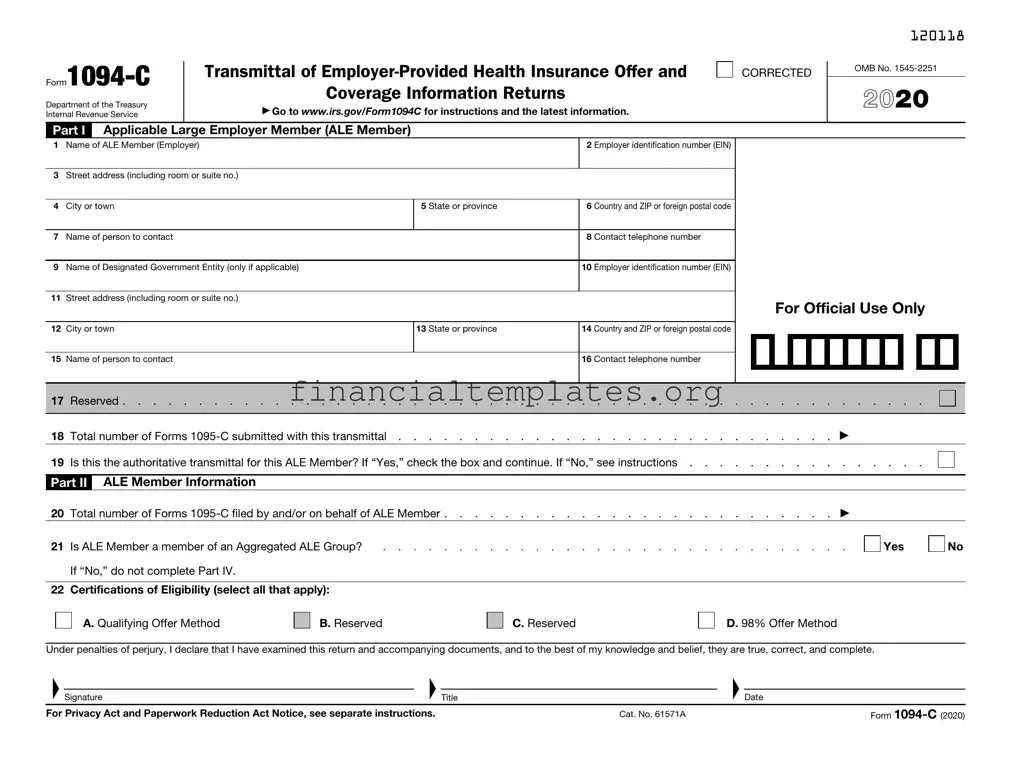
Get IRS 1094-C Form
In the landscape of U.S. tax documentation and compliance, various forms play pivotal roles in ensuring that both individuals and organizations meet their reporting obligations. Among these, the IRS 1094-C form emerges as a crucial document for certain large employers who are tasked with reporting health insurance coverage information under the Affordable Care Act (ACA). This form serves not only as a testimonial of the employer's offer and provision of health insurance to their full-time employees but also acts as a compliance document that aids in the administration of the government's health care policy. Employers required to file this form are categorized under the ACA's employer mandate, which necessitates offering minimum essential coverage that is affordable and meets minimum value to their full-time employees and their children. The intricate nuances of the form’s contents, alongside its implications on employer reporting requirements, underscore its importance in the broader context of federal health policy enforcement and the facilitation of individual health insurance marketplace operations.
IRS 1094-C Example
|
Transmittal of |
||
|
|||
Department of the Treasury |
|
Coverage Information Returns |
|
|
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/Form1094C for instructions and the latest information. |
||
Internal Revenue Service |
|
||
|
|
|
|
Part I |
Applicable Large Employer Member (ALE Member) |
||
CORRECTED
120118
OMB No.
2021
1 Name of ALE Member (Employer) |
2 Employer identification number (EIN) |
|
|
|
|
3Street address (including room or suite no.)
