Get IRS 8233 Form
Dealing with taxes in the United States can sometimes feel overwhelming, especially for individuals who are not citizens or permanent residents but are earning income in the U.S. One particular document, the IRS 8233 form, plays a crucial role for these individuals. This form is essentially a tool that allows nonresident aliens to claim exemption from withholding on compensation for independent personal services and certain types of scholarships or fellowship grants. The reason behind this is treaties the United States might have with other countries, allowing for reduced tax rates or exemptions. Understanding the ins and outs of the IRS 8233 form is vital for anyone in this situation as it directly impacts how much of their earnings will be subject to U.S. income tax. Completing the form requires attention to detail and an understanding of applicable tax treaties, as well as specific information about the individual’s circumstances and their income. It's not just about filling out boxes but understanding the implications of the details you're providing.
IRS 8233 Example
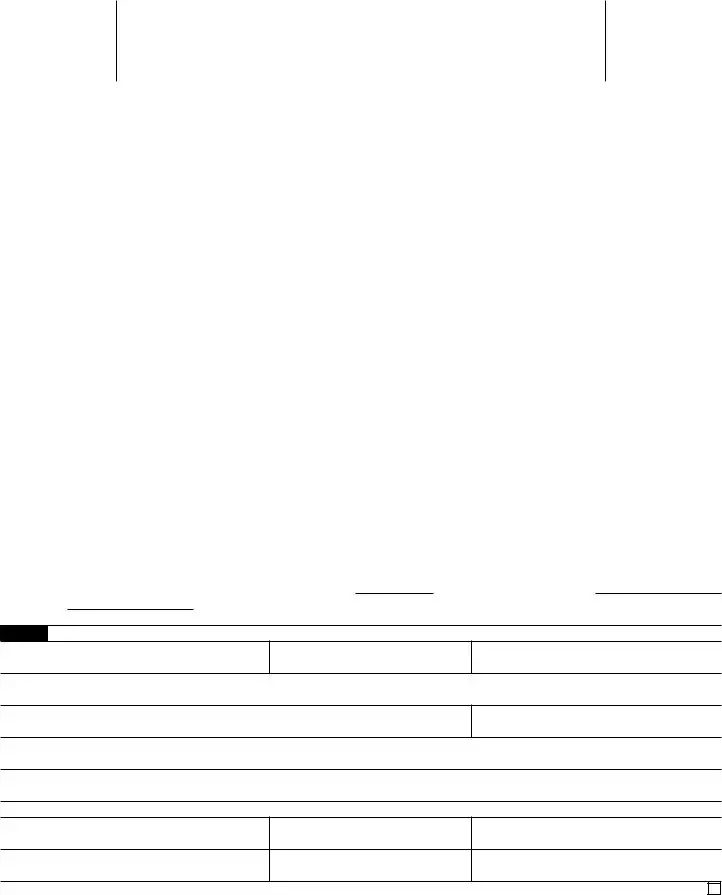
Form 8233
(Rev. September 2018)
Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service
Exemption From Withholding on Compensation for Independent (and Certain Dependent) Personal Services of a Nonresident Alien Individual
Go to www.irs.gov/Form8233 for instructions and the latest information. See separate instructions.
OMB No.
Who Should |
IF you are a nonresident alien individual who is |
THEN, if you are the beneficial owner of that |
Use This Form? |
receiving. . . |
income, use this form to claim. . . |
Note: For |
|
|
Compensation for independent personal |
A tax treaty withholding exemption |
|
definitions of terms |
services performed in the United States |
(Independent personal services, Business |
used in this section |
|
profits) for part or all of that compensation. |
and detailed |
|
|
instructions on |
|
|
required |
|
|
|
|
|
withholding forms |
Compensation for dependent personal |
A tax treaty withholding exemption for part or |
for each type of |
services performed in the United States |
all of that compensation. |
income, see |
|
|
Definitions in the |
|
|
instructions. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Noncompensatory scholarship or fellowship |
A tax treaty withholding exemption for part or |
|
income and personal services income from |
all of both types of income. |
|
the same withholding agent |
|
|
|
|
DO NOT Use |
IF you are a beneficial owner who is. . . |
INSTEAD, use. . . |
|
|
|
This Form. . . |
Receiving compensation for dependent |
Form |
|
||
|
personal services performed in the United |
for how to complete Form |
|
States and you are not claiming a tax treaty |
|
|
withholding exemption for that compensation |
|
|
|
|
|
Receiving noncompensatory scholarship or |
Form |
|
fellowship income and you are not receiving |
agent, Form |
|
any personal services income from the same |
scholarship or fellowship income |
|
withholding agent |
|
|
|
|
|
Claiming only foreign status or treaty benefits |
Form |
|
with respect to income that is not |
|
|
compensation for personal services |
|
|
|
|
This exemption is applicable for compensation for calendar year |
, or other tax year beginning |
|
and ending |
. |
|
Part I Identification of Beneficial Owner (See instructions.)
