Get IRS 5329 Form
Individuals navigating their retirement savings plan often encounter various forms that ensure compliance with tax laws and maximize their financial benefits. Among these documents, the IRS 5329 form plays a crucial role, dealing with additional taxes on retirement plans (including IRAs, annuities, and other tax-favored accounts). This form addresses situations such as early withdrawals, excess contributions, and the failure to take required minimum distributions (RMDs), all of which can have significant tax implications. Completing this form accurately is essential for taxpayers looking to avoid potential penalties and accurately report their retirement account activities. It serves as a tool to communicate with the Internal Revenue Service about specific actions taken within an account that may not be automatically reported by financial institutions but still have tax consequences. Understanding the nuances of the IRS 5329 form can help individuals manage their retirement savings more effectively and stay in good standing with tax requirements.
IRS 5329 Example
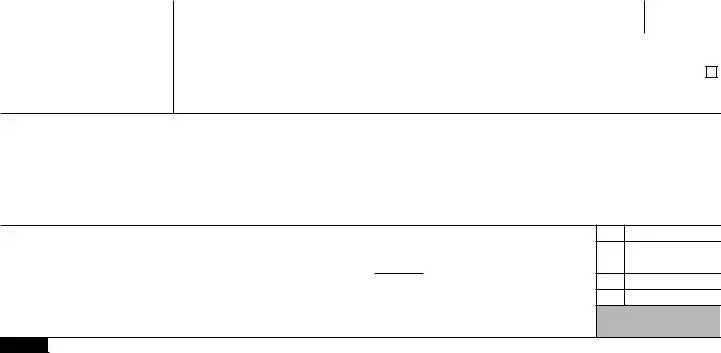
Form 5329 |
|
Additional Taxes on Qualified Plans |
|
||
|
(Including IRAs) and Other |
|
Department of the Treasury |
|
▶ Attach to Form 1040, |
Internal Revenue Service (99) |
|
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/Form5329 for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
|
Name of individual subject to additional tax. If married filing jointly, see instructions.
|
|
Home address (number and street), or P.O. box if mail is not delivered to your home |
||
Fill in Your Address Only |
▲ |
City, town or post office, state, and ZIP code. If you have a foreign address, also complete the |
||
if You Are Filing This |
||||
|
spaces below. See instructions. |
|
||
Form by Itself and Not |
|
|
|
|
With Your Tax Return |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign country name |
Foreign province/state/county |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OMB No.
2021
Attachment
Sequence No. 29
Your social security number
Apt. no.
If this is an amended return, check here ▶
Foreign postal code
If you only owe the additional 10% tax on the full amount of the early distributions, you may be able to report this tax directly on Schedule 2 (Form 1040), line 8, without filing Form 5329. See instructions.
Part I |
Additional Tax on Early Distributions. Complete this part if you took a taxable distribution (other than a qualified |
|
|
disaster distribution) before you reached age 59½ from a qualified retirement plan (including an IRA) or modified |
|
|
endowment contract (unless you are reporting this tax directly on Schedule 2 (Form |
|
|
have to complete this part to indicate that you qualify for an exception to the additional tax on early distributions or for |
|
|
certain Roth IRA distributions. See instructions. |
|
|
|
|
1 Early distributions includible in income (see instructions). For Roth IRA distributions, see instructions . |
1 |
|
2Early distributions included on line 1 that are not subject to the additional tax (see instructions).
|
Enter the appropriate exception number from the instructions: |
. . . . . . . . . |
. |
2 |
|
3 |
Amount subject to additional tax. Subtract line 2 from line 1 |
. |
3 |
||
4 |
Additional tax. Enter 10% (0.10) of line 3. Include this amount on Schedule 2 (Form 1040), line 8 . |
. |
4 |
||
|
Caution: If any part of the amount on line 3 was a distribution from a SIMPLE IRA, you may have |
to |
|
||
|
include 25% of that amount on line 4 instead of 10%. See instructions. |
|
|
|
|
Part II Additional Tax on Certain Distributions From Education Accounts and ABLE Accounts. Complete this part if you included an amount in income, on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 8z, from a Coverdell education savings account (ESA) or a qualified tuition program (QTP), or on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 8p, from an ABLE account.
