Get Irs 2758 Form
The Internal Revenue Service's Form 2758, revised in October 2004, serves a crucial function for various entities grappling with the deadlines imposed by the tax calendar. Designed to assist taxpayers in procuring additional time for filing an array of excise, income, information, and other returns, this application emphasizes the necessity for a meticulous process - including the requirement to file in duplicate. It's important to highlight that this form does not cater to all tax filings; for instance, corporate income tax return filers are directed towards Form 7004, highlighting the segmented approach the IRS employs for extension requests. Moreover, the form intricately details the information necessary for a successful application, from basic identification to the specifics of the tax year in question. Particular significance is placed on the reasons behind seeking an extension, with the IRS setting a clear expectation for a reasonable cause, beyond mere convenience. With the power to nullify the extension if found based on false premises, the seriousness with which this form must be approached becomes evident. Coupling these rigid requirements with the possibility of a granted 10-day grace period under specific conditions, Form 2758 represents a critical tool for taxpayers aiming to navigate the complexities of tax filing deadlines while avoiding penalties for late submissions.
Irs 2758 Example
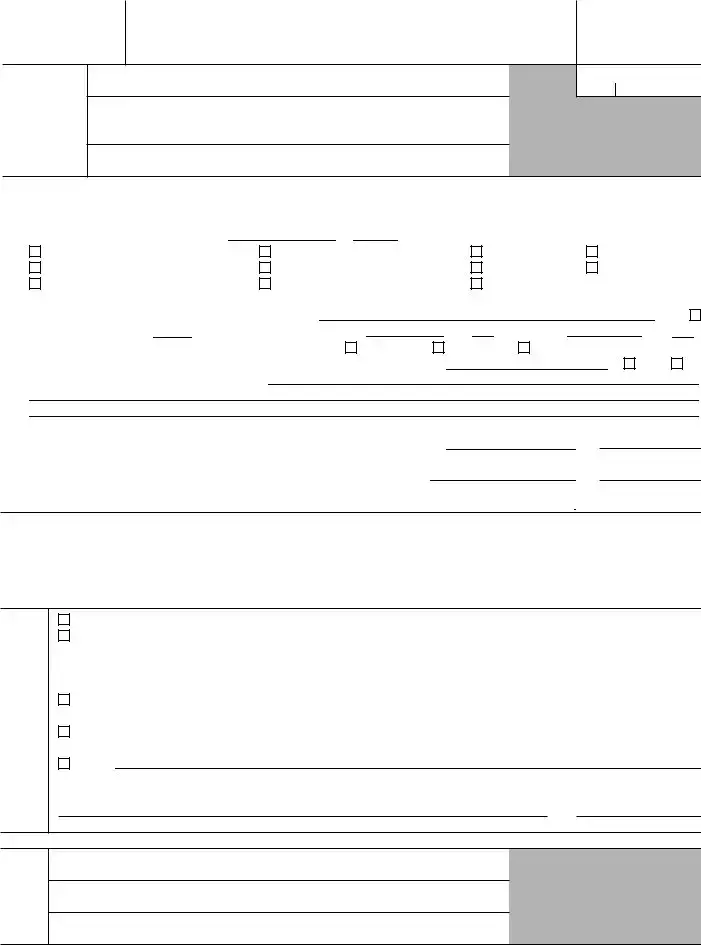
Form 2758 (Rev. October 2004)
Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service
Application for Extension of Time To File
Certain Excise, Income, Information, and Other Returns
� File a separate application in duplicate for each return.
OMB No.
Please type or print.
File the original and one copy by the due date for filing your return. See instructions on back.
Name
Number, street, and room or suite no. (or P.O. box no. if mail is not delivered to street address)
City, town or post office, state, and ZIP code. For a foreign address, see instructions.
