Get IRS 720 Form
Navigating the complexities of tax obligations can often seem daunting, especially when dealing with less commonly encountered forms such as the IRS 720. This particular form plays a critical role for businesses and individuals alike, tasked with the quarterly payment of excise taxes on specific goods, services, and activities. Excise taxes are not as widely understood as income taxes, given their targeted nature, but they are just as important to comply with. Entities dealing with the manufacture, sale, or use of goods and services subject to these taxes must familiarize themselves with IRS 720 to ensure their financial and operational integrity. Beyond merely a requirement, this form encapsulates a wide array of transactions - from environmental fees to communication and air transportation taxes - underpinning its significance in the broader tax framework. The intricacies of filling out and submitting this form correctly cannot be overstated, as errors or omissions can lead to penalties and interest. Understanding its components, the filing deadlines, and the specific excise taxes applicable to your situation is foundational to maintaining compliance with federal tax laws.
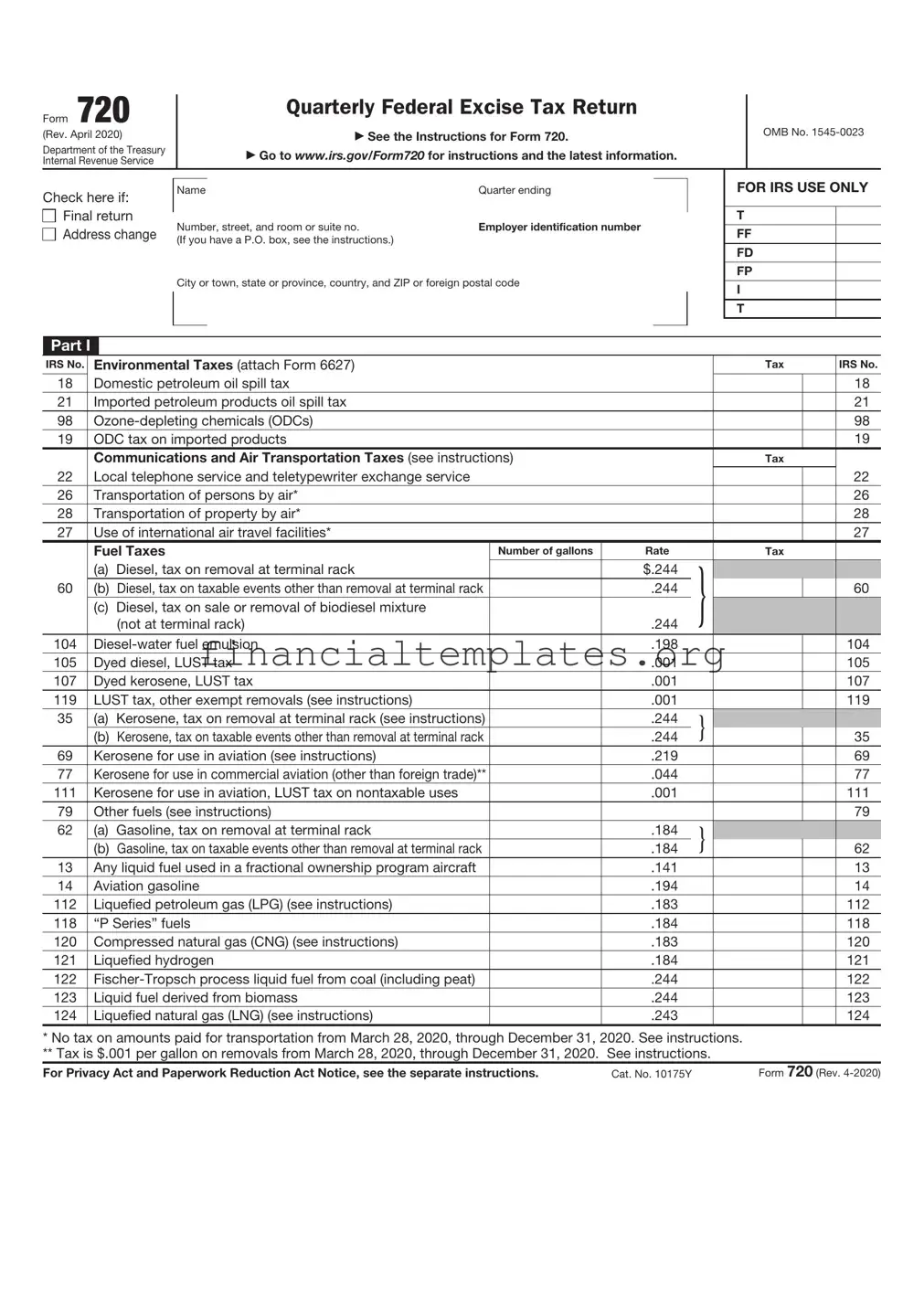
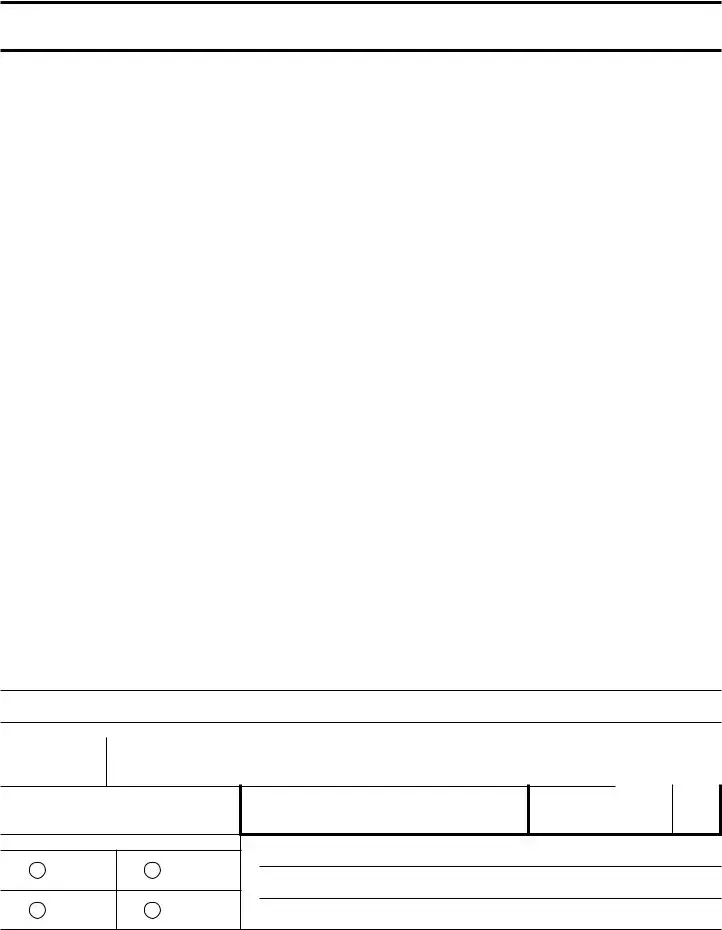
IRS 720 Example

Form 720
(Rev. June 2021)
Department of the Treasury
Internal Revenue Service
Quarterly Federal Excise Tax Return
▶See the Instructions for Form 720.