5 |
Distributions included in income from a Coverdell ESA, a QTP, or an ABLE account |
|
5 |
|
|
6 |
Distributions included on line 5 that are not subject to the additional tax (see instructions) . . . . |
|
6 |
|
|
7 |
Amount subject to additional tax. Subtract line 6 from line 5 |
|
7 |
|
|
8 |
Additional tax. Enter 10% (0.10) of line 7. Include this amount on Schedule 2 (Form 1040), line 8 . . |
|
8 |
|
|
Part III |
Additional Tax on Excess Contributions to Traditional IRAs. Complete this part if you contributed more to your |
||||
|
|
traditional IRAs for 2021 than is allowable or you had an amount on line 17 of your 2020 Form 5329. |
|
|
|
9 |
Enter your excess contributions from line 16 of your 2020 Form 5329. See instructions. If zero, go to line 15 |
9 |
|
||
10If your traditional IRA contributions for 2021 are less than your maximum
|
allowable contribution, see instructions. Otherwise, enter |
|
10 |
|
|
11 |
2021 traditional IRA distributions included in income (see instructions) . . . |
|
11 |
|
|
12 |
2021 distributions of prior year excess contributions (see instructions) . . . |
|
12 |
|
|
13 |
Add lines 10, 11, and 12 |
. . . . . . . . |
|
13 |
|
14 |
Prior year excess contributions. Subtract line 13 from line 9. If zero or less, enter |
14 |
|||
15 |
Excess contributions for 2021 (see instructions) |
. . . . . . . . |
|
15 |
|
16 |
Total excess contributions. Add lines 14 and 15 |
. . . . . . . . |
|
16 |
|
17Additional tax. Enter 6% (0.06) of the smaller of line 16 or the value of your traditional IRAs on December
31, 2021 (including 2021 contributions made in 2022). Include this amount on Schedule 2 (Form 1040), line 8 |
17 |
|
Part IV |
Additional Tax on Excess Contributions to Roth IRAs. Complete this part if you contributed more to your Roth |
|
|
IRAs for 2021 than is allowable or you had an amount on line 25 of your 2020 Form 5329. |
|
18 Enter your excess contributions from line 24 of your 2020 Form 5329. See instructions. If zero, go to line 23 |
18 |
|
19If your Roth IRA contributions for 2021 are less than your maximum allowable
|
contribution, see instructions. Otherwise, enter |
|
19 |
|
|
20 |
2021 distributions from your Roth IRAs (see instructions) |
|
20 |
|
|
21 |
Add lines 19 and 20 |
. . . . . . . . |
|
21 |
|
22 |
Prior year excess contributions. Subtract line 21 from line 18. If zero or less, enter |
22 |
|||
23 |
Excess contributions for 2021 (see instructions) |
. . . . . . . . |
|
23 |
|
24 |
Total excess contributions. Add lines 22 and 23 |
. . . . . . . . |
|
24 |
|
25Additional tax. Enter 6% (0.06) of the smaller of line 24 or the value of your Roth IRAs on December 31,
2021 (including 2021 contributions made in 2022). Include this amount on Schedule 2 (Form 1040), line 8 |
25 |
|
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see your tax return instructions. |
Cat. No. 13329Q |
Form 5329 (2021) |
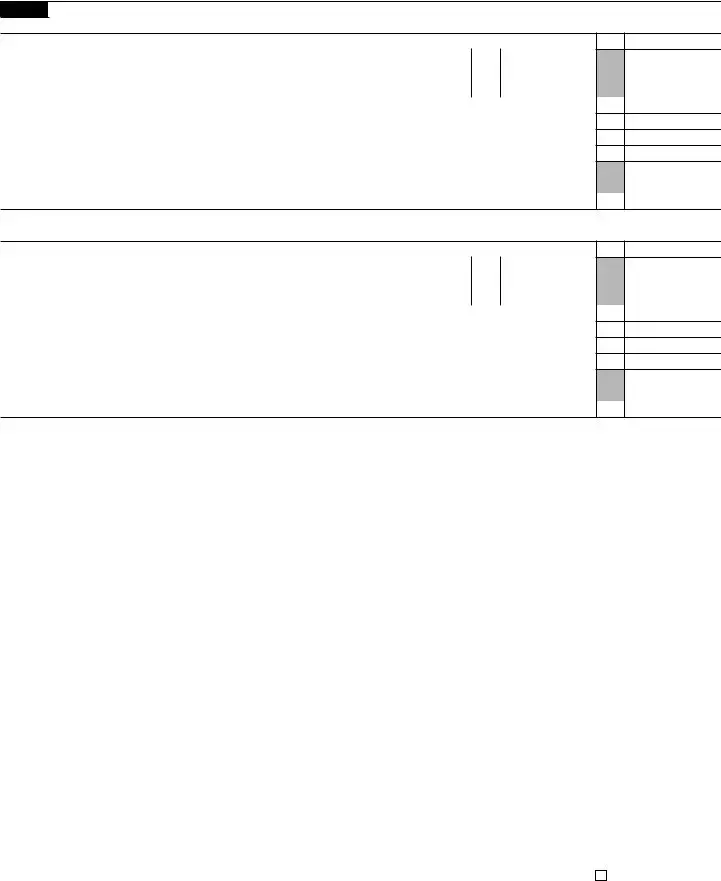
Form 5329 (2021) |
Page 2 |
Part V Additional Tax on Excess Contributions to Coverdell ESAs. Complete this part if the contributions to your Coverdell ESAs for 2021 were more than is allowable or you had an amount on line 33 of your 2020 Form 5329.
26 Enter the excess contributions from line 32 of your 2020 Form 5329. See instructions. If zero, go to line 31 |
26 |
27If the contributions to your Coverdell ESAs for 2021 were less than the
|
maximum allowable contribution, see instructions. Otherwise, enter |
|
27 |
|
|
28 |
2021 distributions from your Coverdell ESAs (see instructions) |
|
28 |
|
|
29 |
Add lines 27 and 28 |
. . . . . . . . |
|
29 |
|