4 |
City or town |
5 |
State or province |
6 |
Country and ZIP or foreign postal code |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Name of person to contact |
|
|
8 |
Contact telephone number |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
Name of Designated Government Entity (only if applicable) |
|
|
10 |
Employer identification number (EIN) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
Street address (including room or suite no.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For Official Use Only |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
City or town |
13 |
State or province |
14 |
Country and ZIP or foreign postal code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
Name of person to contact |
|
|
16 |
Contact telephone number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 Reserved |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 Total number of Forms |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ▶ |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
19 Is this the authoritative transmittal for this ALE Member? If “Yes,” check the box and continue. If “No,” see instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Part II ALE Member Information
20 |
Total number of Forms |
. . . |
. |
. |
. . . . . . . |
▶ |
|
||||
21 |
Is ALE Member a member of an Aggregated ALE Group? |
. . . |
. |
. |
. . . . . . . |
. |
Yes |
||||
|
If “No,” do not complete Part IV. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
Certifications of Eligibility (select all that apply): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
A. Qualifying Offer Method |
|
B. Reserved |
|
C. Reserved |
|
|
|
D. 98% Offer Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined this return and accompanying documents, and to the best of my knowledge and belief, they are true, correct, and complete.
▲ |
|
▲ |
|
▲Date |
Signature |
Title |
No
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see separate instructions. |
Cat. No. 61571A |
Form |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
120218 |
Form |
|
|
|
|
Page 2 |
|||
Part III |
ALE Member |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
(a) Minimum Essential Coverage |
(b) Section 4980H |
(c) Total Employee Count |
(d) Aggregated |
(e) Reserved |
||
|
|
Offer Indicator |
|
|||||
|
|
|
Employee Count for ALE Member |
for ALE Member |
Group Indicator |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Yes |
|
No |
|
|
|
|
23 |
All 12 Months |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
Jan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
Feb |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
Mar |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
Apr |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
May |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
June |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
July |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
Aug |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
Sept |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
Oct |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
Nov |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
Dec |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form
|
|
120316 |
Form |
Page 3 |
|
Part IV |
Other ALE Members of Aggregated ALE Group |
|
Enter the names and EINs of Other ALE Members of the Aggregated ALE Group (who were members at any time during the calendar year).
Name |
EIN |
Name |
36 |
|
51 |
|
||
37 |
|
52 |
38 |
|
53 |
39 |
|
54 |
40 |
|
55 |
41 |
|
56 |
42 |
|
57 |
43 |
|
58 |
44 |
|
59 |
45 |
|
60 |
46 |
|
61 |
47 |
|
62 |
48 |
|
63 |
49 |
|
64 |
50 |
|
65 |
|
|
|
EIN
Form
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose of Form 1094-C | The form serves as a transmittal document for Form 1095-C and provides the IRS with summary information about an employer’s offer of health coverage and the enrollment in this coverage by employees. |
| Applicable Employers | It is required to be filed by employers subject to the Affordable Care Act’s employer mandate, generally those with 50 or more full-time employees, including full-time equivalent employees. |
| Filing Requirement | Employers must file Form 1094-C along with Form 1095-C for each employee who was full-time for one or more months of the calendar year. |
| Deadline for Filing | Form 1094-C must be filed by February 28th if filing on paper, or March 31st if filing electronically, of the year following the calendar year to which the forms relate. |
| Electronic Filing Requirement | Employers filing 250 or more Forms 1095-C must file them electronically, including the transmittal Form 1094-C. |
| Penalties for Non-compliance | Failure to file or correctly report information may result in significant penalties from the IRS, including fees for each return that is late, incomplete, or incorrect. |
| State-specific Forms | Some states have their own healthcare reporting requirements that may necessitate additional forms. The governing laws vary by state, so employers should consult state regulations. |
| Part III of Form 1094-C | This section collects information about the employer’s offer of health insurance coverage, including whether the offer was made to full-time employees and their dependents. |
| Correcting Form 1094-C | If an employer finds an error in a submitted Form 1094-C, they must correct the error and resubmit the form to the IRS, along with a corrected Form 1095-C for any affected employee. |
Guide to Writing IRS 1094-C
Filling out the IRS 1094-C form is a critical process for employers to comply with the Affordable Care Act's reporting requirements. This form serves as a cover sheet for submitting Form 1095-C information returns to the IRS, providing summaries of healthcare coverage offered and provided to employees. The proper completion of this form is paramount to avoid penalties and ensure compliance. Below, you'll find a straightforward, step-by-step guide designed to simplify the process, ensuring accuracy and timeliness in your submission.