Employer identification number
Note: Corporate income tax retur n filers must use FORM 7004 to request an extension of time to file. Partnerships, REMICs, and trusts must use FORM 8736. Organizations filing For ms 990,
1a I request an extension of time until
Form
Form
Form 1041 (estate)
,, to file (check only one):
Form 1042 |
Form 8612 |
Form |
Form 8613 |
Form |
Form 8725 |
Form 8804 Form 8831
bIf the organization does not have an office or place of business in the United States or Puerto Rico, or if your books
|
and records are not kept in the U.S., check this box |
|
|
|
|
� |
|
|
2a |
For the calendar year |
, or other tax year beginning |
|
, 20 |
and ending |
, 20 |
. |
|
b |
If this tax year is for less than 12 months, check reason: |
Initial return |
Final return |
Change in accounting period |
||||
3 |
Has an extension of time to file previously been granted for this tax year? |
|
|
|
Yes |
No |
||
4State in detail why you need the extension
5a If this extension is for Form |
|
8831, enter the tentative tax less any nonrefundable credits. See the instructions |
$ |
bIf this form is for Form 1041 (estate), 1042, or 8804, enter any refundable credits and estimated tax
payments made. Include any prior year overpayment allowed as a credit |
$ |
cBalance due. Subtract line 5b from line 5a. Include your payment with this form, or, if required, deposit
with FTD coupon or by using EFTPS (Electronic Federal Tax Payment System). See the instructions $
Signature and Verification
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined this form, including accompanying schedules and statements, and to the best of my knowledge and belief, it is true, correct, and complete; and that I am authorized to prepare this form.
Signature � |
Title � |
Date � |
File original and one copy. The IRS will show below whether or not your application is approved and will return the copy.
Notice
to
Applicant
To Be
Completed
by the
IRS
We have approved your application. Please attach this form to your return.
We have not approved your application. However, we have granted a
We have not approved your application. After considering the reasons stated in item 4, we cannot grant your request for an extension of time to file. We are not granting the
We cannot consider your application because it was filed after the due date of the return for which an extension was requested.
Other:
Director |
Date |
If you want a copy of this form to be returned to an address other than that shown above, please enter the address to which the copy should be sent.
Please
Type
or
Name
Number, street, and room or suite no. (or P.O. box no. if mail is not delivered to street address)
City, town or post office, state, and ZIP code. For a foreign address, see instructions.
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see back of form. |
Cat. No. 11976B |
Form 2758 (Rev. |
Form 2758 (Rev. |
Page 2 |
|
|
|
|
General Instructions
Section references are to the Internal Revenue Code unless otherwise noted.
Purpose of form. Use Form 2758 to request an extension of time to file any of the returns listed under line 1a, page 1.
When to file. File Form 2758 by the regular due date (or the extended due date if a previous extension was granted) of the return for which an extension is needed. However, to avoid a possible late filing penalty in case your request for an extension is not granted, you should file Form 2758 early enough to allow the IRS to consider your application and reply before the return’s regular or extended due date.
Where to file. Generally, file the original and one copy of this form with the Internal Revenue Service Center serving the taxpayer’s address.
However, file this form with the Internal Revenue Service Center, Philadelphia, PA 19255, if you are requesting an extension for Form 1042,
No blanket requests. File a separate
Form 2758 for each return for which you are requesting an extension of time to file. This extension will apply only to the specific return checked on line 1a. It does not extend the time for filing any related returns. For example, an extension of time for filing an estate’s income tax return will not apply to the individual income tax returns of the beneficiaries.
Also, trustees and disqualified persons filing Form
Reasons for extension. The IRS will grant a reasonable extension of time for filing a return. You must file an application on time and show reasonable cause why the return cannot be filed by the due date. Generally, we will consider the application based on your efforts to fulfill the filing requirements, rather than on the convenience of your tax return preparer. However, if your tax return preparer is not able to complete the return by the due date for reasons beyond his or her control or, in spite of reasonable efforts, you are not able to get professional help in time to file, the IRS will generally grant the extension.
Caution: If an extension is granted and the IRS later determines that the statements made on this form are false and misleading, the extension is null and void. You will be subject to the late filing penalty explained below.
Extension period. Generally, we will not grant an extension of time for more than 90 days unless sufficient need for an extended period is clearly shown. If you need an additional extension of time, file a second Form 2758 before the original extension expires. The total extension may not be for more than 6 months except for taxpayers who are abroad.
Interest. Interest is charged on any tax not paid by the regular due date of the return from the due date until the tax is paid. It will be charged even if you have been granted an extension or have shown reasonable cause for not paying on time.
Late payment penalty. Generally, a penalty of 1⁄2 of 1% of any tax not paid by the due date is charged for each month or part of a month that the tax remains unpaid. The penalty cannot exceed 25% of the amount due. The penalty will not be charged if you can show reasonable cause for not paying on time.