30 |
Prior year excess contributions. Subtract line 29 from line 26. If zero or less, enter |
30 |
|||
31 |
Excess contributions for 2021 (see instructions) |
. . . . . . . . |
|
31 |
|
32 |
Total excess contributions. Add lines 30 and 31 |
. . . . . . . . |
|
32 |
|
33Additional tax. Enter 6% (0.06) of the smaller of line 32 or the value of your Coverdell ESAs on December 31, 2021 (including 2021 contributions made in 2022). Include this amount on Schedule 2
(Form 1040), line 8 |
33 |
|
Part VI |
Additional Tax on Excess Contributions to Archer MSAs. Complete this part if you or your employer contributed |
|
|
more to your Archer MSAs for 2021 than is allowable or you had an amount on line 41 of your 2020 Form 5329. |
|
34 Enter the excess contributions from line 40 of your 2020 Form 5329. See instructions. If zero, go to line 39 |
34 |
|
35If the contributions to your Archer MSAs for 2021 are less than the maximum
|
allowable contribution, see instructions. Otherwise, enter |
|
35 |
|
|
36 |
2021 distributions from your Archer MSAs from Form 8853, line 8 . . . . |
|
36 |
|
|
37 |
Add lines 35 and 36 |
. . . . . . . . |
|
37 |
|
38 |
Prior year excess contributions. Subtract line 37 from line 34. If zero or less, enter |
38 |
|||
39 |
Excess contributions for 2021 (see instructions) |
. . . . . . . . |
|
39 |
|
40 |
Total excess contributions. Add lines 38 and 39 |
. . . . . . . . |
|
40 |
|
41Additional tax. Enter 6% (0.06) of the smaller of line 40 or the value of your Archer MSAs on December 31, 2021 (including 2021 contributions made in 2022). Include this amount on Schedule 2
|
(Form 1040), line 8 |
41 |
|
||||||||||||
Part VII |
|
Additional Tax on Excess Contributions to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs). Complete this part if you, |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
someone on your behalf, or your employer contributed more to your HSAs for 2021 than is allowable or you had an |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
amount on line 49 of your 2020 Form 5329. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
42 |
Enter the excess contributions from line 48 of your 2020 Form 5329. If zero, go to line 47 . . . . |
42 |
|
||||||||||||
43 |
If the contributions to your HSAs for 2021 are less than the maximum |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
allowable contribution, see instructions. Otherwise, enter |
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
44 |
2021 distributions from your HSAs from Form 8889, line 16 |
44 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
45 |
Add lines 43 and 44 |
45 |
|
||||||||||||
46 |
Prior year excess contributions. Subtract line 45 from line 42. If zero or less, enter |
46 |
|
||||||||||||
47 |
Excess contributions for 2021 (see instructions) |
47 |
|
||||||||||||
48 |
Total excess contributions. Add lines 46 and 47 |
48 |
|
||||||||||||
49 |
Additional tax. Enter 6% (0.06) of the smaller of line 48 or the value of your HSAs on December 31, |
|
|
||||||||||||
|
2021 (including 2021 contributions made in 2022). Include this amount on Schedule 2 (Form 1040), line 8 |
49 |
|
||||||||||||
Part VIII |
|
Additional Tax on Excess Contributions to an ABLE Account. Complete this part if contributions to your ABLE |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
account for 2021 were more than is allowable. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
50 |
Excess contributions for 2021 (see instructions) |
50 |
|
||||||||||||
51 |
Additional tax. Enter 6% (0.06) of the smaller of line 50 or the value of your ABLE account on |
