Get IRS 1042-S Form
Navigating the complexities of tax documentation is essential for individuals and organizations involved in international financial transactions. Among the various forms the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) mandates, the IRS 1042-S form stands out due to its specific purpose and the audience it serves. Primarily, it is designed for foreigners who receive certain types of income from U.S. sources, which could range from salaries and wages to scholarships and fellowship grants. This form plays a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with the tax withholding and reporting requirements set by the U.S. tax authorities. It provides a detailed account of the income paid to these individuals and any taxes withheld from their payments. By accurately filling out and submitting the IRS 1042-S form, both the payers and the recipients can navigate the tax landscape more effectively, avoiding potential penalties while ensuring that the correct tax amounts are reported and paid. Understanding the nuances of this form is crucial for anyone involved in managing or receiving international payments subject to U.S. taxation.
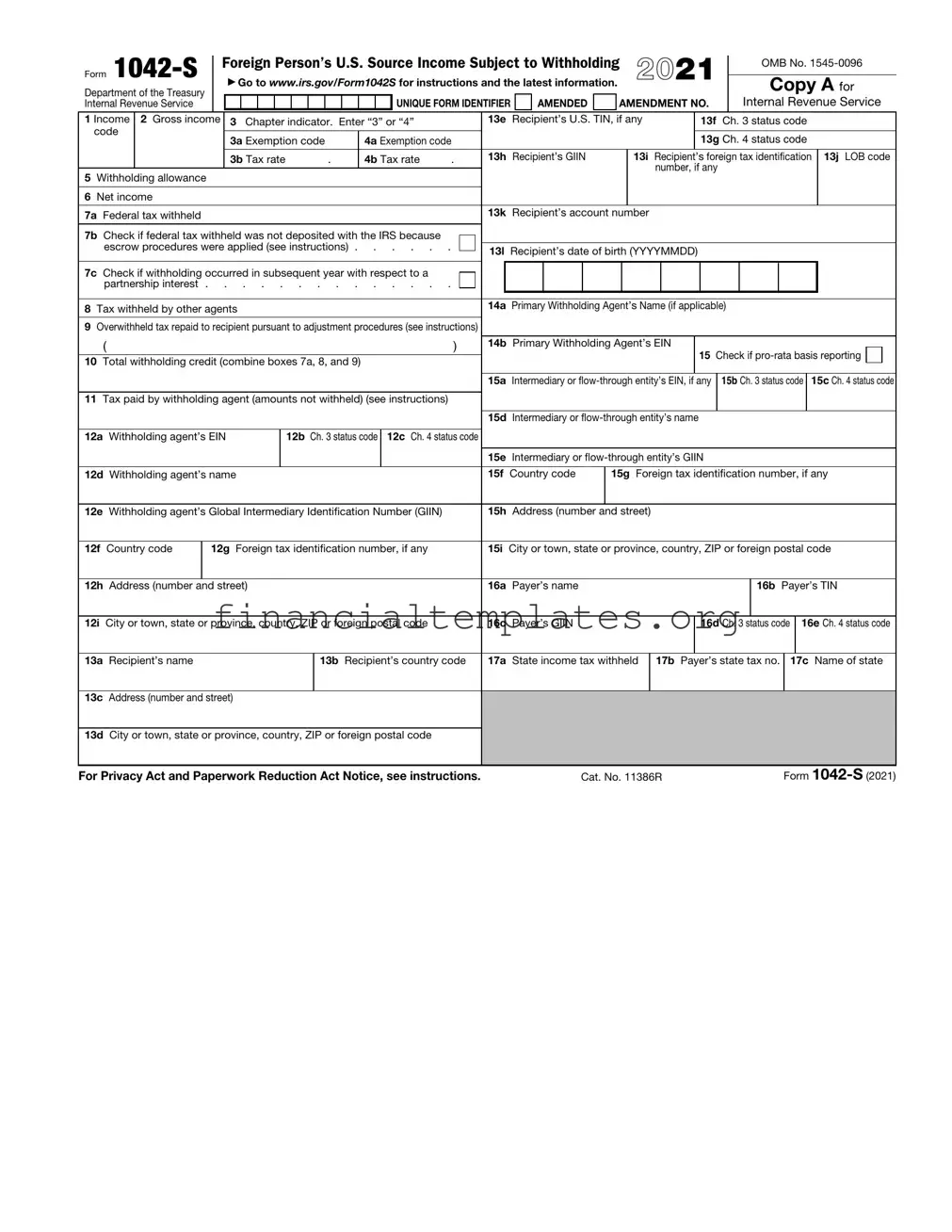
IRS 1042-S Example
|
|
|
Foreign Person’s U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding |
2021 |
|
|
OMB No. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Copy A for |
|||||||||
Form |
|
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/Form1042S for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Internal Revenue Service |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UNIQUE FORM IDENTIFIER |
AMENDED |
|
|
AMENDMENT NO. |
|
|
Internal Revenue Service |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
1 Income |
2 Gross income |
|
3 Chapter indicator. Enter “3” or “4” |
|
|
13e |
Recipient’s U.S. TIN, if any |
|
|
|
13f |
Ch. 3 status code |
||||||||||||||||||||||
code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3a Exemption code |
|
|
4a Exemption code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13g Ch. 4 status code |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
3b Tax rate |
. |
|
4b Tax rate |
. |
|
13h |
Recipient’s GIIN |
|
|
13i Recipient’s foreign tax identification |
13j LOB code |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
number, if any |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
5 Withholding allowance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
6 Net income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
7a Federal tax withheld |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13k |
Recipient’s account number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
7b Check if federal tax withheld was not deposited with the IRS because |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
escrow procedures were applied (see instructions) |
|
|
13l Recipient’s date of birth (YYYYMMDD) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
7c Check if withholding occurred in subsequent year with respect to a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
partnership interest |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
8 Tax withheld by other agents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14a |
Primary Withholding Agent’s Name (if applicable) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
9Overwithheld tax repaid to recipient pursuant to adjustment procedures (see instructions)
( |
) |
|
14b Primary Withholding Agent’s EIN |
15 Check if |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
10 Total withholding credit (combine boxes 7a, 8, and 9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15a Intermediary or |
|||
11Tax paid by withholding agent (amounts not withheld) (see instructions)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15d Intermediary or |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12a |
