Get Irs 8734 Form
The IRS Form 8734, created in January 2004 by the Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service, serves a crucial role for organizations seeking or maintaining tax-exempt status under Section 501(c)(3). This support schedule for the advance ruling period requires detailed financial information, covering tax years from inception to the present, to verify an organization's source of support and operational income. The comprehensive form demands reporting on gifts, grants, contributions, membership fees, gross receipts from related activities, and income from investments and unrelated business activities, among other financial details. The objective is to substantiate compliance with IRS regulations concerning public support criteria and unrelated business income, which affects an organization's tax-exempt status. With sections dedicated to calculating public support percentages, this form aids in determining whether an organization can be classified under specific sections of the 509(a) and 170(b)(1)(A)(vi), essential for charities aiming to benefit fully from their tax-exempt status. Organizations are encouraged to seek guidance through the form's instructions or directly from the IRS Exempt Organizations Customer Services for accurate completion, ensuring they meet the criteria for continuing their mission with the fiscal advantages of tax exemption.
Irs 8734 Example
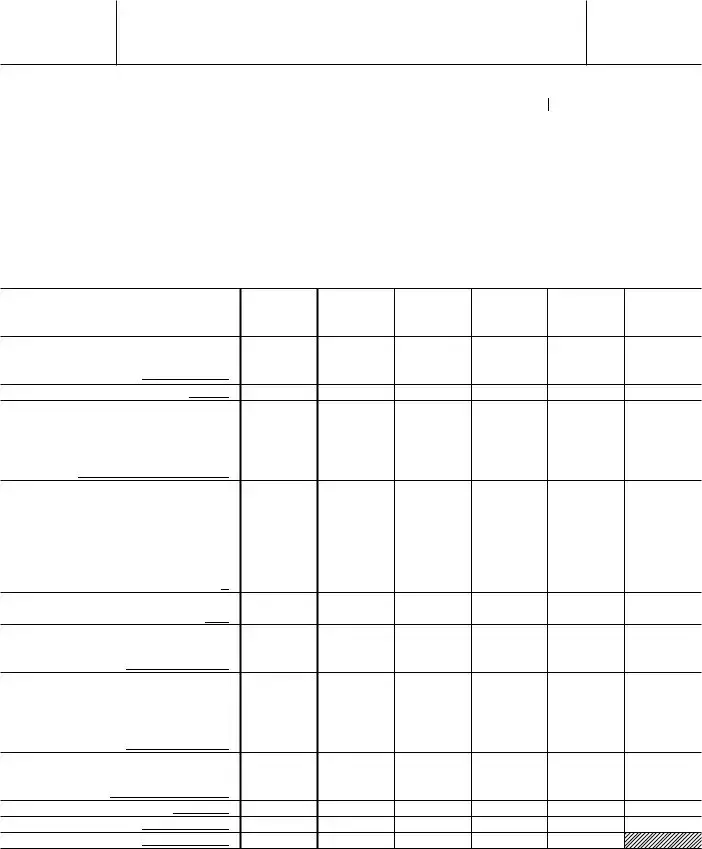
Form 8734 (Rev. January 2004)
Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service
Support Schedule for Advance Ruling Period
Please refer to the separate instructions for assistance in completing this schedule. For
additional help, call IRS Exempt Organizations Customer Services toll free at
OMB No.
For tax years beginning |
, and ending |
|
|
, |
20 |
||
|
Name of organization |
|
|
Employer identification number |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
type. |
Number and street (or P.O. box number if mail is not delivered to street address) |
Room/Suite |
Telephone number |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
Specific |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
City or town, state, and ZIP + 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Instructions. |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Fax number ( |
) |
||
Note: ● Get SCHEDULE A (FORM 990 OR
●If you did not receive any support for a given year, show financial data for the year by indicating
●Year 1 should reflect support received as of the date legally organized, unless otherwise specified in the deter mination letter.