|
|
||||||||||||
|
December 31, 2021. Include this amount on Schedule 2 (Form 1040), line 8 |
51 |
|
||||||||||||
Part IX |
|
Additional Tax on Excess Accumulation in Qualified Retirement Plans (Including IRAs). |
Complete this part |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
if you did not receive the minimum required distribution from your qualified retirement plan. |
|
|
||||||||||
52 |
Minimum required distribution for 2021 (see instructions) |
52 |
|
||||||||||||
53 |
Amount actually distributed to you in 2021 |
53 |
|
||||||||||||
54 |
Subtract line 53 from line 52. If zero or less, enter |
54 |
|
||||||||||||
55 |
Additional tax. Enter 50% (0.50) of line 54. Include this amount on Schedule 2 (Form 1040), line 8 . |
55 |
|
||||||||||||
Sign Here Only if You |
|
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined this form, including accompanying attachments, and to the best of my knowledge and |
|||||||||||||
|
belief, it is true, correct, and complete. Declaration of preparer (other than taxpayer) is based on all information of which preparer has any knowledge. |
||||||||||||||
Are Filing This Form |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
by Itself and Not With |
|
▲ |
|
|
|
|
|
▲ |
|
|
|
|
|||
Your Tax Return |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Your signature |
|
|
|
Date |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Paid |
|
|
Print/Type preparer’s name |
Preparer’s signature |
Date |
|
Check |
if |
PTIN |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Preparer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Firm’s name ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Firm’s EIN ▶ |
|
|
||||||
Use Only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Firm’s address ▶ |
|
|
|
|
Phone no. |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form 5329 (2021) |
Document Specifics
| Fact Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | The IRS Form 5329 is used to report additional taxes on IRAs, other qualified retirement plans, modified endowment contracts, and Coverdell ESAs. |
| 2 | It is specifically designed to calculate taxes related to early withdrawals, excess contributions, and required minimum distributions not taken on time. |
| 3 | Taxpayers may need to file Form 5329 if they have taken early distributions from a retirement plan or have contributed more than the allowable limit in a given tax year. |
| 4 | Form 5329 is also necessary when minimum required distributions, usually mandated to start at age 72, have not been fully taken. |
| 5 | Filing this form can lead to additional taxes owed, but it also provides the opportunity to explain any reasonable cause for the mistake and potentially waive penalties. |
| 6 | While Form 5329 is a federal form, taxpayers must be aware that taking distributions from retirement accounts could also affect their state tax obligations. |
| 7 | This form can be filed separately or with your annual tax return, depending on the situation and timing of when an issue is recognized. |
Guide to Writing IRS 5329
Filling out the IRS 5329 form is a critical step to ensure compliance with tax regulations related to retirement plans and other tax-favored accounts. It's important to approach this task with attention to detail, as this form is used to report additional taxes on IRAs, other qualified retirement plans, and other tax-favored accounts. The steps outlined below will guide you through the process of completing the form correctly, helping to ensure that everything is filed accurately and on time.