Withholding agent’s EIN |
|
12b Ch. 3 status code |
12c Ch. 4 status code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15e |
Intermediary or |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
12d Withholding agent’s name |
15f Country code |
15g Foreign tax identification number, if any |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
12e |
Withholding agent’s Global Intermediary Identification Number (GIIN) |
15h |
Address (number and street) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
12f |
Country code |
12g |
Foreign tax identification number, if any |
15i |
City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
12h |
Address (number and street) |
16a |
Payer’s name |
|
|
|
16b Payer’s TIN |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
12i City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code |
16c |
Payer’s GIIN |
|
|
16d Ch. 3 status code |
|
16e Ch. 4 status code |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
13a |
Recipient’s name |
|
|
13b Recipient’s country code |
17a |
State income tax withheld |
17b Payer’s state tax no. |
17c Name of state |
||||||
13c Address (number and street)
13d City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see instructions. |
Cat. No. 11386R |
Form |
Form |
|
Foreign Person’s U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding |
2021 |
|
|
OMB No. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/Form1042S for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
|
Copy B |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Internal Revenue Service |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UNIQUE FORM IDENTIFIER |
AMENDED |
|
|
|
AMENDMENT NO. |
|
|
for Recipient |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1 Income |
2 Gross income |
|
3 Chapter indicator. Enter “3” or “4” |
|
|
13e |
Recipient’s U.S. TIN, if any |
|
|
|
13f |
Ch. 3 status code |
|||||||||||||||||||||
code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3a Exemption code |
|
|
4a Exemption code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13g Ch. 4 status code |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
3b Tax rate |
. |
|
4b Tax rate |
. |
|
13h |
Recipient’s GIIN |
13i Recipient’s foreign tax identification |
13j LOB code |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
number, if any |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
5 Withholding allowance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
6 Net income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
7a Federal tax withheld |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13k |
Recipient’s account number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
7b Check if federal tax withheld was not deposited with the IRS because |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
escrow procedures were applied (see instructions) |
|
|
13l Recipient’s date of birth (YYYYMMDD) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
7c Check if withholding occurred in subsequent year with respect to a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
partnership interest |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
8 Tax withheld by other agents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14a |
Primary Withholding Agent’s Name (if applicable) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
9Overwithheld tax repaid to recipient pursuant to adjustment procedures (see instructions)
( |
) |
|
14b Primary Withholding Agent’s EIN |
15 Check if |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
10 Total withholding credit (combine boxes 7a, 8, and 9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15a Intermediary or |
|||