- Start by gathering necessary information, including the employer’s identification number (EIN), the name and contact information of the employer, and the total number of 1095-C forms being submitted.
- In Part I, provide the employer's basic information. Fill in the lines for the full name of the Applicable Large Employer member, the EIN, street address, city or town, state or province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code.
- For Part II, if the employer is a member of an Aggregated ALE group, check the box on line 21 and complete Part III by listing the names and EINs of each member of the Aggregated ALE group. If not, simply skip to line 22.
- In line 22, indicate if you are certifying eligibility for any of the transitional relief options. Check the appropriate box(es) if applicable. If none apply, leave this section blank.
- Part III, columns (a) through (e), require detailed information about the ALE member each month. Include the total number of full-time employees, total employee count, information on whether the minimum essential coverage was offered, and if the coverage meets affordability standards.
- In Part IV, list the names and EINs of all the entities that are part of the Aggregated ALE Group, if applicable. Ensure all information is accurate and corresponds with the records for each entity listed.
Upon completing the IRS 1094-C form, review it thoroughly to ensure all information is accurate and complete. Missing or incorrect information can lead to processing delays or penalties. After reviewing, submit the form alongside the corresponding 1095-C forms for all relevant employees by the prescribed deadline. Remember, careful attention to detail and adherence to instructions are the keys to successful compliance with the Affordable Care Act's reporting requirements.
Understanding IRS 1094-C
-
What is the IRS 1094-C Form used for?
The IRS 1094-C form serves a crucial role in compliance with the Affordable Care Act (ACA). It is used by employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent employees to report information about the health insurance coverage, if any, they offered to their full-time employees. This form helps the IRS determine whether an employer has met the ACA's requirements for offering affordable health coverage.
-
Who is required to file the IRS 1094-C form?
Employers with 50 or more full-time or full-time equivalent employees, often referred to as Applicable Large Employers (ALEs), are required to file the IRS 1094-C form. This requirement is part of the employer's responsibility under the ACA's employer mandate.
-
What are the deadlines for filing the IRS 1094-C form?
Typically, the IRS 1094-C form must be filed by February 28th if filing on paper or March 31st if filing electronically for the previous calendar year. However, the IRS may extend these deadlines, so it is essential to stay informed of any announced changes.
-
Can the IRS 1094-C form be filed electronically?
Yes, the IRS 1094-C form can be filed electronically, and it is encouraged for organizations filing 250 or more forms. Filing electronically simplifies the submission process and allows for an extended filing deadline.
-
What information is needed to complete the IRS 1094-C form?
- Employer's name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN)
- The total number of employees for each month of the year
- Information on the health coverage offered to full-time employees, if any
- The total number of 1095-C forms distributed to employees
- Certification of eligibility and offers of health insurance coverage
-
What are the penalties for failing to file the IRS 1094-C?
Employers who fail to file the IRS 1094-C form, or file late, can face significant penalties. The penalty amount depends on how late the form is filed and the size of the employer. The IRS updates these penalties annually, so employers should consult the latest information to stay compliant.
-
How does the IRS 1094-C form affect employees?
While the IRS 1094-C form is primarily a reporting requirement for employers, it indirectly affects employees by ensuring that they receive affordable health coverage as mandated by the ACA. Employees may receive a copy of the related Form 1095-C, which provides detailed information about their own health coverage and is useful for completing their personal tax returns.
Common mistakes
Filing your taxes can sometimes feel like navigating a labyrinth, especially when dealing with forms as complex as the IRS 1094-C. This form, integral to the Affordable Care Act's employer mandate, requires accuracy and a keen eye for detail. Here are four common mistakes people often make when filling out the IRS 1094-C form:
Incorrect Employer Information: It's surprisingly easy to make errors in the basic details about your organization. Mismatching employer identification numbers (EINs) or providing incorrect business names can lead to processing delays or mismatches in IRS records. Always double-check these fundamentals before submission.