●Organizations that filed For m 990 or
|
|
|
|
|
(e) Year 1 |
(f) Total |
Calendar year (or fiscal year beginning in) |
(a) Year 5 |
(b) Year 4 |
(c) Year 3 |
(d) Year 2 |
(See Note |
of Years |
|
|
|
|
|
above.) |
1 through 5 |
1 Gifts, grants, and contributions received. (Do not include unusual grants. See line 14.)
2Membership fees received
3Gross receipts from admissions, merchandise sold or services performed, or furnishing of facilities in any activity that is related to the
organization’s charitable, etc., purpose
4 Gross income from interest, dividends, amounts received from payments on securities loans (section 512(a)(5)), rents, royalties, and unrelated business taxable income (less section 511 taxes) from
businesses acquired by the organization after June 30, 1975
5Net income from unrelated business activities not included in line 4
6Tax revenues levied for your benefit and either paid to you or expended on your behalf
7The value of services or facilities furnished to you by a governmental unit without charge. Do not include the value of services or facilities generally furnished to the public without charge
8Other income. Attach a schedule. Do not include gain (or loss) from sale of capital assets
9Total of lines 1 through 8
10 Line 9 minus line 3
11 Enter 1% of line 9
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see page 6 of separate instructions. |
Cat. No. 10010S |
Form 8734 (Rev. |
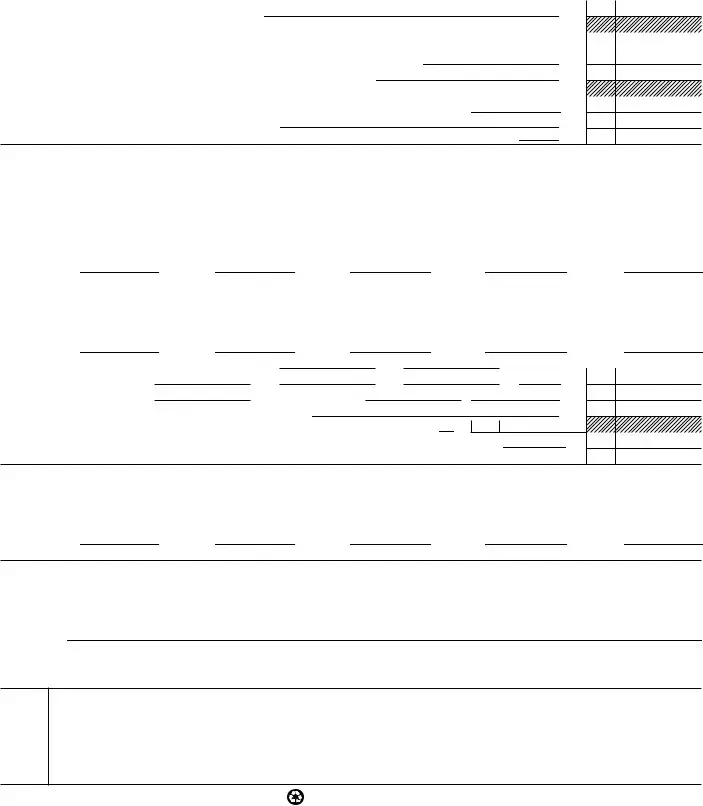

Form 8734 (Rev. |
Page 2 |
12If you are an organization that normally receives a substantial part of your support from a governmental unit or from the general public, complete lines 12a through 12f. (Sections 509(a)(1) and 170(b)(1)(A)(vi)). If you want the IRS to compute your public support test as a section 509(a)(1) and 170(b)(1)(A)(vi) organization, complete only lines 12a and 12b.
