IRS Form 8853 is a detailed document used for reporting information related to Medical Savings Accounts (MSAs) and Long-Term Care contracts through an MSA. Its structure and purpose share similarities with several other IRS documents, designed to cater to specific tax situations and benefits. For instance, the IRS Form 8889 is quite similar to Form 8853 as it deals with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs). Both forms are used to report contributions and distributions associated with their respective accounts, emphasizing the tax implications of these movements. However, while Form 8853 is specific to MSAs and LTC contracts, Form 8889 is dedicated exclusively to HSAs, reflecting the nuances of different healthcare savings options.
The IRS Form 5329 is another document closely related to Form 8853, with a focus on additional taxes on retirement plans, including those on MSAs. While Form 8853 reports contributions and distributions for MSAs and LTC contracts, Form 5329 is broader, covering various retirement accounts and the additional taxes that may apply due to excess contributions or insufficient distributions. This form highlights the fine line between specific account activities and broader tax implications.
Similarly, the IRS Form 1040 Schedule H shares a relationship with Form 8853 in terms of reporting requirements tied to employment taxes for household employees. Though not directly related to healthcare or retirement accounts, the connection lies in the detail and specificity of reporting individual-specific financial information to the IRS. Both forms serve as avenues for taxpayers to report specific types of financial activities, ensuring compliance with federal tax laws.
The IRS Form 8962, used to reconcile or claim the Premium Tax Credit (PTC), also mirrors Form 8853 in its role of reporting specific tax benefits related to healthcare. Form 8962 is critical for individuals who purchase health insurance through the marketplace, allowing them to adjust or claim tax credits. Like Form 8853, which deals with specific health-related savings and spending, Form 8962 addresses the fiscal implications of healthcare choices on an individual’s taxes.
Another comparable document is the IRS Form 5498, which reports IRA contributions. Both Form 5498 and Form 8853 involve the reporting of contributions to tax-advantaged accounts, although they cater to different types of accounts. Form 8853 focuses on MSAs and LTC arrangements, while Form 5498 pertains to various types of Individual Retirement Accounts. The similarity underscores the IRS's role in managing and monitoring tax-advantaged savings avenues.
The IRS Form W-2 is fundamentally about reporting wages and taxes withheld by employers, but it shares a connection with Form 8853 in the broader context of reporting financial information crucial for tax filing. Both forms are pivotal for individuals to accurately complete their tax returns, albeit with Form W-2 focusing on employment income and Form 8853 on specific healthcare savings accounts. The necessity for detailed financial reporting unites them in the ecosystem of tax documentation.
In essence, while each of these forms caters to unique aspects of financial and tax situations, they collectively embody the intricate nature of tax law and compliance. Whether it's managing healthcare savings, reconciling tax credits, or reporting employment income, these documents underscore the critical role of detailed financial reporting in sustaining the integrity of the tax system. The connection between Form 8853 and other IRS forms highlights the diverse considerations taxpayers must navigate to comply with U.S. tax laws.
Dos and Don'ts
Filling out the IRS 8853 form requires attention to detail and an understanding of the specifics. Here's a helpful list of what individuals should and should not do when completing this form:
Do:Read the instructions carefully. The IRS provides detailed instructions for form 8853, which can guide you through each section to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Gather all necessary information ahead of time. This includes amounts paid for medical expenses, Archer MSA contributions, and long-term care insurance premiums, among others.
Double-check your figures. Before submitting, make sure all numbers are correct to avoid delays or audits.
Consider utilizing tax software or a professional. They can help simplify the process and ensure the form is filled out correctly.
Sign and date the form. An unsigned form is considered invalid and will not be processed.
File the form on time. Check the IRS website for the current tax year's deadlines to avoid any late filing penalties.
Rush through filling out the form. Taking your time can prevent mistakes that could lead to problems with the IRS later.
Forget to report all relevant financial activities. This includes any distributions from your Archer MSAs or Medicare Advantage MSAs.
Omit your Social Security number or the Social Security number of any individual for whom the form is filed. Without this, the IRS cannot process the form.
Ignore IRS notices or letters. If the IRS contacts you for further information or clarification, responding promptly can prevent additional issues.
Make corrections on the form with anything other than a blue or black pen. If you make a mistake, it's best to start with a fresh form to ensure readability.
Assume last year's instructions apply. Tax laws change, and so do form instructions. Always use the most current version of the form and its instructions.