1Name of individual who is the beneficial owner
2U.S. taxpayer identification number
3Foreign tax identification number, if any
4Permanent residence address (street, apt. or suite no., or rural route). Do not use a P.O. box.
City or town, state or province. Include postal code where appropriate.
Country (do not abbreviate)
5Address in the United States (street, apt. or suite no., or rural route). Do not use a P.O. box.
City or town, state, and ZIP code
Note: Citizens of Canada or Mexico are not required to complete lines 7a and 7b.
6U.S. visa type
7a Country issuing passport
7b Passport number
8Date of entry into the United States
9a Current nonimmigrant status
9b Date your current nonimmigrant status expires
10 If you are a foreign student, trainee, professor/teacher, or researcher, check this box |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
Caution: See the line 10 instructions for the required additional statement you must attach. |
|
|
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see separate instructions. |
Cat. No. 62292K |
Form 8233 (Rev. |

Form 8233 (Rev. |
Page 2 |
|
Part II |
Claim for Tax Treaty Withholding Exemption |
|
11Compensation for independent (and certain dependent) personal services: a Description of personal services you are providing
b Total compensation you expect to be paid for these services in this calendar or tax year $
12If compensation is exempt from withholding based on a tax treaty benefit, provide: a Tax treaty on which you are basing exemption from withholding
b Treaty article on which you are basing exemption from withholding
c Total compensation listed on line 11b above that is exempt from tax under this treaty $ d Country of residence
Note: Do not complete lines 13a through 13d unless you also received compensation for personal services from the same withholding agent.
13Noncompensatory scholarship or fellowship income:
aAmount $
bTax treaty on which you are basing exemption from withholding
cTreaty article on which you are basing exemption from withholding
dTotal income listed on line 13a above that is exempt from tax under this treaty $
14Sufficient facts to justify the exemption from withholding claimed on line 12 and/or line 13 (see instructions)
Part III Certification
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined the information on this form and to the best of my knowledge and belief it is true, correct, and complete. I further certify under penalties of perjury that:
•I am the beneficial owner (or am authorized to sign for the beneficial owner) of all the income to which this form relates.
•The beneficial owner is not a U.S. person.
•The beneficial owner is a resident of the treaty country listed on line 12a and/or 13b above within the meaning of the income tax treaty
between the United States and that country, or was a resident of the treaty country listed on line 12a and/or 13b above at the time of, or immediately prior to, entry into the United States, as required by the treaty.
Furthermore, I authorize this form to be provided to any withholding agent that has control, receipt, or custody of the income of which I am the beneficial owner or any withholding agent that can disburse or make payments of the income of which I am the beneficial owner.
Sign Here |
▶ Signature of beneficial owner (or individual authorized to sign for beneficial owner) |
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
Part IV |
|
Withholding Agent Acceptance and Certification |
|
Name
Employer identification number
Address (number and street) (Include apt. or suite no. or P.O. box, if applicable.)
City, state, and ZIP code
Telephone number
Under penalties of perjury, I certify that I have examined this form and any accompanying statements, that I am satisfied that an exemption from withholding is warranted, and that I do not know or have reason to know that the nonresident alien individual is not entitled to the exemption or that the nonresident alien’s eligibility for the exemption cannot be readily determined.