a Enter 2% of amount in column (f), line 10 |
bAttach a list showing the name of and amount contributed by each person (other than a governmental
|
unit or publicly supported organization) whose total gifts for Year 5 through Year 1 exceeded the |
||||||
|
amount shown in line 12a. Enter the total of all these excess amounts |
||||||
c |
Total support for section 509(a)(1) test: Enter line 10, column (f) |
||||||
d |
Add: Amounts from |
4 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
column (f) for lines: |
8 |
|
12b |
|
|
|
e |
Public support (line 12c minus line 12d total) |
|
|
|
|||
f |
Public support percentage (line 12e (numerator) divided by line 12c (denominator)) |
||||||
12a |
|
12b |
|
12c |
|
12d |
|
12e |
|
12f |
% |
13If you are an organization that normally receives: (1) more than 331⁄3% of your support from contributions, membership fees, and gross receipts from activities related to your exempt functions, and (2) no more than 331⁄3% of your support from gross investment income and net unrelated business taxable income from businesses acquired by the organization after June 30, 1975, complete lines 13a through 13h. (Section 509(a)(2)). If you want the IRS to compute your public support test as a section 509(a)(2) organization, complete only lines 13a and 13b.
aFor amounts included in lines 1, 2, and 3 that were received from a “disqualified person,” attach a list showing the name of, and total amounts received in each year from, each “disqualified person.” Enter the sum of such amounts for each year:
(Year 5) |
(Year 4) |
(Year 3) |
(Year 2) |
(Year 1) |
bFor any amount included in line 3 that was received from each person (other than “disqualified persons”), attach a list showing the name of, and amount received for each year, that was more than the larger of (1) the amount on line 11 for the year or
(2) $5,000. (Include in the list organizations as well as individuals.) After computing the difference between the amount received and the larger amount described in (1) or (2), enter the sum of these differences (the excess amounts) for each year:
|
(Year 5) |
(Year 4) |
(Year 3) |
(Year 2) |
|
(Year 1) |
|
||
c |
Add: Amounts from column (f) for lines: |
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
6 |
7 |
|
|
13c |
|
|
d |
Add: Line 13a total |
|
and line 13b total |
|
|
|
13d |
|
|
e |
Public support (line 13c total minus line 13d total) |
|
|
|
13e |
|
|||
f |
Total support for section 509(a)(2) test: Enter amount from line 9, column (f) |
13f |
|
|
|
||||
g |
Public support percentage (line 13e (numerator) divided by line 13f (denominator)) |
13g |
% |
||||||
h |
Investment income percentage (line 4, column (f) (numerator) divided by line 13f (denominator)) |
13h |
% |
||||||
14Unusual Grants: For an organization described in line 12 or 13 that received any unusual grants during Year 5 through Year 1, attach a list showing for each year the name of the contributor, the date and amount of the grant, and a brief description of the nature of the grant. Do not include these grants in line 1.
List the amount of unusual grants excluded for each year below.
(Year 5) |
(Year 4) |
(Year 3) |
(Year 2) |
(Year 1) |
15Please list the name and telephone number of an officer, director, or trustee who can be contacted during business hours if we need more information. If someone other than an officer, director, or trustee will represent the organization, attach a properly completed Form 2848, Power of Attorney.
Name:
Type or print name and title.
Phone: |
( |
) |
Fax Number (if available): |
( |
) |
I declare under the penalties of perjury that I am authorized to sign this form on behalf of the above organization and that I have examined this form, including the accompanying attachments, and to the best of my knowledge it is true, correct, and complete.
Please |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Sign |
|
|
|
|
Signature of officer, director, or trustee |
Date |
|||
Here |
||||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||
|
Type or print name and title or authority of signer |
|
||
Form 8734 (Rev.
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Detail |
|---|---|
| Purpose of Form 8734 | Support Schedule for Advance Ruling Period |
| Form Issuer | Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service |
| Relevant OMB Number | 1545-1836 |
| Key Usage | Used by organizations to report support received over a five-year period to determine public support status |
Guide to Writing Irs 8734
Filling out the IRS Form 8734 is a critical step for organizations seeking to provide the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) with required financial data from their advance ruling period. This form helps the IRS assess the public support status of the organization to maintain its tax-exempt status under Section 501(c)(3). Accuracy and completeness are vital to avoid complications or delays. Below are the steps to properly fill out the form. Remember, consulting the separate instructions provided by the IRS or seeking additional help through their Exempt Organizations Customer Services can clarify any uncertainties.