Late filing penalty. A penalty is charged if the return is filed after the due date (including extensions) unless you can show reasonable cause for not filing on time. The penalty is generally 5% of the tax not paid by the regular due date (even if an extension of time to pay has been granted) for each month or part of a month that the return is late, up to a maximum of 25% of the unpaid tax. For an income tax return filed more than 60 days late, the minimum penalty is $100 or the balance of the tax due on the return, whichever is smaller.
Different late filing penalties apply to information returns. See the specific form instructions for details.
Specific Instructions
Address. If your address is outside the United States, or its possessions or territories, enter the information on the line for “City, town or post office, state, and ZIP code” in the following order: city, province or state, and the name of the country. Follow the foreign country’s practice in placing the postal code in the address. Do not abbreviate the country’s name.
If your mailing address has changed since you filed your last return, use Form 8822, Change of Address, to notify the IRS of the change. A new address shown on Form 2758 will not update your record.
Line 1a. Check only one box. You must file a separate Form 2758 for each return for which you are requesting an extension.
Line 1b. If the box on line 1b is checked and your partnership’s books and records are kept outside of the United States and Puerto Rico, Form 8804 is due by the 15th day of the 6th month from the end of the partnership’s tax year. Otherwise, Form 8804 is due on the 15th day of the 4th month from the end of the partnership’s tax year.
Line 4. Describe in detail the reasons causing delay in your filing the return. We cannot approve applications that give incomplete reasons, such as “illness” or “practitioner too busy,” without adequate explanations. If a request for an extension is made only to gain time, we will deny both the extension request and the
Line 5a. See the specific form and instructions to estimate the amount of the tentative tax, reduced by any nonrefundable credits. If you expect this amount to be zero, enter
Line
Caution: If you are requesting an extension of time to file Form 1042, see the deposit rules in the instructions for that form to determine how payment must be made.
Signature. The person who signs this form may be:
●A distributee, or an authorized representative of a distributee, filing Form
●A trustee filing Form
●A principal officer of a corporate organization filing Form 8612 or 8613.
●A trustee or disqualified person filing Form
●A fiduciary, trustee, executor, administrator, or an officer representing the fiduciary or trustee filing Form 1041 for an estate.
●A withholding agent filing Form 1042.
●A person filing Form 8725 or 8831.
●A general partner or limited liability company member of a partnership filing Form 8804.
●An attorney or certified public accountant qualified to practice before the IRS.
●A person enrolled to practice before the IRS.
●A person holding a power of attorney.
Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notices. For the Privacy Act Notice regarding extensions of forms which may be filed by individuals, see the separate instructions for those forms. We ask for the information on this form to carry out the Internal Revenue laws of the United States. You are required to give us the information. We need it to ensure that you are complying with these laws and to allow us to figure and collect the right amount of tax.
You are not required to provide the information requested on a form that is subject to the Paperwork Reduction Act unless the form displays a valid OMB control number. Books or records relating to a form or its instructions must be retained as long as their contents may become material in the administration of any Internal Revenue law. Generally, tax returns and return information are confidential, as required by section 6103.
The time needed to complete and file this form will vary depending on individual circumstances. The estimated average time is:
Recordkeeping |
5 hr. |
Learning about the law |
|
or the form |
12 min. |
Preparing and |
|
sending the form to the IRS |
16 min. |
If you have comments concerning the accuracy of these time estimates or suggestions for making this form simpler, we would be happy to hear from you. You can write to the Internal Revenue Service, Tax Products Coordinating Committee, SE:W:CAR:MP:T:T:SP, 1111 Constitution Ave. NW, Washington, DC 20224. Do not send the tax form to this address. Instead, see Where to file above.