▶Go to www.irs.gov/Form720 for instructions and the latest information.
OMB No.
Check here if:  Final return
Final return

 Address change
Address change
Name |
Quarter ending |
Number, street, and room or suite no. |
Employer identification number |
(If you have a P.O. box, see the instructions.) |
|
City or town, state or province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code
FOR IRS USE ONLY
T
FF
FD
FP
I
T
Part I
IRS No. |
Environmental Taxes (attach Form 6627) |
|
|
|
|
Tax |
|
IRS No. |
18 |
Domestic petroleum oil spill tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
21 |
Imported petroleum products oil spill tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
98 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
98 |
|
19 |
ODC tax on imported products |
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
Communications and Air Transportation Taxes (see instructions) |
|
|
|
Tax |
|
|
|
22 |
Local telephone service and teletypewriter exchange service |
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
26 |
Transportation of persons by air |
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
28 |
Transportation of property by air |
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
27 |
Use of international air travel facilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
Fuel Taxes |
Number of gallons |
Rate |
|
Tax |
|
|
|
|
(a) Diesel, tax on removal at terminal rack |
|
$.244 |
|
} |
|
|
|
60 |
(b) Diesel, tax on taxable events other than removal at terminal rack |
|
.244 |
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
(c) Diesel, tax on sale or removal of biodiesel mixture |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(not at terminal rack) |
|
.244 |
|
|
|
|
|
104 |
|
.198 |
|
|
|
|
104 |
|
105 |
Dyed diesel, LUST tax |
|
.001 |
|
|
|
|
105 |
107 |
Dyed kerosene, LUST tax |
|
.001 |
|
|
|
|
107 |
119 |
LUST tax, other exempt removals (see instructions) |
|
.001 |
|
|
|
|
119 |
35 |
(a) Kerosene, tax on removal at terminal rack (see instructions) |
|
.244 |
|
} |
|
|
|
|
(b) Kerosene, tax on taxable events other than removal at terminal rack |
|
.244 |
|
|
|
35 |
|
69 |
Kerosene for use in aviation (see instructions) |
|
.219 |
|
|
|
|
69 |
77 |
Kerosene for use in commercial aviation (other than foreign trade) |
|
.044 |
|
|
|
|
77 |
111 |
Kerosene for use in aviation, LUST tax on nontaxable uses |
|
.001 |
|
|
|
|
111 |
79 |
Other fuels (see instructions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
79 |
62 |
(a) Gasoline, tax on removal at terminal rack |
|
.184 |
|
} |
|
|
|
|
(b) Gasoline, tax on taxable events other than removal at terminal rack |
|
.184 |
|
|
|
62 |
|
13 |
Any liquid fuel used in a fractional ownership program aircraft |
|
.141 |
|
|
|
|
13 |
14 |
Aviation gasoline |
|
.194 |
|
|
|
|
14 |
112 |
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) (see instructions) |
|
.183 |
|
|
|
|
112 |
118 |
“P Series” fuels |
|
.184 |
|
|
|
|
118 |
120 |
Compressed natural gas (CNG) (see instructions) |
|
.183 |
|
|
|
|
120 |
121 |
Liquefied hydrogen |
|
.184 |
|
|
|
|
121 |
122 |
|
.244 |
|
|
|
|
122 |
|
123 |
Liquid fuel derived from biomass |
|
.244 |
|
|
|
|
123 |
124 |
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) (see instructions) |
|
.243 |
|
|
|
|
124 |
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see the separate instructions. |
Cat. No. 10175Y |
|
Form 720 (Rev. |
|||||

Form 720 (Rev. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Page 2 |
||
IRS No. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rate |
|
|
Tax |
IRS No. |
||
|
Retail |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
33 |
12% of sales price |
|
|
|
33 |
||||||||||
|
Ship Passenger Tax |
|
|
Number of persons |
|
Rate |
|
|
Tax |
|
|||||
29 |
Transportation by water |
|
|
|
|
|
$3 per person |
|
|
|
29 |
||||
|
Other Excise Tax |
|
|
Amount of obligations |
|
Rate |
|
|
Tax |
|
|||||
31 |
Obligations not in registered form |
|
|
|
|
|
$.01 |
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
||
|
Foreign Insurance |
Premiums paid |
|
Rate |
|
|
Tax |
IRS No. |
|||||||
|
|
Casualty insurance and indemnity bonds |
|
|
|
|
|
$.04 |
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
Life insurance, sickness and accident policies, and annuity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
contracts |
|
|
|
|
|
.01 |
|
|
|
|
30 |
||
|
|
Reinsurance |
|
|
|
|
|
.01 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Manufacturers Taxes |
Number of tons |
Sales price |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
36 |
|
|
|
|
|
$1.10 per ton |
|
|
|
|
36 |
||||
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.4% of sales price |
|
|
|
37 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
38 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$.55 per ton |
|
|
|
|
38 |
|||
39 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.4% of sales price |
|
|
|
39 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of tires |
|
Tax |
IRS No. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
108 |
Taxable tires other than bias ply or super single tires |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
108 |
||
109 |
Taxable bias ply or super single tires (other than super single tires designed for steering) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
109 |
||||||
113 |
Taxable tires, super single tires designed for steering |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
113 |
||
40 |
Gas guzzler tax. Attach Form 6197. Check if |
. . . . . |
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|||||||
97 |
Vaccines (see instructions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
97 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sales price |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Reserved for future use |
|
|
|
|
|
2.3% of sales price |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
1 |
Total. Add all amounts in Part I. Complete Schedule A unless |
|
|
|
▶ |
$ |
|
|
|
||||||
Part II |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) Avg. number |
(b) Rate for |
|
(c) Fee (see |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
IRS No. |
instructions) |
|
of lives covered |
avg. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