Signature of withholding agent |
Date |
Form 8233 (Rev.
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The IRS Form 8233 is used to claim exemptions from withholding on compensation for independent personal services of a nonresident alien individual. |
| Eligibility | Nonresident alien individuals performing independent personal services in the United States who wish to claim tax treaty benefits on their income must file this form. |
| Requirements | Filers must provide details such as their name, taxpayer identification number (TIN), and the treaty under which they are claiming exemption. |
| Withholding Agent | The form is typically submitted to the payer of the income, or withholding agent, who then applies the treaty benefits and refrains from withholding taxes as applicable. |
| IRS Review | After submission to the withholding agent, a copy of the form must also be sent to the IRS for review and approval before the exemption can be applied. |
| Frequency | This form must be filed for each tax year in which the exemption is claimed, necessitating annual submission if conditions continue to apply. |
| Governing Law | United States tax law, as governed by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), dictates the use and requirements of Form 8233. |
Guide to Writing IRS 8233
Filling out IRS Form 8233 is essential for individuals who are claiming tax treaty benefits on income earned in the United States. This form allows qualified individuals to reduce the amount of taxes withheld from their U.S. source income. It's crucial for nonresident aliens, such as foreign students, scholars, teachers, and researchers, who often benefit from its provisions. Following a straightforward step-by-step guide can simplify the process, ensuring accurate and timely submission.
- Start by entering your full name at the top of the form, ensuring that it matches the name on your passport and other identification documents.
- Input your U.S. Social Security Number (SSN) or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) in the designated space. If you do not have either, apply for one immediately.
- Fill in your current U.S. address, including the city, state, and ZIP code. If you have a foreign address, include that as well in the appropriate section.
- Specify your country of citizenship in the provided field. This should be the country that has a tax treaty with the United States, from which you are claiming benefits.
- Check the appropriate box to indicate your U.S. visa type, the date you entered the United States, and your current immigration status (e.g., student, teacher, or trainee).
- Detail the type of income you are receiving from U.S. sources that you believe is eligible for tax treaty benefits. Common types include wages, scholarships, or fellowship grants.
- Refer to the tax treaty between the United States and your country of citizenship to determine your eligibility for reduced withholding and the specific article or provision that applies to your income. Insert this information into the form.
- Complete the certification section at the end of the form. Read each statement carefully and ensure that your situation complies with the conditions set out in these statements.
- Sign and date the form in the designated area. If you are using a representative to fill out the form on your behalf, ensure they provide their information and signature in the appropriate section.
- Attach any required documents or additional forms as specified by the IRS instructions for Form 8233. This may include documentation proving residence in your home country or eligibility for treaty benefits.
- Submit the completed Form 8233 to your payer, not to the IRS. Your payer is typically your employer or the institution providing your scholarship or fellowship grant. They will review the form and apply the appropriate rate of withholding to your payments.
After completing and submitting Form 8233, your payer will adjust your withholding to reflect your eligible tax treaty benefits. Please note that processing times can vary, so it is wise to submit the form well in advance of when you expect the reduced withholding to begin. Remember, this form only applies to specific types of income and individuals; not all foreign nationals will qualify. Always consult the specific tax treaty relevant to your country or seek professional advice if you are unsure about your eligibility or how to fill out the form correctly.
Understanding IRS 8233
-
What is the IRS 8233 form and who needs to file it?
The IRS 8233 form, also known as "Exemption From Withholding on Compensation for Independent (and Certain Dependent) Personal Services of a Nonresident Alien Individual," is a document used by nonresident aliens working in the United States to claim exemption from withholding taxes on compensation related to personal services. This form is specifically for those who are eligible under a tax treaty between the United States and their country of residence. Individuals who are providing personal services in the U.S., such as independent contractors, consultants, and certain employees, and who meet the criteria set by a tax treaty, need to file this form to take advantage of its benefits.
-
How do you determine if you are eligible to use Form 8233?