11Tax paid by withholding agent (amounts not withheld) (see instructions)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15d Intermediary or |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12a |
Withholding agent’s EIN |
|
12b Ch. 3 status code |
12c Ch. 4 status code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15e |
Intermediary or |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
12d Withholding agent’s name |
15f Country code |
15g Foreign tax identification number, if any |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
12e |
Withholding agent’s Global Intermediary Identification Number (GIIN) |
15h |
Address (number and street) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
12f |
Country code |
12g |
Foreign tax identification number, if any |
15i |
City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
12h |
Address (number and street) |
16a |
Payer’s name |
|
|
|
16b Payer’s TIN |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
12i City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code |
16c |
Payer’s GIIN |
|
|
16d Ch. 3 status code |
|
16e Ch. 4 status code |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
13a |
Recipient’s name |
|
|
13b Recipient’s country code |
17a |
State income tax withheld |
17b Payer’s state tax no. |
17c Name of state |
||||||
13c Address (number and street)
13d City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code
(keep for your records) |
Form |

U.S. Income Tax Filing Requirements
Generally, every nonresident alien individual, nonresident alien fiduciary, and foreign corporation with U.S. income, including income that is effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business in the United States, must file a U.S. income tax return. However, no return is required to be filed by a nonresident alien individual, nonresident alien fiduciary, or foreign corporation if such person was not engaged in a trade or business in the United States at any time during the tax year and if the tax liability of such person was fully satisfied by the withholding of U.S. tax at the source. Corporations file Form
En règle générale, tout étranger
àIRS.gov et dans toutes les ambassades et tous les consulats des
Por regla general, todo extranjero no residente, todo organismo fideicomisario extranjero no residente y toda sociedad anónima extranjera que reciba ingresos en los Estados Unidos, incluyendo ingresos relacionados con la conducción de un negocio o comercio dentro de los Estados Unidos, deberá presentar una declaración estadounidense de impuestos sobre el ingreso. Sin embargo, no se requiere declaración alguna a un individuo extranjero, una sociedad anónima extranjera u organismo fideicomisario extranjero no residente, si tal persona no ha efectuado comercio o negocio en los Estados Unidos durante el año fiscal y si la responsabilidad con los impuestos de tal persona ha sido satisfecha plenamente mediante retención del impuesto de los Estados Unidos en la fuente. Las sociedades anónimas envían el Formulario
Im allgemeinen muss jede ausländische Einzelperson, jeder ausländische Bevollmächtigte und jede ausländische Gesellschaft mit Einkommen in den Vereinigten Staaten, einschliesslich des Einkommens, welches direkt mit der Ausübung von Handel oder Gewerbe innerhalb der Staaten verbunden ist, eine Einkommensteuererklärung der Vereinigten Staaten abgeben. Eine Erklärung, muss jedoch nicht von Ausländern, ausländischen Bevollmächtigten oder ausländischen Gesellschaften in den Vereinigten Staaten eingereicht werden, falls eine solche Person während des Steuerjahres kein Gewerbe oder Handel in den Vereinigten Staaten ausgeübt hat und die Steuerschuld durch Einbehaltung der Steuern der Vereinigten Staaten durch die Einkommensquelle abgegolten ist. Gesellschaften reichen den Vordruck
Explanation of Codes
Box 1. Income Code.
Code |
Types of Income |
01Interest paid by U.S.