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Form Identification | Form 2758 (Rev. October 2004), Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service |
| Purpose | To request an extension of time to file certain excise, income, information, and other returns. |
| Submission Requirement | A separate application in duplicate for each return, filed by the due date for filing your return. |
| OMB Number | 1545-0148 |
| Exceptions for Specific Forms | Organizations and individuals with specific forms such as FORM 7004, FORM 8736, and FORM 8868, among others, must use those forms instead of Form 2758 for extension requests. |
| Application Deadline | Must be filed by the regular due date (or the extended due date if previously granted) of the return. |
| No Blanket Requests | Each return needing an extension requires a separate Form 2758; one extension does not apply to related returns. |
Guide to Writing Irs 2758
Completing the IRS Form 2758 is a necessary step for entities needing an extension of time to file certain tax returns beyond the prescribed due date. This process begins with understanding the specific type of return you are seeking to delay submission for, as spelled out in the form’s instructions. Each step is crucial for ensuring the form is properly processed, thereby granting the needed extension and avoiding potential penalties associated with late filings.
- First, locate the top section of Form 2758 labeled "Name" and enter the full name of the entity requesting the extension.
- Fill in the "Number, street, and room or suite no." with the entity’s official mailing address. If a street address is not applicable, include the P.O. box number.
- In the space provided for the city, town or post office, state, and ZIP code, type or print the appropriate location information. For entities with a foreign address, special instructions provided in the form should be followed.
- Input the "Employer identification number" in the designated space to ensure the application is accurately matched to the correct entity.
- Directly beneath, select the specific form for which an extension is being requested by checking the corresponding box under item 1a. Be aware that only one form can be selected per application.
- If the entity does not have an office or place of business in the United States or Puerto Rico, or if the books and records are not kept within the U.S., check the box under item 1b.
- Specify the applicable tax year in section 2a by including both the start and end dates.
- If the tax year listed is for less than 12 months, indicate the reason by checking the appropriate box under section 2b: Initial return, Final return, or Change in accounting period.
- In section 3, respond to the query on whether an extension has previously been granted for this tax year by checking ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ accordingly.
- Provide a detailed explanation for the extension request within section 4, ensuring it articulates a clear, legitimate reason grounded in unavoidable circumstances.
- Estimate the tentative tax less any nonrefundable credits for the relevant form in section 5a, and if applicable, enter any refundable credits and estimated tax payments made in section 5b. The balance due is stated in section 5c, which is the amount subtracted from line 5a by line 5b.
- Ensure the form is signed by an authorized individual who can legally represent the entity, filling in the signature, title, and date sections at the bottom of the form.
- Once completed, file the original and a copy of Form 2758 with the appropriate Internal Revenue Service Center by the return’s due date. The address where the form needs to be sent varies depending on the specific circumstances detailed within the form’s filing instructions.
This step-by-step process is designed to navigate entities through the application for an extension, streamlining what can be a complex procedure. Timely and accurate completion of Form 2758 facilitates the extension request, providing entities with additional time to gather the necessary documentation and ensure their tax returns are comprehensive and precise. Once the form is processed, the Internal Revenue Service will issue a notice regarding the approval or denial of the extension request, which will guide further action.
Understanding Irs 2758
-
What is the purpose of IRS Form 2758?
IRS Form 2758 is used to request an extension of time to file certain excise, income, information, and other returns. It is necessary when an individual or entity cannot file a return by the due date and needs additional time. However, it's important to note that separate applications must be filed in duplicate for each return.
-
When should I file Form 2758?
This form should be filed by the regular due date of the return for which an extension is requested. To avoid potential late filing penalties, it is advisable to submit Form 2758 well before the due date, allowing enough time for the IRS to consider and respond to the request.
-
Where do I file Form 2758?
Generally, you should file the original and one copy of Form 2758 with the Internal Revenue Service Center that serves your address. However, certain forms requiring an extension, such as Form 1042 or 3520-A, or requests made by entities without a principal office or business in the United States should be sent to the Internal Revenue Service Center in Philadelphia, PA 19255.
-
Can I request an extension for multiple returns with one Form 2758?
No, blanket requests are not allowed. You must file a separate Form 2758 for each return for which an extension is requested. The extension granted will only apply to the specific return indicated on the form.
-
What information is required to successfully obtain an extension?
You must file the application on time and demonstrate a reasonable cause for the inability to file by the due date. Simply stating you're ill or that your preparer is too busy without adequate explanation is not sufficient. Efforts made to fulfill filing requirements and circumstances beyond your or your preparer's control are considered by the IRS.
-
How long can the extension period be?