Failure to Report All Full-Time Employees: Often, employers overlook or misunderstand the criteria for full-time status. The IRS requires all full-time employees (those working 30 hours or more per week) to be reported. Missing out on including any full-time employee can lead to compliance issues and penalties.
Incorrectly Entered Codes: The 1094-C form comes with a series of indicator codes in Part II, used to convey information about the offered health coverage. Misinterpreting these codes or entering them inaccurately can lead to the IRS receiving incorrect information about the coverage options you provide, affecting your compliance status.
Omitting or Inaccurately Reporting Covered Individuals: For employers offering self-insured health plans, accurately reporting every individual covered is crucial. An incomplete or erroneous count can affect the accuracy of the information provided to the IRS, potentially leading to penalties for non-compliance.
Avoiding these mistakes requires a careful approach and a thorough understanding of the form's requirements. It's vital to:
- Review the instructions provided by the IRS carefully,
- Consult with a tax professional or legal advisor if you’re unsure about any aspect of the form,
- Use the IRS’s resources and tools designed to aid in filling out the form correctly,
- Double-check all entered information before submission to ensure everything is accurate and complete.
By staying informed and vigilant during this process, you can avoid common pitfalls and help ensure your organization remains compliant with the Affordable Care Act's requirements.
Documents used along the form
Employers grappling with health coverage reporting requirements might find the IRS 1094-C form familiar. It serves as a transmittal form for the 1095-C forms, which must be filed by employers with 50 or more full-time employees or equivalents to report the health insurance coverage offered to their employees. Accompanying this crucial document, several other forms and documents are typically utilized to ensure compliance with the Affordable Care Act (ACA) requirements and to streamline the reporting process. Understanding these documents can significantly ease the burden of annual reporting obligations.
- IRS 1095-C: This form provides details on the health insurance coverage offered to each employee. Employers need it to report information on health coverage to the IRS and to employees.
- IRS 1095-B: Issued by health insurance providers, it provides information about individuals' health coverage, including who was covered and when. This form is crucial for individuals proving they have met the health coverage requirements.
- IRS 8962: This form is used for the Premium Tax Credit (PTC). It's filed by individuals who purchase health coverage through the Health Insurance Marketplace and wish to claim the tax credit or reconcile advance payments of the credit.
- Form W-2: The Wage and Tax Statement. Employers report employee annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld from their paychecks. Relevant here because it also reports the cost of employer-sponsored health coverage to employees.
- IRS 1094-B: Similar to the 1094-C, this transmittal form is used by health insurance providers when submitting 1095-B forms to the IRS.
- IRS 945: This annual return reports federal income tax withheld from nonpayroll items, including backup withholding and withholding on pensions, annuities, and IRAs. Employers might use this form in conjunction with ACA reporting if they have withholding obligations unrelated to payroll.
- State-specific health coverage forms: Some states have implemented their health coverage mandates and require additional reporting. These forms vary by state but serve a similar purpose to the 1095 forms, reporting health insurance coverage to state tax authorities.
- Data reporting worksheets: Though not official IRS forms, these internally used documents help employers compile and track the necessary information for ACA reporting. They are especially useful when preparing the 1094-C and 1095-C forms.
In addition to these forms and documents, employers often rely on payroll and benefits administration software to manage and report health coverage information accurately. While the process of ACA reporting may seem daunting, familiarizing yourself with these key forms and utilizing available resources can streamline the task, ensuring that all requirements are met efficiently and accurately.
Similar forms
The IRS 1094-C form, a critical component in reporting information about health insurance coverage offered by employers, shares similarities with the IRS 1095-C form. The 1095-C form provides details about the health insurance coverage offered to each employee, acting as a companion document to the 1094-C. Both are essential for compliance with the Affordable Care Act (ACA) requirements, verifying that employers offer affordable and minimum standard health coverage to their full-time employees.