Eligibility to use Form 8233 depends on several factors. First, you must be a nonresident alien according to U.S. tax laws. Secondly, your home country must have a tax treaty with the United States that provides an exemption from withholding tax on compensation for personal services. To determine your eligibility, review the text of the applicable tax treaty carefully, often available on the IRS website. Factors such as your visa status, the nature of your services, and the duration of your stay in the U.S. may affect your eligibility. It's sometimes beneficial to consult with a tax professional who can provide advice based on your specific circumstances.
-
What information and documents do you need to complete Form 8233?
To complete Form 8233, you will need your personal information, including your name, country of citizenship, U.S. and foreign addresses, and U.S. taxpayer identification number (TIN) or social security number (SSN). Additionally, you should be ready to provide details about the treaty under which you are claiming exemption, such as the article number and the type of income. Documentation that supports your claim, such as your visa, proof of residency in your home country, and a statement from the payer of the income verifying the nature of your relationship and the expected duration of services, might also be required to support your Form 8233 submission.
-
How and when do you submit Form 8233?
Form 8233 should be submitted to the payer of your income (not directly to the IRS) before the compensation is paid or credited to you. The payer is responsible for reviewing your form and, if it meets the requirements, forwarding it to the IRS within five days of acceptance. Ensure that the form is completed accurately and in full to avoid delays. If any information changes, such as your visa status or residency status, you must submit a new Form 8233. Always keep a copy for your records. Late submissions may result in withholding taxes that could have been exempted, so timeliness is crucial.
Common mistakes
Filling out the IRS Form 8233 is crucial for individuals claiming a tax treaty benefit. However, mistakes can easily occur if one is not careful. Here is a detailed list of common errors to be aware of:
Failing to provide complete personal information, such as full name, address, and taxpayer identification number. Every detail needs to be accurate and fully filled out.
Not correctly identifying the type of compensation subjected to the treaty claim. It's critical to specify whether it's for services, royalties, or other income types.
Omitting the tax treaty country and not listing the specific article from the treaty that is being claimed. This information is vital for the IRS to process the claim properly.
Incorrectly stating the amount of income or compensation. This should reflect the expected amount to be exempt under the tax treaty.
Forgetting to sign and date the form. An unsigned form is considered incomplete and will not be processed.
Misinterpreting treaty terms, leading to incorrect claims. Understanding the tax treaty provisions is essential to avoid this mistake.
Skipping the residency certification part. This certification is necessary to verify tax residency in the treaty country.
Failure to attach required documentation, such as proof of residency in the treaty country or eligibility documents for the tax benefit claim.
Using outdated forms or information. Tax laws and forms can change, so it's critical to use the current year's form and guidelines.
Entering information in the wrong sections or boxes. Paying close attention to the instructions for each section can prevent this issue.
Avoiding these mistakes can significantly improve the process of claiming tax treaty benefits and ensure that your form is processed without unnecessary delays. Careful review and adherence to the instructions provided with Form 8233 are key steps to success.
Documents used along the form
Complementing the IRS 8233 form, which is crucial for claiming exemption from withholding on compensation for independent personal services of a nonresident alien individual, there are several forms and documents frequently utilized to manage taxation and compliance for international workers and entities effectively. Each of these forms serves a specific purpose, aiding in the accurate and legal handling of compensation, tax deductions, and reporting to the United States tax authorities.
- W-8BEN Form: This form is completed by foreign individuals to certify their foreign status and claim tax treaty benefits, importantly for those not engaged in a trade or business in the U.S.
- W-9 Form: Used by U.S. persons—including citizens and entities—to provide their Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN), ensuring accurate tax reporting and to verify their identity.
- 1042 Form: Employers fill this out to report the income paid to foreign persons, including salaries, wages, and other forms of compensation, detailing the amounts withheld and paid to the IRS.
- 1042-S Form: This document reports amounts paid to foreign individuals, including nonresident aliens, foreign partnerships, corporations, estates, or trusts, specifying income types and tax withheld.
- W-4 Form: While primarily for U.S. employees to determine tax withholding amounts from their paychecks, this form is occasionally used by nonresident aliens following specific IRS guidance for adjustments.
- W-8ECI Form: Foreign individuals or entities use this form to certify that income linked to U.S. operations is effectively connected with their business activity, thus subject to withholding.