- Start by gathering all necessary documentation, including your Social Security Number (SSN), Individual Retirement Account (IRA) statements, and information on any distributions or contributions that could affect your tax situation.
- On the top of the form, enter your name and SSN as they appear on your tax return. This ensures that your 5329 form is correctly associated with your tax records.
- Proceed to Part I, if applicable, to report any additional taxes on early distributions from retirement plans. For each plan, you'll need to know the amount of the distribution and any exceptions that apply to avoid the extra tax.
- In Part II, fill out the section regarding excess contributions to IRAs if you contributed more than the allowed amount. You will need to calculate the excess contributions and any earnings on those contributions.
- Part III is for those who need to declare additional taxes on excess accumulations in qualified retirement plans. Here, you must determine if the required minimum distributions were met, and if not, calculate the additional tax owed.
- If applicable, complete Part IV to report additional taxes on specific types of distributions from Coverdell Education Savings Accounts (ESAs), Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), and Archer MSAs.
- Review each section carefully, and use the instructions provided by the IRS for Form 5329 to calculate any taxes owed. These instructions offer detailed guidance on how to calculate additional taxes for each scenario.
- Once all applicable sections are completed, double-check your calculations and the information entered on the form for accuracy.
- Sign and date the form. If you're filing jointly, make sure your spouse also signs if required.
- Attach Form 5329 to your tax return if you are filing by paper. If you are e-filing, follow the software's instructions to include Form 5329 with your tax return.
Completing the IRS 5329 form accurately is crucial for reporting additional taxes and complying with federal tax regulations. By following these steps, you can confidently navigate the process and avoid potential issues with your tax return. Remember, the goal is not just to fulfill a requirement, but also to ensure that your retirement savings and other tax-favored accounts are managed in line with current tax laws.
Understanding IRS 5329
The IRS Form 5329 is a document used for reporting additional taxes on IRAs and other tax-favored accounts. Its complexity often leads to a variety of questions. Below, find detailed answers to some of the most commonly asked questions regarding Form 5329.
- What is the purpose of IRS Form 5329?
- Who needs to file Form 5329?
- Can Form 5329 be filed independently?
- What are the penalties for not filing Form 5329?
- How does one calculate additional taxes using Form 5329?
- Where can I find more information about Form 5329?
IRS Form 5329 serves several important functions. Primarily, it is used to report additional taxes on IRAs, Coverdell ESAs, HSAs, and Archer MSAs. These additional taxes can result from early withdrawals, excess contributions, or insufficient distributions. This form allows taxpayers to calculate and report these taxes to the IRS, ensuring compliance with tax laws related to retirement and savings accounts.
Any individual who has incurred additional taxes due to certain activities within their tax-favored accounts must file Form 5329. This includes, but is not limited to, individuals who have made early withdrawals from retirement accounts before reaching the age of 59 ½, exceeded the allowable contribution limits, or failed to take required minimum distributions upon reaching the necessary age. Individuals who find themselves in these situations are required to calculate and report the additional taxes owed using Form 5329.