(see inst.) |
covered life |
|
instructions) |
|
Tax |
IRS No. |
||||||||
|
Specified health insurance policies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
(a) With a policy year ending before October 1, 2020 |
|
|
$2.54 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
(b) With a policy year ending on or after October 1, 2020, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
and before October 1, 2021 |
|
|
|
$2.66 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
133 |
Applicable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
133 |
||
|
(c) With a plan year ending before October 1, 2020 |
|
|
$2.54 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
(d) With a plan year ending on or after October 1, 2020, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
and before October 1, 2021 |
|
|
|
$2.66 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rate |
|
|
Tax |
|
||
41 |
Sport fishing equipment (other than fishing rods and fishing poles) |
|
|
10% of sales price |
|
|
|
41 |
|||||||
110 |
Fishing rods and fishing poles (limits apply, see instructions) |
|
|
|
10% of sales price |
|
|
|
110 |
||||||
42 |
Electric outboard motors |
|
|
|
|
|
3% of sales price |
|
|
|
42 |
||||
114 |
Fishing tackle boxes |
|
|
|
|
|
3% of sales price |
|
|
|
114 |
||||
44 |
Bows, quivers, broadheads, and points |
|
|
|
|
|
11% of sales price |
|
|
|
44 |
||||
106 |
Arrow shafts |
|
|
|
|
|
$.53 per shaft |
|
|
|
106 |
||||
140 |
Indoor tanning services |
|
|
|
|
|
10% of amount paid |
|
|
|
140 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Number of gallons |
|
Rate |
|
|
Tax |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
64 |
Inland waterways fuel use tax |
|
|
|
|
|
$.29 |
|
|
|
|
|
64 |
||
125 |
LUST tax on inland waterways fuel use (see instructions) |
|
|
|
.001 |
|
|
|
|
|
125 |
||||
51 |
Section 40 fuels (see instructions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
51 |
|
117 |
Biodiesel sold as but not used as fuel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
117 |
|
20 |
Floor Stocks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
||||||
2 |
Total. Add all amounts in Part II |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
▶ |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form |
720 (Rev. |
|
Form 720 (Rev. |
Page 3 |
|
Part III |
|
|
3 |
Total tax. Add Part I, line 1, and Part II, line 2 . |
. . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . ▶ |
|||||||
4 |
Claims (see instructions; complete Schedule C) |
. . . . . . . ▶ |
4 |
|
|
|||||
5 |
Deposits made for the quarter . . . |
. ▶ |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Check here if you used the safe harbor rule to make your deposits. |
|
|
|
|
|||||
6 |
Overpayment from previous quarters . |
. ▶ |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7Enter the amount from Form
|
on line 6, if any . . . . . . . . . ▶ |
7 |
|
|
|
|
8 |
Add lines 5 and 6 |
. . . . . . . . ▶ |
8 |
|
|
|
9 |
Add lines 4 and 8 |
. . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . ▶ |
|||
10Balance Due. If line 3 is greater than line 9, enter the difference. Pay the full amount with the return (see instructions) ▶
11Overpayment. If line 9 is greater than line 3, enter the difference. Check if you want the
overpayment: |
Applied to your next return, or |
Refunded to you. |
3
9
10
11
Third Party Designee
Sign
Here
Paid
Preparer
Use Only
Do you want to allow another person to discuss this return with the IRS (see instructions)? |
Yes. Complete the following. |
No |
|||||
Designee name ▶ |
Phone no. ▶ |
Personal identification number (PIN) ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined this return, including accompanying schedules and statements, and to the best of my knowledge and belief, it is true, correct, and complete. Declaration of preparer (other than taxpayer) is based on all information of which preparer has any knowledge.
▲ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
▲ |
|
|
|
|
|
Signature |
|
|
Date |
|
|
|
Title |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Type or print name below signature. ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
Telephone number ▶ |
|
|
|
|||
Print/Type preparer’s name |
|
Preparer’s signature |
|
Date |
|
|
Check |
if |
|
PTIN |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Firm’s name ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Firm’s EIN ▶ |
|
|
|
||
Firm’s address ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Phone no. |
|
|
|
||
Form 720 (Rev.
Form 720 (Rev. |
Page 4 |
|
|
Excise Tax Liability (see instructions) |
|
Schedule A |
|
|
|
|
|
Note: You must complete Schedule A if you have a liability for any tax in Part I of Form 720. Don’t complete Schedule A for Part II taxes or for a
1Regular method taxes
(a) Record of Net |
|
|
Period |
|
|||
Tax Liability |
|
|
|
|
|||
First month |
A |
|
|
B |
|
|
|
Second month |
C |
|
|
D |
|
|
|
Third month |
E |
|
|
F |
|
|
|
Special rule for September |
* |
. . . . . . . . . |
▶ |
G |
|
|
|
(b)Net liability for regular method taxes. Add the amounts for each semimonthly period.
2Alternative method taxes (IRS Nos. 22, 26, 28, and 27)
(a) Record of Taxes |
|
|
Period |
|
|||
Considered as |
|
|
|
|
|||
Collected |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First month |
M |
|
|
N |
|
|
|
Second month |
O |
|
|
P |
|
|
|
Third month |
Q |
|
|
R |
|
|
|
Special rule for September |
* |
. . . . . . . . . |
▶ |
S |
|
|
|
(b)Alternative method taxes. Add the amounts for each semimonthly period.
* Complete only as instructed (see instructions).
Schedule T
Fuel |
Number of gallons |
Diesel fuel, gallons received in a |
|
on Form 720, IRS No. 60(a) |
|
Diesel fuel, gallons delivered in a |
|
|
|
Kerosene, gallons received in a |
|
on Form 720, IRS No. 35(a), 69, 77, or 111 |
|
Kerosene, gallons delivered in a |
|
|
|
Gasoline, gallons received in a |
|
on Form 720, IRS No. 62(a) |
|
Gasoline, gallons delivered in a |
|
|
|
Aviation gasoline, gallons received in a |
|
on Form 720, IRS No. 14 |
|
Aviation gasoline, gallons delivered in a |
|
|
|
|
Form 720 (Rev. |

Form 720 (Rev. |
|
Page 5 |
Schedule C |
Claims |
Month your income tax year ends ▶ |
•Complete Schedule C for claims only if you are reporting liability in Part I or II of Form 720.