- At the top of the form, provide the organization's name and Employer Identification Number (EIN).
- Enter the organization's contact information, including its address, room/suite number if applicable, telephone number, city, state, ZIP+4, e-mail address, and fax number.
- Specify the tax years the form covers at the beginning sections marked for the tax years beginning and ending.
- Refer to SCHEDULE A (FORM 990 OR 990-EZ) for information pertinent to completing the form, as per the note before starting to fill out the form details.
- Input financial data for each category across the columns for Year 1 through Year 5, following the guidance of what to include for:
- Gifts, grants, and contributions received
- Membership fees received
- Gross receipts from related activities
- Gross income from interests, dividends, etc.
- Net income from unrelated business activities not included in line 4
- Tax revenues levied for your benefit
- The value of services or facilities furnished by a governmental unit without charge
- Other income (attach a schedule if necessary)
- Calculate and enter the total support excluding line 3 from line 9, and enter 1% of line 9.
- Provide the detailed information required for lines 12 and 13, depending on your organization's support structure, including attachments as needed for public support test calculations.
- List any unusual grants separately as instructed for line 14, ensuring these are not included in your earlier totals.
- Complete the section for officer, director, or trustee contact information, ensuring the name and telephone number are printed or typed clearly. Attach Form 2848 if representation is by someone other than an officer, director, or trustee.
- The individual authorized to sign on behalf of the organization must sign and date the form, including their title or authority for verification.
After completing and reviewing the form for accuracy, it should be mailed to the appropriate IRS office as directed in the Form 8734 instructions. Accurate and timely submission aids in the smooth continuation of an organization's status, contributing to its operational effectiveness and compliance with federal tax regulations.
Understanding Irs 8734
What is Form 8734 used for in the IRS context?
Form 8734, Support Schedule for Advance Ruling Period, is utilized by the Internal Revenue Service to assess a non-profit organization's financial support during its advance ruling period. Typically, this period covers the first five years of the organization's operations. The IRS uses the information provided in this form to determine whether an organization continues to meet the qualifications for exemption under Section 501(c)(3) based on the nature and amount of its received support.
Who needs to file IRS Form 8734?
Organizations that have received an advance ruling as a publicly supported charity under Section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code are required to file Form 8734. This filing comes after the conclusion of the organization's advance ruling period, which is a five-year test period to evaluate the organization's source of support and operations to confirm that it meets the public support test.
Where can instructions for completing Form 8734 be found?
Detailed instructions for completing Form 8734 can be found in a separate instruction document specifically for this form. These instructions offer guidance on how to accurately report financial and support information. Additionally, organizations can seek help by calling the IRS Exempt Organizations Customer Services at the toll-free number 1-877-829-5500.
When should Form 8734 be filed?
Form 8734 should be filed at the end of the five-year advance ruling period provided to the organization by the IRS. The specific due date is typically tied to the end of the organization's fiscal year, following the expiration of the five-year period from when it was first recognized as a 501(c)(3) entity.
What types of support and revenue should be reported on Form 8734?
The form requires organizations to report various types of support and revenue, including but not limited to:
- Gifts, grants, and contributions received
- Membership fees
- Gross receipts from admissions, merchandise sold, services performed, or facilities furnished in activities related to the organization’s charitable purpose
- Gross income from interest, dividends, rents, royalties, and unrelated business taxable income
- Net income from unrelated business activities not included above
- Tax revenues levied for the organization’s benefit
- The value of services or facilities furnished by a governmental unit without charge, excluding those generally furnished to the public without charge
- Other income, specifying amounts and sources
It is important to exclude unusual grants from these calculations, as detailed in line 14 of the form.
What are "unusual grants," and how should they be reported on Form 8734?
"Unusual grants" refer to substantial donations or contributions that are typically not repetitive and might distort the nature of an organization's usual pattern of public support over the five-year period. These grants should not be included in the totals reported for gifts, grants, and contributions in line 1 of Form 8734. Instead, organizations are required to attach a list showing for each year of the advance ruling period the name of the contributor, the date and amount of each unusual grant, and a brief description of the grant's nature. This allows the IRS to better assess the standard fiscal operations and public support level outside of these extraordinary contributions.