- W-8EXP Form: Completed by foreign governments, international organizations, and other specified entities to claim an exemption from withholding on income derived from the U.S., acknowledging their special tax status.
- W-8IMY Form: Provided by intermediaries (agents, nominees, etc.) or entities acting as intermediaries for payment they receive on behalf of others, detailing the entity's status and obligations.
- SS-4 Form: This application is for an Employer Identification Number (EIN), used by entities, including foreign entities, to report taxes and employee withholdings to the IRS.
For nonresident aliens and international businesses, navigating U.S. tax laws can be complex. By understanding and correctly utilizing these forms in conjunction with the IRS 8233, entities can ensure compliance, claim rightful benefits, and streamline their tax handling processes. Whether it's engaging in personal services or operating a business within the United States, these documents collectively support a structured approach to tax obligations and incentives.
Similar forms
The IRS 8233 form is closely related to the W-8BEN form, which is used by foreign individuals to certify their non-U.S. status and claim any applicable benefits under tax treaty agreements. Like the 8233, the W-8BEN serves to inform the IRS and the payer about the tax status of the individual, thereby determining the correct withholding rates on income. Both forms are essential for non-U.S. residents to ensure compliance with U.S. tax laws and to avoid overpayment of taxes.
Similarly, the W-9 form shares common purposes with the IRS 8233, though it is used by U.S. citizens or resident aliens to provide their taxpayer identification number (TIN) to entities that will pay them income. Both the 8233 and W-9 are fundamental in preventing incorrect withholding by allowing individuals to certify their tax status, but they cater to different populations based on citizenship or resident status.
The 1042-S form is another document related to the IRS 8233. This form reports income paid to a non-U.S. resident that is subject to income tax withholding. It is often the result of the information provided on the 8233, detailing the income exempt from withholding due to tax treaty benefits. Both forms work in tandem to ensure the appropriate taxation levels are applied and accurately reported to the IRS.
The Form 1099 series, particularly Form 1099-INT for interest income, also aligns with the function of the 8233 form. Although primarily for U.S. residents, the 1099 forms report various types of income, from interest and dividends to freelance earnings. The connection lies in the broader context of income reporting and tax withholding — the 8233 form specifically targets nonresident aliens’ exemptions, while the 1099 captures a broad spectrum of income for residents.
Form W-4 is used by employees to indicate their tax situation to employers, dictating how much federal income tax to withhold from their earnings. While it addresses U.S. residents and differs in function from the 8233, which is for nonresident aliens claiming treaty benefits, both documents ultimately guide the withholding process, ensuring that individuals’ tax liabilities are accurately reflected in their earnings.
Finally, the Form 8802, Application for United States Residency Certification, bears similarity in its international context. It is used to request a certificate that the applicant is a resident of the United States for purposes of international tax treaties. While the 8802 facilitates the application of tax treaty benefits through residency certification, the 8233 specifically claims those benefits for nonresident aliens with U.S. income. Both are integral in the international tax compliance process, streamlining the operationalization of tax treaties.
Dos and Don'ts
Filing out the IRS 8233 form is an essential process for certain individuals to claim exemption from withholding on compensation for independent personal services of a nonresident alien individual. Considering its significance, it is vital to approach this task with caution and precision. Below are five things you should and shouldn't do when completing the form:
Do's:
- Read the instructions carefully: Before filling out the form, make sure to thoroughly read the instructions provided by the IRS to understand each section's requirements.
- Provide accurate information: Ensure all personal and tax information you provide is accurate and up-to-date to prevent any issues with the IRS.
- Consult a tax professional: If you're unsure about how to complete the form or if it applies to your situation, consulting with a tax professional can provide clarity and guidance.
- Double-check the treaty benefits: Verify you are eligible for the treaty benefits you are claiming. Incorrect claims can lead to denial of the benefits and potential penalties.
- Sign and date the form: A common oversight is failing to sign and date the form before submission. This step is crucial as it validates the form.
Don'ts:
- Leave sections blank: If a section does not apply to you, instead of leaving it blank, write "N/A" to indicate that it's not applicable. Blank sections may cause delays.
- Guess on answers: Do not make guesses if unsure about what to include in certain parts of the form. It's better to seek clarification than to provide incorrect information.