•Attach a statement explaining each claim as required. Include your name and EIN on the statement (see instructions).
Caution: Claimant has the name and address of the person(s) who sold the fuel to the claimant, the dates of purchase, and if exported, the required proof of export. For claims on lines 1a and 2b (type of use 13 and 14), 3c, 4b, and 5, claimant hasn’t waived the right to make the claim.
1 |
Nontaxable Use of Gasoline |
Note: CRN is credit reference number. |
Period of claim ▶ |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Type of use |
Rate |
Gallons |
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|
a Gasoline (see Caution above line 1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
$.183 |
|
$ |
|
362 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b Exported (see Caution above line 1) |
|
.184 |
|
|
|
411 |
||
2 |
Nontaxable Use of Aviation Gasoline |
Period of claim ▶ |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Type of use |
Rate |
Gallons |
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|
a Used in commercial aviation (other than foreign trade) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
$.15 |
|
$ |
|
354 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b Other nontaxable use (see Caution above line 1) |
|
.193 |
|
|
|
324 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
c Exported (see Caution above line 1) |
|
.194 |
|
|
|
412 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
d LUST tax on aviation fuels used in foreign trade |
|
.001 |
|
|
|
433 |
||
3 |
Nontaxable Use of Undyed Diesel Fuel |
Period of claim ▶ |
|
|
|
|||
Claimant certifies that the diesel fuel did not contain visible evidence of dye.
Exception. If any of the diesel fuel included in this claim did contain visible evidence of dye, attach a detailed explanation and check here . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ▶
|
|
Type of use |
Rate |
Gallons |
|
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nontaxable use |
|
$.243 |
|
$ |
|
|
360 |
|
b |
Use in trains |
|
.243 |
|
|
|
|
353 |
c Use in certain intercity and local buses (see Caution above line 1) |
|
.17 |
|
|
|
|
350 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
d Use on a farm for farming purposes |
|
.243 |
|
|
|
|
360 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
e Exported (see Caution above line 1) |
|
.244 |
|
|
|
|
413 |
|
4 Nontaxable Use of Undyed Kerosene (Other Than Kerosene Used in Aviation) Period of claim ▶
Claimant certifies that the kerosene did not contain visible evidence of dye.
Exception. If any of the kerosene included in this claim did contain visible evidence of dye, attach a detailed
explanation and check here . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ▶
|
Caution: Claims cannot be made on line 4 for kerosene sales from a blocked pump. |
Type of use |
Rate |
Gallons |
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nontaxable use |
|
$.243 |
|
$ |
|
346 |
|
b |
Use in certain intercity and local buses (see Caution above line 1) |
|
.17 |
|
|
|
347 |
c |
Use on a farm for farming purposes |
|
.243 |
|
|
|
346 |
d |
Exported (see Caution above line 1) |
|
.244 |
|
|
|
414 |
e |
Nontaxable use taxed at $.044 |
|
.043 |
|
|
|
377 |
f |
Nontaxable use taxed at $.219 |
|
.218 |
|
|
|
369 |
5 Kerosene Used in Aviation (see Caution above line 1) |
Period of claim ▶ |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Type of use |
Rate |
Gallons |
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kerosene used in commercial aviation (other than foreign |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
trade) taxed at $.244 |
|
$.200 |
|
$ |
|
417 |
b |
Kerosene used in commercial aviation (other than foreign |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
trade) taxed at $.219 |
|
.175 |
|
|
|
355 |
c |
Nontaxable use (other than use by state or local |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
government) taxed at $.244 |
.243 |
|
|
|
346 |
|
d |
Nontaxable use (other than use by state or local |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
government) taxed at $.219 |
.218 |
|
|
|
369 |
|
e |
LUST tax on aviation fuels used in foreign trade |
|
.001 |
|
|
|
433 |
Form 720 (Rev.

Form 720 (Rev. |
Page 6 |
6Nontaxable Use of Alternative Fuel
Caution: There is a reduced credit rate for use in certain intercity and local buses (type of use 5) (see instructions).
|
|
Type of use |
Rate |
Gallons, or gasoline |
|
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|
|
|
or diesel gallon |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
equivalents |
|
|
|
|
a |
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) (see instructions) |
|
$.183 |
|
$ |
|
|
419 |
b |
“P Series” fuels |
|
.183 |
|
|
|
|
420 |
c |
Compressed natural gas (CNG) (see instructions) |
|
.183 |
|
|
|
|
421 |
d |
Liquefied hydrogen |
|
.183 |
|
|
|
|
422 |
e |
|
.243 |
|
|
|
|
423 |
|
f |
Liquid fuel derived from biomass |
|
.243 |
|
|
|
|
424 |
g |
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) (see instructions) |
|
.243 |
|
|
|
|
425 |
h |
Liquefied gas derived from biomass |
|
.183 |
|
|
|
|
435 |
7 Sales by Registered Ultimate Vendors of Undyed Diesel Fuel |
|
Period of claim ▶ |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Registration number ▶ |
|
|
|
||
Claimant certifies that it sold the diesel fuel at a
|
|
Rate |
Gallons |
|
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|
a Use by a state or local government |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$.243 |
|
$ |
|
|
360 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b Use in certain intercity and local buses |
.17 |
|
|
|
|
350 |
|
8 Sales by Registered Ultimate Vendors of Undyed Kerosene |
|
Period of claim ▶ |
|
|
|
||
|
(Other Than Kerosene For Use in Aviation) |
Registration number ▶ |
|
|
|
||
|
Claimant certifies that it sold the kerosene at a |
||||||
|
written consent of the buyer to make the claim. Claimant certifies that the kerosene didn’t contain visible evidence of dye. |
||||||
|
Exception. If any of the kerosene included in this claim did contain visible evidence of dye, attach a detailed |
|
|||||
|
explanation and check here |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . ▶ |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rate |
Gallons |
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|
a |
Use by a state or local government |
|
$.243 |
|
$ |
|
346 |
b |
Sales from a blocked pump |
|
.243 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
c |
Use in certain intercity and local buses |
|
.17 |
|
|
|
347 |
9 |
Sales by Registered Ultimate Vendors of Kerosene For Use in Aviation Registration number ▶ |
|
|||||
•See Caution above line 1.