Common mistakes
Filling out IRS Form 8734 accurately is crucial for organizations to maintain their status and avoid unnecessary issues with the IRS. However, several common mistakes can complicate the process:
- Incorrectly reporting financial figures. Many organizations make the error of inaccurately reporting their gifts, grants, contributions, membership fees, and other income. It's vital to ensure all numbers match those reported in previous filings and financial statements.
- Overlooking unusual grants. Line 14 requires organizations to list any unusual grants separately. Failure to document these grants properly can lead to misrepresentations of an organization's financial health and sources of support.
- Forgetting to attach a schedule for "Other income." Line 8 requires detailed information on other income sources, which must be documented on a separate schedule. This detail is often omitted, causing incomplete submissions.
- Misunderstanding public support calculations. Lines 12 and 13 involve calculations to classify the organization correctly based on its public support status. Misinterpretations of these sections can result in incorrect classification.
- Omitting contact information of an authorized person. The form requires the name and phone number of an officer or trustee who can be contacted for more information. This detail is often missing, which can delay processing.
- Failing to sign the form. An unsigned form 8734 is considered incomplete and will not be processed by the IRS, yet it's a surprisingly common oversight.
- Incomplete details of disqualified persons. When documenting contributions from disqualified persons in the public support test, details are often incomplete, which impacts the accuracy of the support calculation.
- Not using the correct year's form. The IRS occasionally updates its forms. Using an outdated version can lead to submission rejection or the need to resubmit using the correct format.
- Ignoring instructions for zero support years. For years with no financial support, entering -0- or none is necessary, as leaving such fields blank could be interpreted as an oversight or error.
To avoid these errors, organizations are urged to review their Form 8734 submissions carefully and consult the instructions or seek additional help when needed. Ensuring accuracy and completeness in form submissions is fundamental to maintaining good standing with the IRS and ensuring continued support for your organization's mission.
Documents used along the form
When organizations complete and submit IRS Form 8734 to report on their financial activities during a predetermined advance ruling period, they often need to accompany it with other forms and documents. These additional forms ensure the IRS has a comprehensive understanding of the organization's financial status and compliance. The following documents are commonly used alongside Form 8734:
- Form 990 or 990-EZ: A vital form for non-profit organizations, this document provides details on the organization's income, expenses, and overall financial health. It is crucial for demonstrating compliance with IRS regulations for maintaining tax-exempt status.
- Schedule A (Form 990 or 990-EZ): Specifically required for organizations exempt under Section 501(c)(3), this schedule offers in-depth information about the organization's public support. It is directly referenced in Form 8734 for calculating public support percentages.
- Form 2848, Power of Attorney: This form is necessary if someone other than an officer, director, or trustee will represent the organization in its dealings with the IRS. It designates an individual to act on the organization's behalf, enabling them to receive confidential information and make decisions.
- Unusual Grants List: For organizations that received any unusual grants during the period covered by Form 8734, a detailed list of these grants must be attached. This list should include the names of contributors, dates, amounts, and a brief description of each grant, which helps the IRS understand the nature of these contributions.
- Documentation of Income and Expenses: While not a specific form, comprehensive documentation supporting the information reported on Form 8734 and related schedules (including bank statements, receipts, and ledgers) is crucial. These records substantiate the financial data reported to the IRS.
Accurately completing and submitting Form 8734 and its accompanying documents is essential for non-profit organizations to maintain their tax-exempt status and demonstrate their financial accountability. Proper documentation and record-keeping facilitate this process, ensuring organizations comply with IRS requirements while supporting their mission.
Similar forms
The IRS Form 990 or 990-EZ, specifically Schedule A, bears resemblance to Form 8734 in its function of assessing and detailing an organization's financial health and compliance with IRS regulations for maintaining tax-exempt status. Similar to Form 8734, Schedule A requires organizations to report on their revenue streams, including public support, gifts, and contributions, which are pivotal for demonstrating compliance with the public support test, ensuring their operations align with exempt purposes.