Yes, Form 5329 can be filed separately from your standard tax return. While it is often submitted alongside Form 1040, the IRS allows for the independent filing of Form 5329 in situations where taxpayers need to pay additional taxes or claim refunds for overpaid taxes related to their retirement or savings accounts. It is important, however, to ensure that all relevant tax forms are correctly filed and timely submitted to the IRS.
Failing to file Form 5329 can result in significant penalties. The IRS can impose additional taxes and penalties for underreported income due to excess contributions, early withdrawals, or late distributions not properly disclosed through Form 5329. It is crucial to accurately report all information to avoid potential financial penalties and ensure compliance with federal tax laws.
Calculating additional taxes using Form 5329 involves a clear understanding of the specific reasons these taxes are being assessed. For example, early withdrawal taxes are calculated as a percentage of the amount withdrawn before eligibility; excess contribution taxes are calculated based on the amount that exceeds the annual limit; and insufficient minimum distribution taxes are calculated using the difference between the amount that should have been distributed and what was actually distributed. The form provides detailed instructions for calculating these and other applicable taxes.
For more detailed instructions and the most current information regarding Form 5329, visiting the official IRS website is recommended. The IRS provides comprehensive guidance, including instructions for completing and filing the form, definitions of terms, and explanations of penalties. Additionally, tax professionals can offer personalized advice based on an individual's financial situation, ensuring accurate compliance with tax regulations.
Common mistakes
Neglecting to report all distributions: Individuals sometimes forget or are unaware that they need to report all distributions received from their retirement accounts, including early distributions and excess contributions.
Failing to calculate additional taxes correctly: The form requires you to compute additional taxes for specific types of distributions or contributions. Errors in calculation can lead to underpayment of taxes owed, attracting penalties.
Misunderstanding the exceptions: There are several exceptions to the penalties for early distributions. Misinterpreting those exceptions or applying them incorrectly can result in unnecessary payment of additional taxes.
Overlooking the waiver for penalties: Individuals who qualify under certain conditions can request a waiver for penalties. Not seeking this waiver when eligible can lead to paying penalties that could have been avoided.
Incorrectly reporting the distribution code: Each type of distribution has a specific code. Using the wrong distribution code when filling out the form can lead to issues with the IRS, including the assessment of unexpected taxes or penalties.
Omitting the form when required: In some cases, filers assume that they do not need to file Form 5329 with their tax return. However, if you have any situations that require additional taxes or have received distributions, you must file the form to avoid penalties.
Entering incorrect personal information: Simple mistakes like incorrect Social Security numbers or names can delay the processing of the form or lead to IRS discrepancies.
Failing to attach supporting documentation: When claiming exceptions or reporting distributions, you must provide adequate supporting documentation. Failure to attach the necessary documents can result in the denial of your claims.
Not keeping a copy for personal records: Once the form is completed and sent, it is critical to keep a copy for your records. This can help if there are any questions or audits by the IRS in the future.
Avoiding these mistakes can significantly smooth the process of dealing with these portions of your tax returns. Always review your forms carefully and seek professional advice if you're unsure about any aspects of your filing requirements.
Documents used along the form
The IRS Form 5329 is commonly used by taxpayers to report additional taxes on IRAs, other retirement plans, and various tax-favored accounts. When submitting Form 5329, individuals may also need to complete and submit additional forms or provide other documents. These forms vary based on the individual's specific tax situation, such as their income sources, deductions, and any applicable credits. Below is a list of documents that are often used alongside IRS Form 5329.
- Form 1040: The U.S. Individual Income Tax Return is the primary federal income tax form for individuals. Taxpayers use this form to report their annual income, claim tax deductions and credits, and calculate the amount of federal income tax owed or refund due.
- Form 8606: This form is used to report nondeductible contributions to IRAs. It helps taxpayers keep track of their IRA basis, which is essential for determining the taxable part of any IRA distributions not previously taxed.
- Schedule R: Schedule R is attached to Form 1040 for taxpayers who are claiming a credit for the elderly or the disabled. It calculates the allowable amount of the credit based on the individual's age, income, and disability status.