•Claimant sold the kerosene for use in aviation at a
|
|
Type of use |
Rate |
Gallons |
|
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use in commercial aviation (other than foreign trade) taxed at $.219 |
|
$.175 |
|
$ |
|
|
355 |
|
b |
Use in commercial aviation (other than foreign trade) taxed at $.244 |
|
.200 |
|
|
|
|
417 |
c |
Nonexempt use in noncommercial aviation |
|
.025 |
|
|
|
|
418 |
d |
Other nontaxable uses taxed at $.244 |
|
.243 |
|
|
|
|
346 |
e |
Other nontaxable uses taxed at $.219 |
|
.218 |
|
|
|
|
369 |
f |
LUST tax on aviation fuels used in foreign trade |
|
.001 |
|
|
|
|
433 |
10 Sales by Registered Ultimate Vendors of Gasoline |
Registration number ▶ |
|
|
|
||||
Claimant sold the gasoline at a
|
|
Rate |
Gallons |
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|
a Use by a nonprofit educational organization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$.183 |
|
$ |
|
362 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b Use by a state or local government |
.183 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Form |
720 (Rev. |
|
Form 720 (Rev. |
Page 7 |
|
|
11 Sales by Registered Ultimate Vendors of Aviation Gasoline |
Registration number ▶ |
Claimant sold the aviation gasoline at a
|
|
|
Rate |
|
Gallons |
Amount of claim |
|
CRN |
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use by a nonprofit educational organization |
|
$.193 |
|
|
$ |
|
|
324 |
|
b |
Use by a state or local government |
|
.193 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
12 |
Biodiesel or Renewable Diesel Mixture Credit |
Period of claim ▶ |
|
Registration number ▶ |
|
||||
|
Biodiesel mixtures. Claimant produced a mixture by mixing biodiesel with diesel fuel. The biodiesel used to produce the |
||||||||
|
mixture met ASTM D6751 and met EPA’s registration requirements for fuels and fuel additives. The mixture was sold by the |
||||||||
|
claimant to any person for use as a fuel or was used as a fuel by the claimant. Claimant has attached the Certificate for |
|
|||||||
|
Biodiesel and, if applicable, the Statement of Biodiesel Reseller. Renewable diesel mixtures. Claimant produced a mixture by |
||||||||
|
mixing renewable diesel with liquid fuel (other than renewable diesel). The renewable diesel used to produce the renewable |
||||||||
|
diesel mixture was derived from biomass, met EPA’s registration requirements for fuels and fuel additives, and met ASTM |
||||||||
|
D975, D396, or other equivalent standard approved by the IRS. The mixture was sold by the claimant to any person for use as |
||||||||
|
a fuel or was used as a fuel by the claimant. Claimant has attached the Certificate for Biodiesel and, if applicable, Statement of |
||||||||
|
Biodiesel Reseller, both of which have been edited as discussed in the instructions for line 12. See the instructions for line 12 |
||||||||
|
for information about renewable diesel used in aviation. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Rate |
Gal. of biodiesel or |
Amount of claim |
|
CRN |
||
|
|
|
|
renewable diesel |
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Biodiesel (other than |
|
$1.00 |
|
|
$ |
|
|
388 |
|
b |
|
1.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
390 |
|
c |
Renewable diesel mixtures |
|
1.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
307 |
13 Alternative Fuel Credit and Alternative Fuel Mixture Credit |
|
Registration number ▶ |
|
||||||
For the alternative fuel mixture credit, claimant produced a mixture by mixing taxable fuel with alternative fuel. Claimant certifies that it (a) produced the alternative fuel, or (b) has in its possession the name, address, and EIN of the person(s) that sold the alternative fuel to the claimant; the date of purchase; and an invoice or other documentation identifying the amount of the alternative fuel. The claimant also certifies that it made no other claim for the amount of the alternative fuel, or has repaid the amount to the government. The alternative fuel mixture was sold by the claimant to any person for use as a fuel or was used as a fuel by the claimant.
|
|
|
Gallons, or |
|
|
|
|
|
Rate |
gasoline or diesel |
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|
|
|
|
gallon equivalents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(see instructions) |
|
|
|
a |
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)* |
$.50 |
|
$ |
|
426 |
b |
“P Series” fuels |
.50 |
|
|
|
427 |
c |
Compressed natural gas (CNG)* |
.50 |
|
|
|
428 |
d |
Liquefied hydrogen |
.50 |
|
|
|
429 |
e |
.50 |
|
|
|
430 |
|
f |
Liquid fuel derived from biomass |
.50 |
|
|
|
431 |
g |
Liquefied natural gas (LNG)* |
.50 |
|
|
|
432 |
h |
Liquefied gas derived from biomass* |
.50 |
|
|
|
436 |
i |
Compressed gas derived from biomass* |
.50 |
|
|
|
437 |
|
* You can’t claim the alternative fuel mixture credit for this fuel. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
14 |
Other claims. See the instructions. For lines 14b and 14c, see the Caution above line 1 on page 5. |
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|||
a |
Section 4051(d) tire credit (tax on vehicle reported on IRS No. 33) |
|
|
$ |
|
366 |
b |
Exported dyed diesel fuel and exported gasoline blendstocks taxed at $.001 |
|
|
|
415 |
|
c |
Exported dyed kerosene |
|
|
|
|
416 |
d |
|
|
|
|
|
|
e |
Registered credit card issuers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of tires |
Amount of claim |
CRN |
|
f |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Taxable tires other than bias ply or super single tires |
|
|
$ |
|
396 |
|
g |
Taxable tires, bias ply or super single tires (other than super single tires designed for steering) |
|
|
|
304 |
|
h |
Taxable tires, super single tires designed for steering |
|
|
|
|
305 |
i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
j |
|
|
|
|
|
|
k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
Total claims. Add amounts on lines 1 through 14. Enter the result here and on Form 720, Part III, line 4. 15 |
|
|
|
||
Form 720 (Rev.
Form
Purpose of Form
Complete Form
If you have your return prepared by a third party and a payment is required, provide this payment voucher to the return preparer.