Extensions are generally not granted for more than 90 days unless a clear need for a longer period is shown. It's possible to request an additional extension by filing a second Form 2758 before the expiry of the original extension, but the total extension period cannot exceed six months, except for taxpayers abroad.
-
Does Form 2758 extend the time to pay taxes?
No, Form 2758 extends the time to file the return but does not extend the time to pay any taxes owed. To avoid interest and penalties, you should pay the estimated tax amount by the original due date. Ensuring you include the balance due with your extension request or make a payment using the appropriate method is crucial.
-
Who can sign Form 2758?
The form can be signed by: distributees or their authorized representatives; trustees; principal officers of corporate organizations; fiduciaries, trustees, executors, or administrators of an estate; withholding agents; general partners or LLC members of a partnership; attorneys or certified public accountants; persons enrolled to practice before the IRS; or persons holding a power of attorney.
Common mistakes
Not filing a separate application for each return needed: People often make the mistake of trying to request extensions for multiple returns on a single Form 2758. This form requires a separate application for each return.
Filing late: Another common mistake is not filing Form 2758 by the due date of the return for which an extension is needed. It’s vital to submit the application early enough to allow time for the IRS to respond before the original or extended due date.
Incorrect filing address: Depending on the type of return and the taxpayer's location, there are specific IRS Service Centers where Form 2758 must be filed. Using the wrong address can delay processing.
Inadequate reasons for extension: The IRS requires a detailed explanation of why the extension is needed. General reasons like "too busy" or "out of town" without thorough explanation are not sufficient and can lead to denial.
Not estimating taxes accurately: For certain forms, the applicant must enter an estimate of the tentative tax less any nonrefundable credits (line 5a) and/or refundable credits and payments (line 5b). Incorrect estimates can affect the balance due calculation.
Not signing the form: The form must be signed by an authorized individual, such as a principal officer for a corporate organization or a trustee for an estate. Unsigned forms will not be processed.
Common mistakes include not understanding the specific requirements for each type of return listed in Form 2758 and not realizing that this form does not extend the time to pay taxes due. Ensuring the form is complete, accurate, and submitted on time, with proper reasons for the extension and an accurate estimation of taxes due, can help avoid delays and penalties.
Documents used along the form
When preparing documentation related to IRS Form 2758, several other forms and documents might be relevant and useful. These documents facilitate comprehensive compliance with IRS requirements, support the extension application, and ensure accurate financial reporting. Below are descriptions of up to six such forms that are commonly used in conjunction with Form 2758.
- Form 7004 (Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns): This form is used by corporations, partnerships, REMICs, and trusts to request an automatic extension of time to file various business and information returns.
- Form 8809 (Application for Extension of Time to File Information Returns): Primarily used by businesses and organizations to request an extension of time to file information returns such as Forms W-2, 1099, and 1098. This form is crucial for entities that need additional time to gather or verify information required for submission.
- Form 8868 (Application for Extension of Time To File an Exempt Organization Return): Non-profit and tax-exempt organizations use this form to request an extension of time to file their annual tax returns. Forms affected include 990, 990-EZ, 990-PF, among others.
- Form 1040-ES (Estimated Tax for Individuals): While requesting an extension to file, individuals may need to estimate and pay taxes due using Form 1040-ES. This form helps avoid penalties for underpayment of estimated tax throughout the year.
- Form 8822 (Change of Address): If there’s been a change of address since the last filing, this form notifies the IRS of the new address to ensure that any correspondence or returned documents reach the taxpayer promptly.
- Form 4868 (Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return): Used by individuals to request an extension of time to file their personal income tax return (Form 1040). It’s relevant for taxpayers who also need to file Form 2758 in association with their business or other income-related duties.
Each of these documents serves its unique purpose in the spectrum of tax preparation and filing. They play significant roles, from securing additional time for accurate submission of returns to adjusting taxpayer details and estimating taxes due. Being aware of these forms and understanding their use is crucial for complete and timely compliance with IRS regulations.
Similar forms
The Form 7004, Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns, parallels the IRS Form 2758 in its primary function—to request more time for filing tax-related documents. While Form 2758 caters to a specific subset of taxes, including certain excise, income, information, and other returns, Form 7004 is directed towards businesses requiring additional time to file their income tax and information returns. Both forms necessitate that the filer submits the request by the original due date of the return to avoid late filing penalties, illustrating the core similarity in their procedural use.