- Form 5498: Form 5498 is an informational form that IRA trustees send to both the IRS and the account holder, detailing contributions, rollovers, conversions, and the fair market value of the account at the end of the year. Although individuals do not file this form themselves, its information can be crucial for accurately completing Form 5329 and other tax documents.
- Form 1099-R: Distributed by plan administrators, Form 1099-R reports distributions from pensions, annuities, retirement or profit-sharing plans, IRAs, and insurance contracts. This information is vital for completing Form 5329 when certain distributions are subject to additional taxes or penalties.
These documents play a crucial role in the tax filing process, ensuring that individuals accurately report income, contributions, distributions, and other pertinent information to the IRS. Each form contributes to a comprehensive view of a taxpayer's financial situation and potential tax liabilities or savings. Understanding how these forms work together can help taxpayers navigate the complexity of tax law and meet their obligations with greater confidence.
Similar forms
The IRS 5329 form is closely related to Form 1040, the individual income tax return. Both forms are integral to the U.S. tax reporting system, with Form 1040 serving as the primary method for individuals to report their income, calculate taxes owed, and claim deductions or credits. Similarly, Form 5329 is used to report additional taxes on things like retirement plans and other tax-favored accounts. While Form 1040 captures the broader picture of an individual's tax status, Form 5329 addresses specific issues and penalties related to the misuse or misreporting of retirement funds.
Form 5498 is another document closely connected to Form 5329, as it involves individual retirement accounts (IRAs). Financial institutions use Form 5498 to report IRA contributions to the IRS. This is directly relevant to Form 5329, which is used by taxpayers to report any discrepancies or issues related to these contributions, such as excess contributions or insufficient distributions. The information provided on Form 5498 can directly affect the reporting on Form 5329, as it establishes the basis for many of the calculations needed on the latter.
Form 8862, "Information To Claim Certain Credits After Disallowance," shares a connection with Form 5329 through its focus on rectifying previous tax reporting errors. While Form 8862 specifically relates to reclaiming eligibility for certain tax credits (like the Earned Income Tax Credit) after they have been disallowed, Form 5329 deals with addressing tax issues related to retirement accounts. Both forms represent mechanisms for taxpayers to correct or amend past mistakes or oversights in their tax filings, potentially reducing their tax burdens or avoiding penalties.
Finally, Form 8606, which is used to report nondeductible contributions to IRAs, is similar to Form 5329 in that both deal with the intricacies of retirement account contributions. Form 8606 helps taxpayers track their IRA basis to ensure that they are not taxed again upon withdrawal, whereas Form 5329 covers additional taxes due to specific activities or lack thereof within IRAs and other tax-advantaged accounts. Both forms are essential for accurately reporting activities within retirement accounts to ensure compliance with tax regulations and to optimize tax treatment of these funds.
Dos and Don'ts
The IRS Form 5329 is used to report additional taxes on IRAs and other tax-favored accounts. When filling out this form, following certain guidelines can help ensure the process is carried out correctly and efficiently. Here are the do's and don'ts to consider:
Do:- Read the instructions carefully before beginning, as they provide the necessary information on how to accurately complete the form.
- Use the most current version of Form 5329 to ensure compliance with the latest tax laws and regulations.
- Check your math twice to avoid errors that could result in incorrect tax calculations.
- Include your Social Security Number (SSN) so that your tax information is accurately recorded by the IRS.
- Attach Form 5329 to your tax return if you're required to file it as part of your annual tax documents.
- Estimate amounts; ensure all numbers are accurate and based on your financial documents.
- Ignore IRS notices regarding previous errors on Form 5329; correct any mistakes and respond promptly.
- Forget to sign the form if filing on paper, as an unsigned form may be considered invalid.
Misconceptions
The IRS Form 5329 is a document that often puzzles taxpayers. It deals with additional taxes on retirement plans, including IRAs, and other tax-favored accounts. Here, we'll clear up some common misunderstandings that cause confusion and worry.