Don’t file Form
Specific Instructions
Box 1. If you don’t have an EIN, you may apply for one online by visiting www.irs.gov/EIN. You may also apply for an EIN by faxing or mailing Form
Box 2. Enter the amount paid from line 10 of Form 720.
Box 3. Darken the circle identifying the quarter for which the payment is made. Darken only one circle.
Box 4. Enter your name and address as shown on Form 720.
•Enclose your check or money order made payable to “United States Treasury.” Be sure to enter your
EIN (SSN for
•Detach the completed voucher and send it with your payment and Form 720. See Where To File in the Instructions for Form 720.
Form
Department of the Treasury
Internal Revenue Service
1Enter your employer identification number (EIN). See instructions.
3Tax Period
1st
Quarter
2nd
Quarter
|
Form |
▼ |
Detach here and mail with your payment and Form 720. ▼ |
|
|
Payment Voucher |
|
OMB No. |
||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
▶ Don’t staple or attach this voucher to your payment. |
|
2021 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
2 |
|
Dollars |
|
|
Cents |
|
|
Enter the amount of your payment. ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
Make your check or money order payable to “United States Treasury.” |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
4 Enter your business name (individual name if sole proprietor). |
|
|
|||
3rd |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quarter |
|
Enter your address. |
|
|
||
4th |
|
|
|
|
||
|
City or town, state or province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code |
|
|
|||
Quarter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The IRS Form 720 is used by taxpayers to report and pay federal excise taxes on specific goods, services, and activities. |
| Filing Frequency | This form is filed quarterly, with due dates falling on the last day of the month following the end of the quarter. |
| Payment Method | Taxpayers can pay the taxes reported on Form 720 electronically through the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS), or by check or money order. |
| Who Must File | Form 720 is required to be filed by businesses that manufacture or sell certain goods and services subject to federal excise taxes, as well as entities that use certain types of equipment, facilities, or products. |
| Governing Law | Federal excise tax laws, as outlined by the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) and administered by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), govern the requirements and provisions related to Form 720. |
Guide to Writing IRS 720
Filling out the IRS Form 720 can seem like a daunting task at first glance, but with a clear set of instructions, you can navigate through it with ease. This form is designed for businesses to report and pay federal excise taxes on specific goods, services, and activities. Completing it accurately ensures compliance with tax obligations and helps avoid potential penalties. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you through the process.
- Begin by downloading the latest version of IRS Form 720 from the official Internal Revenue Service website. Ensure you're using the correct version for the current tax period.
- Enter your business name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN) in the designated sections at the top of the form. If your address has changed since your last filing, check the box indicating a new address.
- Choose the quarter for which you are filing in the box provided at the top of the form. The IRS requires this form to be filed quarterly.
- Examine Part I of the form, which lists various taxable products and services. If your business deals with any listed items, enter the appropriate amounts and calculations in the corresponding sections.
- In Part II, focus on the items that apply to your business operations. This section covers a broader range of services and products not included in Part I. If applicable, enter the required information.
- Carefully calculate the total taxes due by adding up the amounts from Parts I and II. Ensure all calculations are correct to avoid errors that could result in penalties.
- If you're claiming any credits or have made prior payments that reduce your current tax liability, eport these amounts in the designated section. This could lower the total amount of taxes due.
- Review the entire form to confirm that all information is accurate and complete. Mistakes or omissions could delay processing and potentially lead to fines.
- Sign and date the form at the bottom. An authorized signer, typically someone with significant responsibility in the business, must sign. The signature attests to the accuracy of the information provided.
- Follow the instructions on the form for submission, which might include mailing it to a specific address or filing electronically, depending on your circumstances and the total amount of tax reported.
- Keep a copy of the completed form and any acknowledgment of submission for your records. This documentation is crucial for future reference, audits, or questions about your filing.
After submitting IRS Form 720, you'll have fulfilled an essential business obligation for the quarter. It's a good practice to review your operations before the next due date to ensure that all taxable services and products are accounted for, keeping your business compliant and ahead of deadlines.
Understanding IRS 720
-
What is the IRS Form 720, and who needs to file it?
IRS Form 720 is known as the Quarterly Federal Excise Tax Return. It is used by businesses to report and pay excise taxes on specific goods, services, and activities. If your business deals with goods such as gasoline, tobacco, or indoor tanning services, you might need to file this form. The requirement to file isn't about the size of your business but rather if your operations involve excise-taxable products or services. Businesses must file this form quarterly to stay in compliance with federal tax obligations.
-
When are the deadlines for filing Form 720?
The IRS requires Form 720 to be filed quarterly. The deadlines for submission are as follows:
- First Quarter (January 1 to March 31) - Due by April 30
- Second Quarter (April 1 to June 30) - Due by July 31
- Third Quarter (July 1 to September 30) - Due by October 31
- Fourth Quarter (October 1 to December 31) - Due by January 31 of the following year
These deadlines are important to remember to avoid any late fees or penalties.
-
How can you file IRS Form 720?
You can file IRS Form 720 in two ways: electronically, using the IRS e-file system, or by mail with a paper form. While both methods are accepted, the IRS encourages electronic filing for its speed and security. If you choose to file electronically, you may need to use an IRS-approved software or consult a tax professional to help you file correctly. If you're mailing the form, make sure to send it to the IRS address specified for Form 720 submissions.
-
What happens if you file Form 720 late or incorrectly?
Filing Form 720 late or with errors can lead to penalties and interest on the taxes owed. The penalty for late filing is usually 5% of the unpaid taxes for each month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. If the return is filed more than 60 days late, the minimum penalty could be either $210 or 100% of the unpaid tax, whichever is less. Errors on the form can lead to a delay in processing and might require filing an amended return, which could also accrue additional charges. To avoid these issues, double-check your form for accuracy and file it on time.
Common mistakes
Filling out the IRS Form 720, which pertains to quarterly federal excise taxes, can sometimes be complicated. People often find themselves making mistakes that could have been avoided with a bit more care and understanding of the requirements. To help guide you, here are eight common errors individuals make during this process:
Not verifying the correct version of the form. The IRS occasionally updates its forms, and using an outdated version can lead to an incorrect filing.
Failing to report all taxable operations. Some activities are less obvious in their applicability but must still be included.
Misunderstanding the tax rates and categories. Each category on Form 720 has its specific rate, which can change, leading to underpayment or overpayment if not updated.
Incorrect calculation of liabilities. Arithmetic errors or misunderstanding how to calculate the tax can result in discrepancies.