Form 8736, Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File U.S. Return for Partnership, REMIC, or for Certain Trusts, also shares commonality with Form 2758 by serving as a mechanism to request extra time for filing taxes. Specifically targeting partnerships, real estate mortgage investment conduits (REMICs), and certain trusts, Form 8736 accommodates a different taxpayer subgroup compared to Form 2758. Despite this distinction in audience, both forms offer a relief pathway for filers unable to meet the original filing deadline, underlining their similarity in purpose and functionality.
Organizations seeking more time to file forms such as 990, 990-EZ, and others can utilize Form 8868, Application for Extension of Time To File an Exempt Organization Return. Much like Form 2758, Form 8868 assists taxpayers in requesting additional filing time, albeit tailored for exempt organizations. Both documents are crucial for compliant tax practices, allowing varied entities—the former extending to a broad range of taxpayers, and the latter to tax-exempt organizations—to manage and fulfill their filing obligations within an extended timeframe.
Form 8809, Application for Extension of Time To File Information Returns, resembles Form 2758 in that it applies to a broad range of information returns, such as Form 1042-S for foreign persons. Its main purpose is to grant filers a reprieve from the original due date, a hallmark feature shared with Form 2758. Both forms cater to distinct tax document requirements, yet their similarity lies in the fundamental service they provide—extending the filing deadline to ensure thorough and accurate tax reporting.
Form 4868, Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, though aimed at individual filers, shares a common goal with IRS Form 2758: to provide taxpayers additional time to file their returns. Despite serving different tax filer categories, with Form 4868 specifically designed for individual income tax returns, both forms are instrumental in alleviating the pressure of the filing deadline, emphasizing their role in taxpayer assistance and compliance.
Form 2350, Application for Extension of Time To File U.S. Income Tax Return, particularly serves U.S. citizens and resident aliens abroad who need more time to qualify for certain tax benefits. This form's specialized focus contrasts with the broader application range of Form 2758, but parallels it in providing a means to extend filing deadlines under specific criteria, thereby reflecting a shared purpose in facilitating tax compliance under extenuating circumstances.
Form 5558, Application for Extension of Time To File Certain Employee Plan Returns, offers a targeted approach to extending deadlines for filing pension and benefit plan returns. While this form caters to a niche aspect of tax obligations, its core functionality aligns with that of Form 2758—both enable an extension for filers under particular classifications, underscoring their similar utility in tax administration despite differing scopes.
Form 7004, distinct from its aforementioned use for businesses, also supports specific requests for extension related to foreign trusts by filing Form 3520-A, highlighting the versatility and wide applicability of extension applications across various tax responsibilities. This aspect of Form 7004 demonstrates a broader parallel with Form 2758 concerning the wide-ranging impact of extension applications in tax practice, embodying the critical role of these documents in ensuring comprehensive compliance and reporting.
Finally, Form 8992, U.S. Shareholder Calculation of Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income (GILTI), does not directly offer an extension but necessitates accurate and timely filing influenced by the extensions granted through forms like 2758. While not an extension form, the meticulous filing requirements and the potential need for additional time to gather and calculate international income underscore the indirect relationship between specific tax obligations and the general utility of filing extensions as facilitated by forms like IRS 2758.
In summary, while each of these documents serves different segments of the taxpaying public and pertains to varied types of tax obligations, the underlying similarity among them and Form 2758 is their provision for additional time to file. This critical function ensures taxpayers can meet their filing obligations accurately and comprehensively, reflecting the overarching goal of the tax filing extension system.
Dos and Don'ts
When filing the IRS Form 2758, navigating the do’s and don'ts ensures a smoother process for requesting an extension of time to file certain tax returns. By adhering to these guidelines, taxpayers can improve their chances of having their extension request approved without unnecessary delays or issues.
- Do file Form 2758 by the original due date of your return to avoid potential late filing penalties.
- Do file a separate application in duplicate for each return for which you're requesting an extension.
- Do provide a detailed explanation in Line 4 regarding why you need the extension to clearly state your case to the IRS.
- Do check the correct box on Line 1a to indicate for which form you're requesting an extension; this is crucial for correct processing.
- Do ensure that you sign and date the form to validate your request officially. Unsigned forms are not processed.