02Interest paid on real property mortgages
03Interest paid to controlling foreign corporations
04Interest paid by foreign corporations
05Interest on
|
22 |
Interest paid on deposit with a foreign branch of a domestic |
|
Interest |
30 |
corporation or partnership |
|
Original issue discount (OID) |
|||
|
29 |
Deposit interest |
|
|
31 |
||
|
33 |
Substitute |
|
|
51 |
Interest paid on certain actively traded or publicly offered |
|
|
|
securities1 |
|
|
54 |
Substitute |
|
|
|
or publicly offered securities1 |
|
Dividend |
06 |
Dividends paid by U.S. |
|
07 |
Dividends qualifying for direct dividend rate |
||
|
|||
|
08 |
Dividends paid by foreign corporations |
|
34 |
Substitute |
|
40 |
Other dividend equivalents under IRC section 871(m) |
Dividend |
|
(formerly 871(l)) |
52 |
securities1 |
|
|
Dividends paid on certain actively traded or publicly offered |
|
|
53 |
Substitute |
|
|
publicly offered securities1 |
|
09 |
Capital gains |
|
10 |
Industrial royalties |
|
11 |
Motion picture or television copyright royalties |
|
12 |
Other royalties (for example, copyright, software, |
|
|
broadcasting, endorsement payments) |
Other |
13 |
Royalties paid on certain publicly offered securities1 |
14 |
Real property income and natural resources royalties |
|
|
15 |
Pensions, annuities, alimony, and/or insurance premiums |
|
16 |
Scholarship or fellowship grants |
|
17 |
Compensation for independent personal services2 |
|
18 |
Compensation for dependent personal services2 |
|
19 |
Compensation for teaching2 |
See back of Copy C for additional codes
1This code should only be used if the income paid is described in Regulations section
2If compensation that otherwise would be covered under Income Codes 17 through 20 is directly attributable to the recipient’s occupation as an artist or athlete, use Income Code 42 or 43 instead.
Form |
|
|
Foreign Person’s U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding |
2021 |
|
|
OMB No. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/Form1042S for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
Copy C for Recipient |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Internal Revenue Service |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UNIQUE FORM IDENTIFIER |
|
|
AMENDED |
|
|
|
AMENDMENT NO. |
|
Attach to any Federal tax return you file |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1 Income |
2 Gross income |
|
|
3 Chapter indicator. Enter “3” or “4” |
|
|
13e |
Recipient’s U.S. TIN, if any |
|
|
|
13f |
Ch. 3 status code |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
3a Exemption code |
|
|
4a Exemption code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13g Ch. 4 status code |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
3b Tax rate |
. |
|
4b Tax rate |
. |
|
13h |
Recipient’s GIIN |
13i Recipient’s foreign tax identification |
13j LOB code |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
number, if any |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
5 Withholding allowance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
6 Net income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
7a Federal tax withheld |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13k |
Recipient’s account number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
7b Check if federal tax withheld was not deposited with the IRS because |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
escrow procedures were applied (see instructions) |
|
|
13l Recipient’s date of birth (YYYYMMDD) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
7c Check if withholding occurred in subsequent year with respect to a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
partnership interest |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
8 Tax withheld by other agents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14a |
Primary Withholding Agent’s Name (if applicable) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
9Overwithheld tax repaid to recipient pursuant to adjustment procedures (see instructions)
( |
) |
|
14b Primary Withholding Agent’s EIN |
15 Check if |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
10 Total withholding credit (combine boxes 7a, 8, and 9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15a Intermediary or |
|||
11Tax paid by withholding agent (amounts not withheld) (see instructions)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15d Intermediary or |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12a |
Withholding agent’s EIN |
|
12b Ch. 3 status code |
12c Ch. 4 status code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15e |
Intermediary or |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
12d Withholding agent’s name |
15f Country code |