Form 1023, the Application for Recognition of Exemption under Section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code, parallels Form 8734 in its initial evaluation of an organization's structure and planned activities to determine eligibility for tax-exempt status. While Form 1023 is used at the outset of an organization’s life to establish its exempt status, Form 8734 is utilized subsequently to provide supporting financial documentation over a specified period, underscoring both forms' roles in the continuum of exempt status verification.
Form 1041, the U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts, shares similarities with Form 8734 in terms of reporting financial information to the IRS, although for different entities and purposes. Both forms entail detailed income reporting and may include information on gifts, grants, and types of income, serving to maintain transparency with the IRS and ensure the correct tax treatment.
Form 8868, the Application for Extension of Time to File an Exempt Organization Return, is linked to Form 8734 by the shared context of tax reporting for nonprofit organizations. While Form 8868 deals with extending filing deadlines, its relation to Form 8734 arises from the necessity of timely and accurate financial reporting by tax-exempt entities, emphasizing the importance of compliance with filing requirements.
Form 990-PF, the Return of Private Foundation, similarly involves detailed financial disclosures, akin to those found in Form 8734, but specifically for private foundations. Both documents require reporting on income, grants, and contributions to ensure adherence to the regulatory and financial obligations governing tax-exempt entities, highlighting the oversight role of the IRS in the nonprofit sector.
Form 8282, Donee Information Return, although centered on the reporting of charitable donations received, interacts with Form 8734 through the lens of nonprofit financial management and IRS reporting requirements. Form 8282's focus on tracking the disposition of charitable donations complements the financial oversight and accounting transparency that Form 8734 aims to ensure for organizations during their advance ruling period.
Form 8283, Noncash Charitable Contributions, complements Form 8734 in its accounting for an organization's received donations, specifically non-cash items. Both forms serve to document the value of contributions to nonprofit organizations, reinforcing the importance of transparency and accurate reporting in maintaining tax-exempt status and public trust.
Dos and Don'ts
When filing out the IRS Form 8734, which is a Support Schedule for Advance Ruling Period, organizations must follow specific guidelines to ensure accurate submission. This document serves for tax years beginning and ending in the specified years for organizations exempt under Section 501(c)(3). To assist with this process, here are seven dos and don'ts to keep in mind:
Do:- Read the separate instructions provided with the form thoroughly before beginning.
- Ensure you have access to Schedule A (Form 990 or 990-EZ) as this contains essential information needed for filling out Form 8734.
- Contact IRS Exempt Organizations Customer Service for additional help if needed. They offer toll-free support.
- Print or type all information clearly to avoid any misunderstandings or processing delays.
- Provide a complete breakdown of financial data for each year, even if no support was received in a given year by marking -0- or none.
- Accurately report gifts, grants, and contributions, excluding unusual grants as specified.
- Sign the form and declare under the penalties of perjury that the form, including attachments, is true, correct, and complete.
- Overlook the necessity to attach a properly completed Form 2848 if someone other than an officer, director, or trustee will represent the organization.
- Include the value of services or facilities generally furnished to the public without charge in the value of services or facilities furnished by a governmental unit without charge.
- Forget to attach a list showing names and amounts contributed by each person whose total gifts exceeded the amount shown in specific sections of the form.
- Omit unusual grants from your gifts, grants, and contributions total, but do attach a list showing details for each unusual grant received.
- Fail to list the name and telephone number of an officer, director, or trustee who can be contacted during business hours for further information.
- Ignore instructions to attach lists for amounts received from “disqualified persons” or for any amount exceeding the specified thresholds.
- Submit the form without reviewing or confirming the accuracy of all the information and documentation attached.