- Don't forget to include any due payments with your Form 2758; this form does not extend the time for tax payment.
- Don't wait until the last minute to submit this form; submitting it close to the deadline may not leave enough time for IRS response.
- Don't use Form 2758 if you belong to one of the categories that must use a different form for extension requests as specified in the instructions.
- Don't omit your Employer Identification Number (EIN) or other identifying information, as it ensures your request is correctly attributed to your tax records.
Filing Form 2758 with accuracy and attention to these points will assist in the timely and successful processing of your extension request. Remember, this extension applies only to the filing of the return, not to any payment due, so plan accordingly to avoid interest and penalties.
Misconceptions
Understanding the IRS Form 2758 can be complex, and several misconceptions surround its purpose and use. Here, we aim to clarify some of these misconceptions to provide a clearer understanding of the form and its requirements.
Misconception 1: Form 2758 grants an extension for any IRS tax filing.
In reality, Form 2758 is specifically used to request an extension of time to file certain excise, income, information, and other returns. It is not a universal form for all types of tax filings. For example, corporate income tax return filers must use Form 7004, not Form 2758, to request an extension.Misconception 2: Submitting Form 2758 automatically extends the payment deadline for taxes owed.
Submitting Form 2758 only requests an extension to file the return, not an extension to pay any taxes owed. Interest and penalties may still apply for taxes not paid by the original due date.Misconception 3: You can use Form 2758 for an extension on personal income tax returns.
Form 2758 cannot be used for personal income tax extensions. Individuals looking to extend the filing deadline for personal income taxes must use Form 4868.Misconception 4: Filing Form 2758 can grant extensions longer than six months.
Generally, the IRS does not grant extensions longer than six months, except for taxpayers who are out of the country. The form itself outlines that the extension period is typically limited to 90 days unless a clear need for a longer extension is demonstrated.Misconception 5: You can file a blanket request on Form 2758 for multiple returns.
Each return requiring an extension necessitates its own Form 2758. This form does not allow for blanket requests, which means a separate application must be filed in duplicate for each individual return.Misconception 6: The reasons for requesting an extension can be vague or generic.
When requesting an extension via Form 2758, the reasons must be detailed and specific. Generic reasons such as "too busy" or "out of the country" without adequate explanation are insufficient. The IRS requires a clear and substantial reason for the delay in filing.
By dispelling these misconceptions, taxpayers can better understand how and when to use Form 2758 accurately, ensuring compliance with IRS requirements and avoiding unnecessary penalties.
Key takeaways
Filling out and using the IRS Form 2758 involves several key steps and understandings for requesting an extension for time to file various returns. Below are six essential takeaways to guide you through this process:
- Submit Applications Early: It's advisable to file Form 2758 well before the original or extended filing deadline. This timing ensures the IRS has enough time to consider your request and respond, helping you avoid potential late filing penalties.
- Separate Applications for Each Return: You must file a separate application in duplicate for each tax return needing an extension. This individual approach is important because an extension granted for one return does not extend the filing period for any related returns.
- Detailed Reasons for Extension: When requesting an extension, the IRS requires you to provide a detailed explanation of why the return cannot be filed by the due date. Vague reasons like "illness" without further explanation are insufficient and may result in a denial of the extension request.
- No Extension for Payment Deadline: Importantly, Form 2758 does not extend the time to pay taxes due. To avoid interest and penalties, it's critical to pay the estimated tax owed with your extension request.
- Signature Requirements: The form must be signed by an authorized individual. Depending on the type of return being extended, this can include a principal officer, trustee, executor, or even a certified public accountant or attorney representing the filer.
- Specific Exclusions: Form 2758 cannot be used for extending the filing time for all types of returns. For instance, corporate income tax filers must use Form 7004, and partnerships, REMICs, and trusts should use Form 8736, highlighting the importance of choosing the correct form for your specific filing needs.
By following these guidelines, individuals and entities can navigate the process of requesting tax filing extensions more efficiently, ensuring compliance with IRS requirements and avoiding unnecessary penalties.
Popular PDF Documents
Tax POA 3520-PIT - Offers a straightforward approach to authorizing a qualified representative to address and manage personal income tax obligations.
Formula for Marked Price - Summarizes the key components that affect the financial outcomes of taxis operated by contracted drivers.
