Get IRS 7004 Form
Navigating the complexities of tax deadlines can often feel like a daunting task for businesses and certain individuals managing estates or trusts. Fortunately, there's a relief valve provided by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the shape of Form 7004. This form is essentially a request for additional time to file the more comprehensive tax returns that businesses, including partnerships, corporations, and entities taxed as corporations, are required to submit. What makes Form 7004 particularly valuable is its broad applicability, offering an extension for a diverse range of tax forms. Notably, it doesn't extend the time to pay any taxes due; rather, it offers a grace period for gathering necessary documentation and ensuring the accuracy of the tax returns filed. By understanding the ins and outs of how this form works, who can use it, and the deadlines for submission, entities can navigate tax season with a bit more ease and confidence, reducing the risk of penalties associated with late filings.
IRS 7004 Example
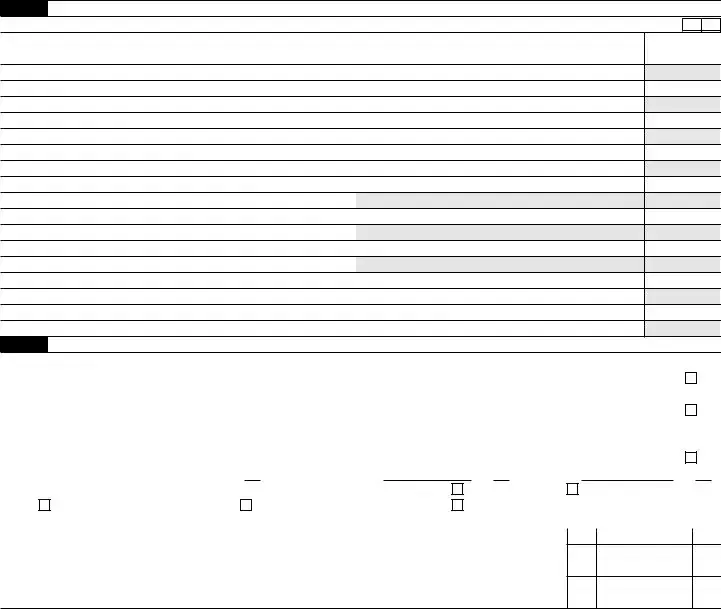
Form 7004 |
Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File Certain |
|
||||
Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns |
|
OMB No. |
||||
(Rev. December 2018) |
|
|
|
|||
File a separate application for each return. |
|
|
||||
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
||||
Go to www.irs.gov/Form7004 for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
||||
Internal Revenue Service |
|
|
||||
|
Name |
|
|
Identifying number |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Number, street, and room or suite no. (If P.O. box, see instructions.) |
|
|
||||
or |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
City, town, state, and ZIP code (If a foreign address, enter city, province or state, and country (follow the country’s practice for entering postal code).) |
||||||
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: File request for extension by the due date of the return. See instructions before completing this form.
Part I Automatic Extension for Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns. See instructions.