Misconceptions
There are many misconceptions about IRS Form 8734, which is essential for nonprofit organizations during their initial period of tax-exempt status. Clarifying these misunderstandings helps ensure that these organizations can maintain their tax-exempt status and accurately report their finances to the IRS. Here are four common misconceptions and the truths behind them:
- Only Needed Once at Formation: Some believe that Form 8734 is a one-time requirement during the formation of a nonprofit. This is incorrect. In reality, this form is used to report support and financial data for five years following the issuance of the advance ruling period, providing the IRS with required information to confirm the organization's continued eligibility for tax-exempt status.
- It's the Same as Form 990: Another confusion is equating Form 8734 with Form 990 or 990-EZ. While related, these forms serve different purposes. Form 990 or 990-EZ is an annual reporting requirement for most exempt organizations, detailing their financial activities each year. Form 8734 specifically gathers information over a five-year period to assess an organization's public support status and is typically filed after this period completes.
- Income Reporting Is Comprehensive: There's an assumption that all income needs to be reported on Form 8734. However, it instructs organizations not to include unusual grants and other specific types of income. This targeted approach allows the IRS to evaluate the organization's regular sources of support and revenue without skewing the data with non-repeating or exceptional funds.
- Public Support Calculation Is Not Required: Some might think that they don't need to calculate their public support percentage. This is a mistake, as sections of Form 8734 require organizations to compute and report their public support percentage. This calculation is crucial for the IRS to determine whether the organization meets the public support test, affecting their tax-exempt status.
Understanding the specific requirements and purpose of IRS Form 8734 is important for tax-exempt organizations. This ensures compliance with tax laws and helps maintain their crucial tax-exempt status, supporting their mission and activities.
Key takeaways
The IRS Form 8734 is a critical document for maintaining the status of organizations previously granted an advance ruling as a public charity. It serves a pivotal function in ensuring these entities continue to meet the necessary public support criteria over the initial five-year period. Here are four key takeaways about filling out and using the IRS Form 8734:
- Comprehensive Documentation: The form requires detailed information about gifts, grants, contributions, membership fees, and other income over a five-year period. It's vital for organizations to meticulously document all their sources of support and revenue, not only to fill out the form accurately but also to provide substantiation in case of an audit. Organizations are advised to keep thorough records of all financial transactions during these initial years.
- Necessity for Schedule A (Form 990 or 990-EZ): Form 8734 complements Schedule A of Form 990 or 990-EZ, which is the main form used by public charities to report annually to the IRS. Information from Schedule A, Part IV-A, is essential for completing Form 8734, highlighting the interconnectedness of IRS documentation. Prior knowledge and completion of these forms can streamline the process, ensuring accuracy and consistency in reporting.
- Calculations for Public Support Test: Two pivotal sections (lines 12 and 13) on the form help determine whether an organization meets the public support criteria under sections 509(a)(1) and 170(b)(1)(A)(vi) or section 509(a)(2), respectively. These calculations ascertain the level of public support as a percentage of total support, a crucial factor in retaining public charity status. Understanding the nuances of these tests can aid organizations in analyzing their fundraising strategies and financial planning.
- Exclusion of Unusual Grants: Line 14 specifically instructs organizations to list any unusual grants received during the five-year period but to exclude them from the total support calculations. Unusual grants are typically substantial contributions that, due to their size, may skew the understanding of the organization's usual level of support. Identifying and properly reporting such grants is essential for an accurate assessment of an organization's public support.
In conclusion, filling out and using the IRS Form 8734 is a crucial step for organizations in the phase of proving their status as a public charity post the advance ruling period. By providing detailed financial information, adhering to specific IRS requirements for documentation, understanding the public support test calculations, and accurately reporting unusual grants, organizations can successfully navigate this process. Proper completion and submission of this form can solidify an organization's status as a public charity, ensuring its eligibility for tax-deductible contributions and other benefits of this status.
Popular PDF Documents
Health Insurance Marketplace Statement - If you're expecting to claim the Premium Tax Credit, the information on your 1095-A form is critical to determining your eligibility and the amount.
How to Cancel Carefirst Insurance - For subscribers under CareFirst’s specific plans not obtained through an employer or exchange, this form is tailored to facilitate your cancellation needs.