- Ignore the form's specific requirements: Each part of the form might have different requirements, such as providing specific documents. Failure to comply can result in an incomplete submission.
- Use white-out or correction tape: If you make an error, start with a new form. Corrections made with white-out or tape can cause processing delays or even rejections.
- Submit without reviewing: Always review the completed form to ensure all information is correct and that no sections have been mistakenly overlooked.
Misconceptions
The IRS 8233 form, officially known as the "Exemption From Withholding on Compensation for Independent (and Certain Dependent) Personal Services of a Nonresident Alien Individual," often comes with its share of misunderstandings. Here are six common misconceptions about the form:
All nonresident aliens need to file Form 8233. This is not accurate. Only nonresident aliens who receive compensation for personal services performed in the United States and who are claiming an exemption from withholding under a tax treaty need to file this form.
Filing Form 8233 automatically means your income is not taxed. Filing Form 8233 does not guarantee that your income will not be taxed. It simply notifies the IRS and the payer of your claim for exemption under a tax treaty. Whether the exemption is granted depends on the specifics of the treaty and your individual circumstances.
Form 8233 applies to all types of income. Incorrect. Form 8233 is specifically for individuals receiving compensation for personal services. Other types of income, such as scholarships or grants, dividends, and rental income, are not covered by this form.
The process is the same for all taxpayers. The specifics of filing Form 8233 can vary significantly based on the tax treaty between the United States and the taxpayer's country of tax residency. Different treaties have different provisions, making the process quite unique for each individual.
Once submitted, Form 8233 lasts indefinitely. This statement is false. Generally, Form 8233 needs to be submitted each tax year for which the exemption is claimed, meaning the process must be repeated annually.
If the IRS rejects Form 8233, there's no recourse. This is not the case. If the IRS questions or rejects your Form 8233, you may provide additional documentation or clarification. In many cases, issues can be resolved through communication with the IRS or by consulting a tax professional.
Key takeaways
The IRS Form 8233, Exemption From Withholding on Compensation for Independent (and Certain Dependent) Personal Services of a Nonresident Alien Individual, serves a vital role for nonresident aliens working in the United States. It allows individuals to claim exemption from withholding on income related to personal services, under a relevant tax treaty. Understanding the complexities and importance of this form can help in ensuring compliance with U.S. tax laws and in maximizing potential benefits. Below are key takeaways to consider when filling out and using the IRS 8233 form.
- Determine Eligibility: Not everyone can file Form 8233. It's important for individuals to first verify their eligibility to claim a tax treaty benefit. Eligibility largely depends on one's tax residency status, the specific tax treaty between the United States and the individual’s country of tax residence, and the nature of the compensation received.
- Accurate Information: Accuracy is paramount when completing the form. Individuals must provide detailed information about their identity, including their visa type, tax identification number (such as a Social Security Number or an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number), and the specifics of the tax treaty under which they are claiming exemption. Misinformation can lead to denial of the exemption and possible penalties.
- Employer Responsibilities: Employers have obligations too. After receiving a completed Form 8233, the employer must review it for accuracy and completeness, then forward it to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). The employer must also ensure that any exempted income is properly excluded from federal withholding and reported on Form 1042-S, Foreign Person’s U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding, at the end of the year.
- Annual Submission: This is not a one-time task. Each tax year, individuals must submit a new Form 8233 if they wish to continue claiming the treaty benefits. Changes in personal circumstances, tax laws, or treaty terms may affect eligibility from year to year, requiring a fresh evaluation and submission.
It's crucial for both individuals and employers to have a clear understanding of the IRS Form 8233. Proper completion and timely submission can help in avoiding unnecessary withholdings and ensuring compliance with the tax obligations in the United States.
Popular PDF Documents
Form 8852 - The IRS Form 8582 is designed to help taxpayers calculate the amount of passive activity loss (PAL) allowed for deduction in a given tax year, ensuring compliance with regulations limiting such deductions.
IRS 8396 - This form acts as a key element for taxpayers to gain financial benefits from their investment in a home, aligning with broader fiscal policies to encourage homeownership.