1 Enter the form code for the return listed below that this application is for . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Application |
Form |
Application |
Is For: |
Code |
Is For: |
|
01 |
|
Form |
Form |
|
Form |
02 |
Form |
Form 1041 (bankruptcy estate only) |
03 |
Form |
Form 1041 (estate other than a bankruptcy estate) |
04 |
Form |
Form 1041 (trust) |
05 |
Form |
Form |
06 |
Form 1120S |
Form |
07 |
Form |
Form 1042 |
08 |
Form |
Form 1065 |
09 |
Form 8612 |
Form 1066 |
11 |
Form 8613 |
Form 1120 |
12 |
Form 8725 |
Form |
34 |
Form 8804 |
Form |
15 |
Form 8831 |
Form |
16 |
Form 8876 |
Form |
17 |
Form 8924 |
Form |
18 |
Form 8928 |
Form |
19 |
|
Form Code
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
35
36
Part II All Filers Must Complete This Part
2If the organization is a foreign corporation that does not have an office or place of business in the United States,
check here . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3If the organization is a corporation and is the common parent of a group that intends to file a consolidated return,
|
check here |
|
|||
|
If checked, attach a statement listing the name, address, and employer identification number (EIN) for each member |
|
|||
|
covered by this application. |
|
|
|
|
4 |
If the organization is a corporation or partnership that qualifies under Regulations section |
|
|||
5a |
The application is for calendar year 20 |
, or tax year beginning |
, 20 , and ending |
, 20 |
. |
b |
Short tax year. If this tax year is less than 12 months, check the reason: |
Initial return |
Final return |
|
|
|
Change in accounting period |
Consolidated return to be filed |
Other (See |
|
|
6 Tentative total tax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6
7 Total payments and credits. See instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7
8 Balance due. Subtract line 7 from line 6. See instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see separate instructions. |
Cat. No. 13804A |
Form 7004 (Rev. |
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose of Form 7004 | The IRS Form 7004 is used to request an automatic extension of time to file certain business income tax, information, and other returns. |
| Extension Duration | This form typically grants a six-month extension to the filing deadline for most forms it covers. However, the duration can vary depending on the specific tax form being extended. |
| Applicable Entities | Form 7004 is applicable to a wide range of entities including corporations, partnerships, trusts, and estates. |
| Not an Extension to Pay | It's important to note that filing Form 7004 does not extend the time to pay any taxes owed. It only extends the filing deadline for the return itself. |
| Filing Deadlines | The filing deadline for Form 7004 is based on the original due date of the return for which the extension is being requested. This deadline varies depending on the specific tax return. |
Guide to Writing IRS 7004
Filling out the IRS 7004 form is an important step for businesses seeking an extension of time to file their certain tax returns. This process ensures that businesses can meet their obligations without incurring penalties for late submission. Here are the steps to correctly fill out the form:
- Begin by identifying the type of form you are requesting an extension for. This determines the code you will need to enter in Part I, line 1.
- In Part I, line 2, if applicable, provide the specific tax form number for which the extension is being requested.
- For foreign corporations that do not have an office or place of business in the U.S., check the box on line 3.
- If the organization is a group filing, check the box on line 4 and ensure all the requirements for a group return are met.
- Enter the taxpayer's name and address in the designated area. If the address has changed since the last filing, make sure to reflect this change.
- Input the taxpayer identification number (TIN) in the space provided.
- For businesses with a fiscal year-end that is not December 31, enter the tax year end date in the format MM/DD/YYYY in Part II.
- If the request is for a short tax year or a change in the tax year, specify the reason in the space provided in Part II.
- Part III requires the tentative total amount of tax for the year, which should be as accurate as possible.
- In Part III, also include the total payments already made, including withholding and estimated tax payments.
- Sign and date the form. If prepared by someone other than the taxpayer, that person should also provide their information as requested on the form.
Once the IRS 7004 form is correctly filled out, it should be submitted by the original due date of the return for which the extension is requested. It is crucial to follow the specific mailing or electronic filing instructions provided by the IRS for this form to ensure it is processed correctly. Filing this form does not extend the time to pay any taxes owed but can help avoid penalties associated with late filing of the return itself.
Understanding IRS 7004
-
What is IRS Form 7004?
IRS Form 7004, officially titled "Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns," serves a crucial purpose. It allows businesses to obtain an automatic extension of time to file their tax returns. This form is applicable for various types of business entities, including corporations, partnerships, and certain trusts and estates. It's important to note that while this form extends the filing deadline, it does not extend the time to pay any taxes owed. To avoid penalties, businesses should estimate and pay any owed taxes by the original due date.
-
Who needs to file Form 7004?
Form 7004 is intended for multiple types of business entities seeking more time to file their tax returns. These include corporations that follow a calendar year or a fiscal year, partnerships, and multi-member LLCs that are treated as partnerships for tax purposes. Additionally, certain trusts, estates, and real estate mortgage investment conduits (REMICs) needing extra time to compile their information may also use Form 7004. It's critical for entities to determine their eligibility and file Form 7004 by the original due date of their return to avoid potential late-filing penalties.
-
How do you file Form 7004?
Form 7004 can be filed electronically or on paper, depending on your preference and the specific requirements of the tax return for which an extension is being requested. Filing electronically is often faster and reduces the risk of errors. Businesses can use various IRS-authorized e-file providers to submit their Form 7004. If filing on paper, the form should be sent to the IRS address specified in the form's instructions, which varies based on the location of the filer and the type of tax return. Ensure the form is fully completed to prevent delays or rejections.