Only for the retired: A big misconception is that Form 5329 is just for retired people. In reality, it concerns anyone with retirement accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s, regardless of age. It's about reporting specific transactions that may not follow standard rules, affecting both young savers and retirees alike.
It's only about penalties: While Form 5329 is indeed used to report additional taxes due to certain non-compliant activities, it's not solely focused on penalties. It's also a way to claim exemptions or report distributions not properly flagged by other forms.
Automatic filing by banks or institutions: Some people think that banks or financial institutions automatically file Form 5329 for them. That's not the case. Individuals are responsible for filing Form 5329 when necessary, as it requires personal information about their distributions and taxes.
You only file it when you withdraw from your IRA early: Early withdrawals from an IRA or other retirement accounts are a common reason to file Form 5329. However, other scenarios also necessitate its use, such as excess contributions, certain rollovers, or failing to take required minimum distributions after reaching a certain age.
No need to file if corrected excess contributions: If you've made an excess contribution to your IRA but corrected it within the allowable timeframe, you might think you don't need to file Form 5329. However, filing is still important to report the action taken and potentially avoid additional taxes.
Filing is complicated and needs a tax professional: While it's true that tax forms can be daunting, Form 5329 is designed to be straightforward if you have all the necessary information. Many people can complete it on their own, and software programs can guide you through it step by step.
Only for negative situations: It’s a common mistake to associate Form 5329 solely with mistakes or unfavorable events concerning retirement accounts. This form also allows taxpayers to report conditions that exempt them from penalties, essentially serving as a way to mitigate or avoid additional charges.
It's a one-time form: Thinking you only need to file Form 5329 once is a mistake. You may need to file it in any year when the applicable situations occur, such as taking distributions under specific exceptions or dealing with excess contributions for consecutive years.
No impact on federal tax return: Form 5329 directly affects your federal tax return because it calculates additional taxes or penalties that add to your overall tax liability. Ignoring it can result in owing more taxes or facing interest and penalties for underpayment.
Extensions for filing don't apply: Some believe that if they have an extension to file their tax return, it doesn't apply to Form 5329. This isn't true. An extension to file your tax return also includes additional forms like the 5329, allowing you extra time to gather information and report accurately.
Understanding Form 5329's purpose and requirements can save taxpayers from unnecessary stress and potential financial penalties. With proper attention and management, handling Form 5329 can be straightforward and help ensure your retirement savings remain on track.
Key takeaways
The IRS Form 5329 is a document used by taxpayers in the United States to report additional taxes on qualified plans, including IRAs, and other tax-favored accounts. Here are five key takeaways regarding filling out and using the IRS Form 5329:
- Identify If You Need to File: Typically, you need to file Form 5329 if you have early distributions, excess contributions to IRAs, or missed minimum required distributions. This form helps calculate any additional taxes owed.
- Determine Additional Taxes: Form 5329 is used to calculate extra taxes due to specific retirement account activities that do not comply with IRS rules. This includes a 10% early withdrawal penalty before age 59½, a 6% tax on excess contributions, and a 50% tax on insufficient minimum distributions.
- Gather Necessary Information: Before filling out Form 5329, gather all relevant financial statements and contribution records. This data is crucial for accurately reporting amounts and calculating any additional tax owed.
- Understand the Parts of Form 5329: The form is divided into multiple sections, each addressing different scenarios like early distributions or excess contributions. Ensure you only fill out the sections that apply to your situation to avoid unnecessary complications.
- File Form 5329 Timely: Submitting Form 5329 on time is important to avoid penalties and interest. It should generally be filed alongside your annual tax return, but specific situations might require different timing. Check the current IRS guidelines to confirm the due date for your circumstances.
Popular PDF Documents
433a Instructions - The IRS 433-A (OIC) is tailored for taxpayers seeking mercy from the IRS, using in-depth financial analysis to plead their case.
How to Chargeback - Fill out this form to contest a payment amount you received versus what you billed Amerigroup for a particular service.