Similar in function to the IRS 1094-C form, the IRS 1094-B form serves as a transmittal document for the 1095-B forms. While the 1094-C is used by large employers, the 1094-B is utilized by providers of health coverage, including insurance companies and small employers that provide employer-sponsored health insurance. Both forms play a pivotal role in reporting individuals' health coverage information to the IRS.
The IRS 1095-B form is akin to the 1095-C form but is used by small employers and health insurance providers to report on individuals’ health coverage. Whereas the 1095-C form is more relevant to individuals employed by large employers, the 1095-B provides necessary health coverage information from other sources, showcasing how these documents collectively ensure compliance with health coverage reporting under the ACA.
Similar to the IRS 1094-C, the W-2 form is an essential document for employees, providing a summary of their annual earnings and the taxes withheld. Both forms are submitted to the IRS and serve to ensure compliance with federal tax obligations, offering a detailed account of an individual’s employment and financial status throughout the fiscal year.
The IRS Form 940 resembles the 1094-C in its role of reporting to the federal government, focusing on unemployment taxes employers must pay. Like the 1094-C ensures compliance with health insurance reporting requirements, Form 940 ensures employers contribute to the federal unemployment tax system, aiding workers who have lost their jobs.
IRS Form 941 shares a foundational relationship with the 1094-C form, as both are intended for employer reporting. While the 1094-C pertains to reporting health insurance coverage, Form 941 is used to report employees' federal income tax withholdings and Social Security and Medicare taxes. The critical nature of both ensures that employers meet their respective reporting responsibilities.
Form W-3, similar to the IRS 1094-C, functions as a summary report, but for W-2 forms submitted by an employer. It consolidates information regarding the total earnings, Social Security wages, Medicare wages, and withholding for all employees. Both the W-3 and the 1094-C compile detailed employment information for submission to government bodies, ensuring accurate reporting and compliance.
The IRS Form 8955-SSA is analogous to the 1094-C, as it also involves reporting specific information to the federal government, specifically deferred vested benefits information under the plan. This ensures that employees' rights to pensions are accurately recorded and reported, similar to how the 1094-C monitors compliance with health coverage provisions under the ACA.
Form 5500, required by the Department of Labor, shares common goals with the 1094-C form by requiring annual reporting from pension and welfare benefit plans. This ensures transparency and compliance with rules governing the management and operation of these plans, paralleling the health insurance reporting obligations mandated by the 1094-C form for employers.
The IRS 1099 forms, particularly relevant to freelance and contract workers, provide information on various types of income outside of traditional employment. While significantly different in specifics, they share the 1094-C's underlying intent of ensuring individuals and entities report their income or benefits to the IRS accurately, facilitating a comprehensive tax reporting system.
Finally, the IRS Form 4868, while not directly related to employment or health coverage reporting, is similar in providing a means for compliance with federal tax obligations by allowing taxpayers to request an extension to file their income tax return. This parallels the 1094-C's role in promoting compliance with federal mandates, albeit in the realm of health insurance.
Dos and Don'ts
Filling out the IRS 1094-C form, a crucial document required for reporting an individual's health insurance offerings under the employer mandate of the Affordable Care Act, demands attention to detail and an understanding of the form’s requirements. Ensuring the form is completed accurately is vital for both employers and employees to comply with federal regulations. Below are essential dos and don'ts that should be followed when handling this important document:
Do:
- Verify all employee information for accuracy before submission, including full names, social security numbers, and coverage details. This step is critical in preventing errors that could lead to processing delays or penalties.
- Use the official IRS instructions for the 1094-C form as a guide. These instructions offer valuable insights and specific guidelines on how to fill out each section correctly.
- Include all necessary information regarding health coverage offerings, even if some parts may seem redundant or unnecessary. Every detail contributes to a comprehensive understanding of the coverage provided.
- Keep a copy of the completed form and any correspondence from the IRS regarding the form. This record-keeping can be incredibly important for reference in future queries or audits.
Don't:
- Overlook the importance of the deadlines. Submitting the 1094-C form late can lead to penalties. Always aim to have the form prepared and sent well before the due date to avoid any last-minute issues.
- Fill out the form without checking the latest updates or versions from the IRS. Tax laws and form requirements can change, and using an outdated version of the form could result in inaccuracies or rejections.