-
When is the deadline to file Form 7004?
The deadline for filing Form 7004 coincides with the original due date of the business's tax return. For most corporations operating on a calendar year basis, this would be March 15. Partnerships and S corporations also share this due date. However, entities operating on a fiscal year basis will have a different deadline based on their specific tax year end. It's essential to mark this date and ensure that Form 7004 is filed on or before this deadline to obtain the extension. Remember, filing Form 7004 does not extend the time to pay any taxes due.
-
What happens if I don't file Form 7004 on time?
Not filing Form 7004 by the due date can lead to complications. The primary consequence is the inability to receive an extension for filing your tax return, potentially subjecting your business to late-filing penalties. These penalties are usually calculated based on the tax owed and the length of the delay in filing. To mitigate these consequences, businesses are encouraged to file Form 7004 before the deadline and to estimate and pay any owed taxes to reduce or avoid penalties related to late payment. If you're facing challenges in meeting your tax obligations, consider consulting with a tax professional for assistance and guidance.
Common mistakes
The IRS Form 7004 is an essential document for businesses seeking an extension to file their tax returns. However, errors in completing this form can lead to delays, penalties, or the rejection of the request for extension. Below are five common mistakes made during the filling out process:
-
Not Checking the Correct Tax Form Box - When businesses file Form 7004, they must indicate the specific tax return for which they are requesting an extension. A frequent error is not checking the correct box for the tax form associated with their business type, leading to processing delays.
-
Inaccurate Tax Identification Numbers (TIN) - Providing incorrect Tax Identification Numbers, such as an Employer Identification Number (EIN), severely impacts the processing of Form 7004. Common errors include transposition of numbers or entering an incorrect number.
-
Incorrect Tax Year - Applicants often misstate the tax year for which the extension is requested. This mistake could result in an extension for the wrong year, potentially leading to penalties for not filing on time for the intended tax year.
-
Failing to Calculate or Pay Estimated Taxes - Form 7004 does not extend the time for payment of any taxes owed. A common misunderstanding is that filing this form also extends the payment deadline. Businesses need to estimate and pay any owed taxes by the original due date to avoid penalties.
-
Late Submission - Waiting until the last minute to file Form 7004 can be risky. If the form is submitted late, the IRS may deny the request for an extension, leading to penalties for late filing. Ensuring the form is submitted well before the deadline is crucial for a successful extension request.
By avoiding these mistakes, businesses can ensure a smoother process in requesting an extension for filing their tax returns, allowing them to remain in good standing with the IRS while managing their financial planning effectively.
Documents used along the form
Filing taxes is a complex process that requires various forms and documents, depending on the taxpayer's circumstances. The IRS Form 7004 is a request for an automatic extension of time to file certain business income tax, information, and other returns. However, to navigate the intricacies of tax filings, several other documents often accompany the Form 7004. This range of documents helps ensure businesses meet their tax obligations accurately and thoroughly.
- IRS Form 1120 - U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return, is for corporations to report their income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits to the IRS.
- IRS Form 1065 - U.S. Return of Partnership Income, required for partnerships to declare their financial income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits.
- IRS Form 1041 - U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts, used by estates and trusts for reporting income, deductions, and gains.
- IRS Form 8868 - Application for Extension of Time To File an Exempt Organization Return, is for non-profits seeking more time to file their tax returns.
- IRS Form 1120-S - U.S. Income Tax Return for an S Corporation, this form is for S corporations to report their income, losses, and dividends.
- IRS Form 3520-A - Annual Information Return of Foreign Trust With a U.S. Owner, required for foreign trusts with American owners.
- IRS Form 5471 - Information Return of U.S. Persons With Respect To Certain Foreign Corporations, needed by U.S. citizens and residents who are officers, directors, or shareholders in certain foreign corporations.
- IRS Form 8865 - Return of U.S. Persons With Respect to Certain Foreign Partnerships, for U.S. persons who have interests in foreign partnerships.