Overlooking the deadlines for quarterly submissions. Late submissions can incur penalties and interest.
Omitting necessary signatures and dates. An unsigned or undated form is considered incomplete by the IRS and can delay processing.
Not maintaining proper records. Should the IRS require proof of operations or exemptions claimed, lack of documentation can present significant challenges.
Ignoring the need for amendments to previous quarters. If mistakes are discovered from past submissions, individuals should file an amended return to correct the record.
While these errors can be common, they are also avoidable. Taking the time to double-check calculations, ensure all applicable operations are reported, and understand the latest tax codes related to your submission can help significantly. Always keep accurate and detailed records of your taxable operations and consult the IRS guidelines or a tax professional if you're unsure about your filing. Avoiding these mistakes not only helps streamline the process but also minimizes the risk of facing penalties or audits from the IRS.
Documents used along the form
Preparing and filing taxes correctly requires attention to detail and an understanding of which forms and documents are needed for specific circumstances. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Form 720 is a crucial document for many taxpayers, particularly those engaged in businesses involving the sale or use of particular goods, services, and activities subject to excise taxes. However, Form 720 rarely stands alone in the filing process. A variety of other forms and documents are often required to provide a complete picture of a taxpayer's obligations and entitlements. Here are several key documents that are frequently used in conjunction with Form 720:
- Form 2290: This form is known as the Heavy Highway Vehicle Use Tax Return. It is used by individuals, limited liability companies (LLCs), corporations, partnerships, or any other type of organization owning vehicles with a taxable gross weight of 55,000 pounds or more and which are used on public highways.
- Form 8849: The Claim for Refund of Excise Taxes form is required for taxpayers seeking a refund or claiming a credit for certain types of excise taxes. This form is often filed alongside Form 720 to adjust or claim credits on previously reported excise tax liabilities.
- Form 4136: This is the Credit for Federal Tax Paid on Fuels form. Businesses that use fuel for off-highway business purposes, in farming, in commercial fishing, and various other eligible uses can claim a credit for the fuel taxes paid.
- Form 637: The Application for Registration (For Certain Excise Tax Activities) is crucial for businesses that must register for specific activities related to excise taxes. This includes manufacturers, producers, and importers of taxable goods and services.
- Form 720-TO: Terminal Operator Report is used by terminal operators to report receipts and disbursements of all liquid products to and from all tanks and pipelines at their facilities, which are under a taxable situation.
- Form 720-CS: Carrier Summary Report is filed by carriers who transport bulk alcohol, gasoline, and other taxable fuel products across terminals, providing details on the origin and destination of the products.
- Form 11-C: Occupational Tax and Registration Return for Wagering, used by businesses accepting wagers or conducting wagering pools and lotteries. This form registers the entity for the appropriate occupational tax.
- Form 730: A Monthly Tax Return form for wagers, required to be filed by those who are in the business of accepting wagers, both legal and illegal, under federal law.
- Schedule A (Form 720): This is part of the IRS Form 720 used to detail the excise tax liability by IRS number and includes the rate of tax. It is crucial for accurately reporting and calculating the taxes owed.
When handling excise taxes and associated filings, it is important to gather all relevant information and documents to ensure compliance with tax laws. Each of these forms plays a vital role in the reporting, payment, and reconciliation of excise tax liabilities. Being familiar with them can help taxpayers and their advisors navigate the complexities of excise taxes more effectively, avoiding common pitfalls and ensuring that all obligations are met in a timely manner.
Similar forms
The IRS 720 form, known as the Quarterly Federal Excise Tax Return, is a tool used by businesses to report and pay federal excise taxes on specific goods, services, and activities. Documents similar to the IRS 720 form share the commonality of tax filing, payment reporting, or government-regulated financial obligations. One such document is the IRS 940 form, which is used by employers to report their annual Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) taxes. Similar to the IRS 720, the 940 form helps manage and fund unemployment benefits at the federal level, requiring periodic attention from the filer to remain in compliance.
The IRS 941 form serves a related, although distinct, purpose from the IRS 720. Employers use the 941 form to report income taxes, Social Security tax, or Medicare tax withheld from employees’ paychecks. Additionally, this form accounts for the employer's portion of Social Security or Medicare tax. Like the 720, it plays a critical role in compliance and financial reporting for businesses, underscoring the government's role in overseeing employment and income-related matters.
Another document with similarities to the IRS 720 is the IRS 944 form. This is designed for small employers whose annual liability for Social Security, Medicare, and withheld federal income taxes is $1,000 or less. The form simplifies reporting by allowing these small businesses to report taxes annually instead of quarterly, similar to how the 720 form streamlines excise tax reporting on a quarterly basis.
The Schedule B (Form 941), Report of Tax Liability for Semiweekly Schedule Depositors, is closely tied to the 941 form and by extension shares similarities with the 720. It's used by businesses that accumulate a tax liability exceeding a specific threshold and must make deposits on a semi-weekly basis. Although it deals with payroll taxes rather than excise taxes, it reflects the methodical, periodic reporting structure aimed at more frequent filers, similar to the quarterly reporting seen with the IRS 720 form.
The Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) forms also bear resemblance to the IRS 720, particularly for businesses involved in the production, distribution, and sale of alcohol and tobacco products. These forms are essential for complying with federal regulations on these products, similar to how the 720 form addresses federal excise taxes on a range of goods and services, including fuel, air transportation, and health-related services.
The IRS W-2 form, which employers use to report wages, tips, and other compensation paid to employees, as well as withheld taxes, also shares a functional similarity to the IRS 720. Although the W-2 is more directly related to employee income and tax withholding, both forms are integral to tax reporting and compliance, reinforcing the connection between business operations and government regulation.
The IRS 1099 forms, which document various types of income from sources other than wages, salaries, and tips, align with the IRS 720 in their role in tax reporting. Certain types of 1099 forms might be used by businesses to report payments that could also be subject to excise taxes, demonstrating how both forms contribute to a comprehensive fiscal reporting and compliance structure.
The Heavy Highway Vehicle Use Tax Return, or IRS 2290 form, is utilized by businesses operating heavy vehicles on public highways. Similar to the IRS 720, this form addresses a specific segment of business activity that is regulated and taxed by the federal government, emphasizing the breadth of operational tax reporting necessary for legal compliance and financial accountability.