15g Foreign tax identification number, if any |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
12e |
Withholding agent’s Global Intermediary Identification Number (GIIN) |
15h |
Address (number and street) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
12f |
Country code |
12g |
Foreign tax identification number, if any |
15i |
City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
12h |
Address (number and street) |
16a |
Payer’s name |
|
|
|
16b Payer’s TIN |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
12i City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code |
16c |
Payer’s GIIN |
|
|
16d Ch. 3 status code |
|
16e Ch. 4 status code |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
13a |
Recipient’s name |
|
|
13b Recipient’s country code |
17a |
State income tax withheld |
17b Payer’s state tax no. |
17c Name of state |
||||||
13c Address (number and street)
13d City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code
Form

Explanation of Codes (continued)
|
20 |
Compensation during studying and training2 |
|
|
23 |
Other income |
|
|
24 |
Qualified investment entity (QIE) distributions of capital |
|
|
|
gains |
|
|
25 |
Trust distributions subject to IRC section 1445 |
|
|
26 |
Unsevered growing crops and timber distributions by a trust |
|
|
|
subject to IRC section 1445 |
|
|
27 |
Publicly traded partnership distributions subject to IRC |
|
|
|
section 1446 |
|
|
28 |
Gambling winnings3 |
|
|
32 |
Notional principal contract income4 |
|
Other |
35 |
Substitute |
|
36 |
Capital gains distributions |
||
|
|||
|
37 |
Return of capital |
|
|
38 |
Eligible deferred compensation items subject to IRC section |
|
|
|
877A(d)(1) |
|
|
39 |
Distributions from a nongrantor trust subject to IRC section |
|
|
|
877A(f)(1) |
41Guarantee of indebtedness
42Earnings as an artist or
43Earnings as an artist or
44Specified federal procurement payments
50Income previously reported under escrow procedure6
55Taxable death benefits on life insurance contracts
Boxes 3a and 4a. Exemption Code (applies if the tax rate entered in box 3b or 4b is 00.00).
CodeAuthority for Exemption Chapter 3
01Effectively connected income
02Exempt under IRC7
03Income is not from U.S. sources
04Exempt under tax treaty
05Portfolio interest exempt under IRC
06QI that assumes primary withholding responsibility
07WFP or WFT
08U.S. branch treated as U.S. Person
09Territory FI treated as U.S. Person
10QI represents that income is exempt
11QSL that assumes primary withholding responsibility
12Payee subjected to chapter 4 withholding
22QDD that assumes primary withholding responsibility
23Exempt under section 897(l)
24Exempt under section 892
Chapter 4
13Grandfathered payment
14Effectively connected income
15Payee not subject to chapter 4 withholding
16Excluded nonfinancial payment
17Foreign Entity that assumes primary withholding responsibility
18U.S.
19Exempt from withholding under IGA8
20Dormant account9
21
Boxes 12b, 12c, 13f, 13g, 15b, 15c, 16d, and 16e. Withholding Agent, Recipient, Intermediary, and Payer Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 Status Codes.
Type of Recipient, Withholding Agent, Payer, or Intermediary Code
Chapter 3 Status Codes
03Territory
04Territory
05U.S.
06U.S.
07U.S.
08Partnership other than Withholding Foreign Partnership
09Withholding Foreign Partnership
See back of Copy D for additional codes
2If compensation that otherwise would be covered under Income Codes 17 through 20 is directly attributable to the recipient’s occupation as an artist or athlete, use Income Code 42 or 43 instead.
3Subject to 30% withholding rate unless the recipient is from one of the treaty countries listed under Gambling winnings (Income Code 28) in Pub. 515.
4Use appropriate Interest Income Code for embedded interest in a notional principal contract.
5Income Code 43 should only be used if Letter 4492, Venue Notification, has been issued by the Internal Revenue Service (otherwise, use Income Code 42 for earnings as an artist or athlete). If Income Code 42 or 43 is used, Recipient Code 22 (artist or athlete) should be used instead of Recipient Code 16 (individual), 15 (corporation), or 08 (partnership other than withholding foreign partnership).
6Use only to report gross income the tax for which is being deposited in the current year because such tax was previously escrowed for chapters 3 and 4 and the withholding agent previously reported the gross income in a prior year and checked the box to report the tax as not deposited under the escrow procedure. See the instructions to this form for further explanation.
7This code should only be used if no other specific chapter 3 exemption code applies.
8Use only to report a U.S. reportable account or nonconsenting U.S. account that is receiving a payment subject to chapter 3 withholding.