Each of these documents plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with U.S. tax law. While the Form 7004 provides an extension, actually completing the tax obligation requires attention to the specific forms applicable to the entity's circumstances. Understanding and utilizing these forms correctly can save businesses from potential penalties and interest on unpaid taxes due to inaccuracies or omissions. Taxpayers often find it beneficial to seek guidance from a tax professional to navigate these requirements efficiently.
Similar forms
The IRS Form 7004, known as the Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns, shares similarities with several other tax-related documents. These similarities often revolve around the purpose of alleviating taxpayers' burdens by offering extensions, corrections, or adjustments for various tax situations.
IRS Form 4868, the Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, closely resembles Form 7004 in its foundational purpose. While Form 7004 is targeted at businesses needing more time to file their income tax and other returns, Form 4868 performs a similar function for individuals. Both forms do not extend the time to pay any taxes owed but simply provide additional time to file the required documentation.
IRS Form 8809, the Application for Extension of Time to File Information Returns, is another document similar to Form 7004. This form is used by payers or issuers who need additional time to file information returns, such as Forms 1099, 1098, W-2G, and others. Like Form 7004, Form 8809 helps filers avoid penalties by allowing them more time to gather and report accurate information.
Form 1138, Extension of Time for Payment of Taxes by a Corporation Expecting a Net Operating Loss Carryback, similarly grants corporations a deferral but specifically for the payment of taxes, rather than filing. Corporations anticipating a loss in the current year that can be carried back to offset profits in previous years use this form. This extension parallels Form 7004’s intention to provide relief under specific circumstances, focusing on payments rather than filings.
IRS Form 5558, Application for Extension of Time to File Certain Employee Plan Returns, offers an extension for filing certain employee plan returns, particularly Form 5500 series. Here, the similarity to Form 7004 lies in the provision of additional time for filers to ensure the completeness and accuracy of their submissions. Both forms are designed to help filers avoid penalties due to late submissions.
IRS Form 8868, Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File an Exempt Organization Return, is directly related to Form 7004 in providing tax-related filing extensions. However, Form 8868 is specifically for tax-exempt organizations needing more time to file their returns. Both forms recognize and address the need for additional time to compile necessary information and documentation accurately.
Form 2350, Application for Extension of Time to File U.S. Income Tax Return, is tailored for U.S. citizens and residents abroad who expect to qualify for special tax treatment. While it provides an extension to file an individual income tax return, much like Form 7004 does for businesses, it acknowledges the additional complexities faced by those living outside the U.S.
Lastly, IRS Form 7004 is paralleled by Form 1127, Application for Extension of Time for Payment of Tax Due to Undue Hardship. Although Form 1127 pertains to requesting more time to pay taxes rather than file returns, its foundation is the alleviation of financial burden and hardship. This form, like Form 7004, demonstrates the IRS’s recognition of situations where taxpayers, due to exceptional circumstances, require additional time to meet their tax obligations.
Dos and Don'ts
When it comes to filling out the IRS 7004 form, which is the application for automatic extension of time to file certain business income tax, information, and other returns, there are clear dos and don'ts that can streamline the process, ensure accuracy, and avoid common mistakes. By following these guidelines, you can confidently navigate the completion of this form.
Do:
- Ensure you have the correct tax year and form number before starting. This avoids confusion and ensures your extension request is processed smoothly.
- Double-check your Employer Identification Number (EIN), business name, and address for accuracy. These details must match the IRS records to avoid processing delays.
- Clearly indicate the specific tax form for which you are requesting an extension. The IRS 7004 form covers multiple forms, so specifying the right one is crucial.
- Calculate your total tax liability and enter the correct amount. If you estimate this amount, do so as accurately as possible to avoid underpayment penalties.
- File the form by the due date of your original tax return to ensure your extension is granted. Late filings may not be accepted, resulting in penalties.
Don't:
- Don’t overlook the need to sign and date the form, if required. An unsigned form may be considered invalid and could lead to rejection of your extension request.
- Don’t leave fields blank. If a section does not apply, fill it with “N/A” or “0,” as appropriate. Incomplete forms can lead to processing delays.
- Don’t forget to check your state's filing requirements. Some states do not automatically accept the federal extension and may require a separate application.
- Don’t estimate your tax liability too low. This can result in interest and penalties on the amount underpaid.