- Guess on any information. If there is uncertainty about what is required in certain sections, it is better to seek clarification than to submit incorrect information. Misinformation can lead to complications and potential legal challenges down the road.
- Ignore error notices from the IRS. If errors are identified after submission, it is crucial to address and correct them promptly. Ignoring these notices can exacerbate the issue and increase the likelihood of penalties.
Misconceptions
The IRS 1094-C form plays a critical role in how organizations report health insurance coverage offered to their employees under the Affordable Care Act (ACA). However, there are several misconceptions surrounding this form that can lead to confusion and errors in compliance. Below are four common misunderstandings:
- Only large corporations need to file the IRS 1094-C. This statement is misleading. The requirement to file the IRS 1094-C form applies to any employer considered an Applicable Large Employer (ALE) under the ACA. An ALE is defined as an employer with 50 or more full-time employees, including full-time equivalent employees, on average during the previous year. This definition means that not only large corporations but also mid-sized businesses may need to file depending on their employee count.
- The IRS 1094-C form only needs to be filed annually. While it’s true that the form is filed annually, this description simplifies the process too much. Employers must collect and maintain monthly data on health insurance coverage throughout the year. This ongoing data collection is crucial because the form requires detailed information for each month about the offer of insurance to employees. Therefore, the filing involves a year-long process of data management and not just a once-a-year event.
- If you outsource payroll, you don't need to worry about the IRS 1094-C. Outsourcing payroll does not absolve employers of their responsibilities to comply with ACA reporting requirements. While a third-party payroll service can assist in gathering data and even submitting forms on behalf of an organization, the legal responsibility for accurate and timely filing remains with the employer. It’s important for employers to ensure their payroll provider fully understands ACA requirements and accurately reports the necessary information on forms 1094-C and 1095-C.
- Correcting mistakes on the IRS 1094-C is a straightforward process. Unfortunately, amending errors on the IRS 1094-C can be complex. The process depends on the nature and extent of the mistakes. Simple errors may require a corrected submission, but significant inaccuracies can lead to penalties or necessitate more involved communications with the IRS to resolve. Employers should exercise utmost care in preparing their filings to avoid complications that arise from needing to correct submitted information.
Understanding these misconceptions is vital for employers to ensure compliance with the ACA and avoid potential penalties. Staying informed about the requirements and seeking guidance when necessary can help tremendously in navigating the complexities of IRS Form 1094-C reporting.
Key takeaways
The IRS Form 1094-C is an important document for employers required to comply with the Affordable Care Act's (ACA) Employer Mandate. Here are four key takeaways about filling out and using this form effectively:
- The form serves as a cover sheet for the 1095-C forms, which report health insurance coverage offered to employees. Its primary role is to provide a summary to the IRS, making accuracy paramount.
- Employers classified as Applicable Large Employers (ALEs), typically those with 50 or more full-time employees, including full-time equivalents, in the previous year, are required to file Form 1094-C. It's essential to understand your organization's classification to comply appropriately.
- Filing deadlines are critical. Form 1094-C, along with the 1095-C forms for all full-time employees, must usually be filed by February 28th if filing on paper, or March 31st if filing electronically, of the year following the reported year. Late filings can lead to penalties, making timely submission crucial.
- Electronic filing is mandatory for organizations filing 250 or more forms. However, it's encouraged for all employers due to its efficiency and reliability. For those with fewer forms, electronic filing is an option that can simplify the process and help avoid mistakes.
Paying close attention to these key points can help ensure compliance with the ACA's reporting requirements, avoiding penalties while ensuring that employees are accurately informed about their health coverage options. As always, consulting with a professional for complex situations is advisable to navigate the specifics of your organization's needs.
Popular PDF Documents
Ohio Energy Company - For adjustments or errors in credit entries, FirstEnergy can initiate debit entries to the employee's account.
Minnesota No Sales Tax - Contractors working with exempt organizations may use the ST3 form to purchase materials for specific projects tax-free.
Broward Tax Collector Plantation - Crucial for maintaining the integrity and safety of the business environment in Miami through regulatory compliance.