Misconceptions
The IRS 8853 form is an essential document for taxpayers who have specific types of health or long-term care insurance policies. However, there are several misconceptions about this form that can lead to confusion. Below are eight common misunderstandings, explained to shed light on the actual requirements and purposes of IRS Form 8853.
- It's only for the elderly: One common misconception is that Form 8853 is only relevant for elderly taxpayers. In truth, this form is used by individuals of all ages who have a Medical Savings Account (MSA) or participate in a Long-Term Care Insurance contract. Age is not a determining factor for its necessity.
- You need to file it separately: Another misunderstanding is that Form 8853 must be filed separately from your tax return. Actually, this form should be submitted as part of your annual tax return, accompanying your Form 1040 or a similar income tax return form.
- It's complicated to fill out: While tax forms can be daunting, Form 8853 is designed to be straightforward for those who are familiar with their insurance policy details. With the right information on hand, completing this form can be simpler than expected.
- It's only for deductions: Many people believe that Form 8853 is only for claiming deductions on your taxes. However, its purpose extends beyond just deductions; it's crucial for providing the IRS with information about contributions to and distributions from MSAs and LTC contracts.
- There's no benefit to filing it: Contrary to the belief that there's no real benefit to filing Form 8853, submitting this form can actually provide financial advantages. By properly reporting, taxpayers might be eligible for deductions or can avoid tax penalties related to their accounts.
- Any healthcare plan qualifies: A significant misconception is the idea that any healthcare plan qualifies for reporting on Form 8853. In reality, only specific MSAs and LTC plans that meet IRS criteria should be reported on this form.
- It doesn't affect your tax return: It's wrongly assumed that information provided on Form 8853 does not impact your overall tax return. In contrast, the data submitted can affect taxable income, potentially lowering your tax liability or influencing your refund amount.
- Information provided can't be corrected: Finally, there's a myth that once you submit Form 8853, the information cannot be corrected if mistakes are found later. The truth is, amendments can be made by filing a corrected tax return along with an amended Form 8853, allowing taxpayers to rectify errors.
Understanding these misconceptions about IRS Form 8853 can lead to more accurate tax filings and potentially better financial outcomes for taxpayers. It's important to approach tax documentation with clear, correct information to ensure compliance and optimize benefits.
Key takeaways
Filling out the IRS Form 8853 is essential for taxpayers who want to accurately report certain health and medical savings accounts transactions. Here are 10 key takeaways that can help ensure the process is done correctly and efficiently.
- Understanding Eligibility: Before proceeding, determine if you're eligible to use Form 8853. This form is designed for individuals participating in Archer Medical Savings Accounts (MSAs) or long-term care insurance contracts, including those involved with Medicare Advantage MSAs.
- Separate Accounts, Separate Forms: If you have more than one MSA or Medicare Advantage MSA, you need to fill out a separate Form 8853 for each account.
- Detailing Contributions and Distributions: It's crucial to accurately report the total contributions made to your MSA and the distributions taken from it throughout the tax year.
- Medical Expenses Documentation: For distributions to be tax-free, they must be used for qualified medical expenses. Keeping detailed records and receipts of these expenses is advisable should you need to provide proof.
- Use the Correct Tax Year: Ensure you're using the version of Form 8853 that corresponds to the tax year you're reporting for. IRS forms are updated annually.
- Employer Contributions: If your employer contributes to your MSA, these contributions should also be reported on Form 8853.
- Calculating Deductions: Form 8853 is used to calculate the deduction for MSA contributions. This deduction can reduce your taxable income.
- Spouse’s Accounts: If you're filing a joint return and your spouse also has an MSA, you each must fill out your own Form 8853 to report your individual accounts.
- IRS Penalties: Incorrect or incomplete forms can lead to penalties. Ensuring your Form 8853 is correctly filled out and submitted on time is vital to avoid potential fines.
- Filing Deadlines: Pay attention to the IRS's deadlines for when your tax return and Form 8853 must be submitted. Usually, the deadline is April 15 of the year following the reported tax year unless an extension is requested and approved.
Filling out IRS Form 8853 with attention to detail and a careful review of the instructions can help taxpayers accurately report their health and medical savings and avoid possible issues. Always refer to the latest IRS guidelines and consider consulting with a tax professional if you have questions or unique situations.
Popular PDF Documents
1095 Form - Failure to provide a 1095-C form to employees can result in significant penalties against an employer.
E File Extension - Temporary residents and expatriates find Form 4868 essential for navigating the complexities of filing U.S. taxes while living abroad.