The IRS 1040 form, which is used by individuals to file their annual income taxes, indirectly relates to the data captured in IRS 720 when businesses pass along tax liabilities to consumers in the price of goods and services. Although primarily for individual taxpayers, the interplay between consumer cost and business tax obligations underlines the importance of understanding how different forms of taxation influence the economy and compliance landscape.
Lastly, the IRS 8300 form, used for reporting cash payments over $10,000 received in a trade or business, intersects with the IRS 720's emphasis on reporting and compliance. While the 8300 form targets anti-money laundering efforts and the tracking of significant cash transactions, like the 720, it highlights the role of businesses in maintaining financial integrity and adhering to federal tax laws and regulations.
Dos and Don'ts
Preparing and filing IRS Form 720, often known as the Quarterly Federal Excise Tax Return, involves navigating specific IRS codes and regulations. This process can appear daunting, but understanding what to do and what to avoid can make it smoother and ensure compliance with the tax laws. Below are essential tips to consider during this process:
Things You Should Do:
Review All Instructions: Carefully read the IRS instructions for Form 720. These guidelines are updated periodically, and being familiar with the latest information can help avoid mistakes.
Double-Check Your Figures: Before submitting, ensure all the numbers are accurate. Mistakes in your calculations can result in penalties or require submitting an amended return.
Use the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS): Make your payments electronically if possible. It's secure, efficient, and provides instant confirmation for your records.
Keep Detailed Records: Maintain thorough records of all transactions that necessitate the filing of Form 720, including payment receipts and applicable exemption certificates. These documents will be invaluable in case of an audit.
Things You Shouldn't Do:
Do Not Estimate Tax Amounts: Ensure all entries are based on actual transactions and precise calculations. Estimations can lead to discrepancies and potential penalties.
Avoid Late Filings: Submit your form and any accompanying payment by the due date to avoid late fees and potential interest charges. Late submissions can also increase the risk of audits.
Do Not Ignore IRS Notices: If you receive any communications from the IRS related to your Form 720, respond promptly. Ignoring notices can lead to additional fines and complications.
Never Leave Sections Blank: If a section does not apply, enter "N/A" or "0," as appropriate. Incomplete forms can be flagged for errors, causing delays or inquiries.
Fulfilling your tax obligations with attention to detail and adherence to IRS guidelines is crucial. By being meticulous and proactive when dealing with IRS Form 720, you can navigate the complexities of federal excise taxes more confidently and efficiently.
Misconceptions
The IRS 720 form, often surrounded by myths and misunderstandings, is a crucial document for many businesses in the United States. It's a quarterly federal excise tax return used by taxpayers to report and pay taxes on specific goods, services, and activities. To clarify, here are eight common misconceptions about the IRS 720 form:
It's only for large corporations: A prevalent misconception is that the IRS 720 form is exclusive to big corporations. In reality, any business, regardless of size, that deals with goods or services subject to federal excise tax must file it.
It covers all taxes: Another misunderstanding is thinking that form 720 encompasses all types of taxes a business might owe. In truth, it specifically relates to excise taxes, which are taxes paid on certain goods, services, and activities.
It's filed annually: It's easy to assume that, like many tax forms, you only need to deal with IRS form 720 once a year. However, this form is filed quarterly, meaning businesses need to submit it four times a year.
There's only one type of excise tax: This is far from the truth. Excise taxes can be environmental, communications, air transportation, fuel, and several other types. Each category has different rates and rules.
Filing late doesn't have penalties: Waiting too long to file or neglecting to file form 720 can lead to penalties and interest. The IRS takes deadlines seriously, so it's essential to file on time.
Digital goods and services are exempt: In the modern market, many transactions occur digitally. It's a common misconception that digital goods and services are not subject to excise taxes. Depending on the nature of the good or service, excise taxes may very well apply.
Only U.S.-based businesses need to file it: If a business operates within U.S. territories or in some cases, interacts significantly with U.S. customers, it may be responsible for filing form 720. Nationality is not the sole criteria; economic activities within U.S. jurisdiction also trigger tax obligations.
Fixing mistakes on a submitted form is a hassle: Everyone makes mistakes, and the IRS is aware of this. Amending a previously filed form 720 is not as troublesome as some might think. The process involves filling out a form correctly and sending it back, albeit attention to detail to minimize errors is advisable.
Understanding the specific responsibilities and requirements associated with IRS form 720 is essential for businesses to comply with federal tax obligations properly. Dispelling these misconceptions is the first step in ensuring your business is on the right track.
Key takeaways
The IRS Form 720, also known as the Quarterly Federal Excise Tax Return, is a tax form that businesses must complete on a quarterly basis if they deal in goods and services subject to excise taxes. Understanding how to properly fill out and use this form is crucial for compliance and avoiding unnecessary penalties. Here are key takeaways to consider:
- Know Which Taxes Apply: The first step in correctly utilizing Form 720 is to determine whether your business deals in goods or services that are subject to federal excise taxes. These can range from environmental taxes, communication and air transportation taxes, to fuel taxes, among others. Each category has specific rates and rules.
- Filling Out the Form: Accuracy is key when completing Form 720. The form is divided into Parts I and II, where different types of excise taxes are reported. It's important to thoroughly review each part and only report the taxes that apply to your business. Overlooking or misreporting can lead to penalties.
- Quarterly Submission: Form 720 must be filed quarterly. The due dates are April 30, July 31, October 31, and January 31 for the respective quarters. Businesses must adhere to these deadlines to avoid late filing fees and interest on any taxes owed.
- Payment Methods: There are several ways to pay the excise taxes due on Form 720, including electronic funds transfer, credit or debit card, or check or money order. Choosing the most convenient and reliable payment method will ensure timely and secure tax payments.
Accurate and timely submission of Form 720 is crucial for businesses to remain compliant with federal tax obligations. Understanding the specific requirements and deadlines associated with this form helps prevent legal complications and financial penalties. Businesses are encouraged to consult with tax professionals if they are unsure about any aspect of their tax responsibilities related to excise taxes.
Popular PDF Documents
Write the Lists Which Should Accompany the Statement of Affairs, in Case of a Winding Up by Court? - A form where debtors must disclose income from employment, business operations, and other activities for both the current and the preceding two years.
What Is 990 Tax Form - Can influence an organization’s eligibility for grants and other forms of financial assistance that require proof of public charity status.