- Don’t file a paper form if you can file electronically. Electronic filing is faster, reduces errors, and provides immediate confirmation that the IRS has received your request.
Misconceptions
Filing taxes can often feel overwhelming, especially when dealing with less familiar forms like the IRS 7004. This form is essential for businesses that need more time to file their tax returns. However, misconceptions about this form can lead to errors and complications. Here are six common misunderstandings about the IRS 7004 form demystified.
It grants an extension to pay taxes: A prevalent misconception is that the IRS 7004 form allows extra time to pay taxes. However, this is not the case. The form only extends the filing deadline for the tax return. Taxes owed are still due by the original deadline, and failing to pay on time might result in penalties and interest charges.
Filing is complex and requires a tax professional: Many believe that filing IRS 7004 is a complicated process requiring professional help. While tax professionals can provide valuable assistance, especially for complex business structures, the form itself is straightforward. Instructions provided by the IRS guide filers through the process, making it possible for individuals to complete it on their own if they prefer.
It provides a six-month extension for all business types: Another common misunderstanding is that IRS 7004 uniformly grants a six-month extension to all businesses. The reality is more nuanced. The length of the extension varies depending on the business type and tax year. Some entities may receive a five-month extension, while others qualify for six or even seven months. It's crucial to check the specific guidelines for your business entity.
The form can be filed anytime before the extended deadline: Many taxpayers mistakenly believe they can file Form 7004 at any point before the extended deadline. However, to obtain the extension, the form must be filed by the original due date of the return. Waiting too long to file 7004 will not secure the desired extension, leading to late filing penalties.
Electronic filing is not available for Form 7004: Despite the digital age, some businesses assume they must mail in Form 7004, adding unnecessary delay and potential for loss. In reality, the IRS encourages electronic filing, which is available for this form. E-filing is faster, secure, and provides immediate confirmation of submission, making it the preferred method.
Every business is eligible for an extension with Form 7004: While IRS 7004 is broadly applicable, not every business entity is eligible for an extension. Certain exclusions and conditions must be met, and these are outlined in the form's instructions. It's important for businesses to review these criteria carefully to ensure eligibility before banking on an extension.
Clarifying these misconceptions about the IRS 7004 form helps taxpayers approach extensions with the correct information, reducing errors and unnecessary stress during tax seasons. When in doubt, consulting the IRS guidelines or a tax professional can provide clarity and direction.
Key takeaways
Filing the IRS 7004 form is a crucial step for businesses looking to extend their tax filing deadline. Understanding the nuances of this form can significantly streamline your tax preparation process. Here are key takeaways to ensure you're filling out and utilizing the IRS 7004 form correctly:
- Understand Who Needs It: The IRS 7004 form is designed for businesses, including corporations, partnerships, and certain trusts, needing more time to file their income tax returns.
- Know the Deadlines: Be aware of the deadlines for submitting Form 7004, which vary depending on the type of business and tax year structure. Missing the deadline can result in penalties.
- Automatic Extension: Submitting Form 7004 automatically grants businesses a 6-month extension to file their tax return, but remember, this extension applies to filing, not to any taxes owed.
- Exact Tax Liability: While Form 7004 does not require the exact amount of tax liability, having a close estimate can help avoid underpayment penalties.
- Electronically Filing: Filing Form 7004 electronically is the quickest way to ensure it's received and processed by the IRS, reducing potential delays or errors.
- Keep a Copy: Always keep a copy of the submitted Form 7004 for your records, along with the confirmation from the IRS that it has been accepted.
- Paying Taxes Owed: Remember, filing Form 7004 does not extend the time to pay any taxes owed. Ensure you estimate and pay any owed taxes by the original due date to avoid interest and penalties.
- State Returns: Check the requirements for any state tax returns, as some states require a separate extension request or have different rules and deadlines.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you're unsure about any aspects of filling out or filing Form 7004, consult with a tax professional. Accurate and timely submission can save your business from unnecessary stress and potential financial penalties.
Popular PDF Documents
Employer's Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return - The IRS uses information from this form to allocate funds to state unemployment agencies accordingly.
Mp Commercial Tax 49 - A step-by-step guide to downloading Form 49 on mptax.mp.gov.in, simplifying compliance for businesses.