9Use only if applying the escrow procedure for dormant accounts under Regulations section
Form |
|
|
Foreign Person’s U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding |
2021 |
|
|
OMB No. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/Form1042S for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
Copy D for Recipient |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Internal Revenue Service |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UNIQUE FORM IDENTIFIER |
|
|
AMENDED |
|
|
|
AMENDMENT NO. |
|
|
Attach to any state tax return you file |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1 Income |
2 Gross income |
|
|
3 Chapter indicator. Enter “3” or “4” |
|
|
13e |
Recipient’s U.S. TIN, if any |
|
|
|
13f |
Ch. 3 status code |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
3a Exemption code |
|
|
4a Exemption code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13g Ch. 4 status code |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
3b Tax rate |
. |
|
4b Tax rate |
. |
|
13h |
Recipient’s GIIN |
13i Recipient’s foreign tax identification |
13j LOB code |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
number, if any |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
5 Withholding allowance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
6 Net income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
7a Federal tax withheld |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13k |
Recipient’s account number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
7b Check if federal tax withheld was not deposited with the IRS because |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
escrow procedures were applied (see instructions) |
|
|
13l Recipient’s date of birth (YYYYMMDD) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
7c Check if withholding occurred in subsequent year with respect to a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
partnership interest |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
8 Tax withheld by other agents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14a |
Primary Withholding Agent’s Name (if applicable) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
9Overwithheld tax repaid to recipient pursuant to adjustment procedures (see instructions)
( |
) |
|
14b Primary Withholding Agent’s EIN |
15 Check if |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
10 Total withholding credit (combine boxes 7a, 8, and 9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15a Intermediary or |
|||
11Tax paid by withholding agent (amounts not withheld) (see instructions)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15d Intermediary or |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12a |
Withholding agent’s EIN |
|
12b Ch. 3 status code |
12c Ch. 4 status code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15e |
Intermediary or |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
12d Withholding agent’s name |
15f Country code |
15g Foreign tax identification number, if any |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
12e |
Withholding agent’s Global Intermediary Identification Number (GIIN) |
15h |
Address (number and street) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
12f |
Country code |
12g |
Foreign tax identification number, if any |
15i |
City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
12h |
Address (number and street) |
16a |
Payer’s name |
|
|
|
16b Payer’s TIN |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
12i City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code |
16c |
Payer’s GIIN |
|
|
16d Ch. 3 status code |
|
16e Ch. 4 status code |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
13a |
Recipient’s name |
|
|
13b Recipient’s country code |
17a |
State income tax withheld |
17b Payer’s state tax no. |
17c Name of state |
||||||
13c Address (number and street)
13d City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code
Form

Explanation of Codes (continued)
10Trust other than Withholding Foreign Trust
11Withholding Foreign Trust
12Qualified Intermediary
13Qualified Securities
14Qualified Securities
15Corporation
16Individual
17Estate
18Private Foundation
19International Organization
20Tax Exempt Organization (Section 501(c) entities)
21Unknown Recipient
22Artist or Athlete
23Pension
24Foreign Central Bank of Issue
25Nonqualified Intermediary
26Hybrid entity making Treaty Claim
35Qualified Derivatives Dealer
36Foreign
37Foreign
27Withholding Rate
28Withholding Rate
29PAI Withholding Rate
30PAI Withholding Rate
31Agency Withholding Rate
32Agency Withholding Rate
Chapter 4 Status Codes
01U.S. Withholding
02U.S. Withholding
03Territory
04Territory
05Participating
06Participating
07Registered
08Registered
09Registered
10Certified
11Certified
12Certified
13Certified
14Certified
15Nonparticipating FFI
16
17U.S.
18U.S.
19Passive NFFE identifying Substantial U.S. Owners
20Passive NFFE with no Substantial U.S. Owners
21Publicly Traded NFFE or Affiliate of Publicly Traded NFFE
22Active NFFE
23Individual
24Section 501(c) Entities
25Excepted Territory NFFE
26Excepted
27Exempt Beneficial Owner
28Entity Wholly Owned by Exempt Beneficial Owners
29Unknown Recipient
30Recalcitrant Account Holder
31Nonreporting IGA FFI
32Direct reporting NFFE
33U.S. reportable account
34Nonconsenting U.S. account
35Sponsored direct reporting NFFE
36Excepted
37Undocumented Preexisting Obligation
38U.S.
39Account Holder of Excluded Financial Account11
40Passive NFFE reported by FFI12
41NFFE subject to 1472 withholding
50U.S. Withholding
Pooled Reporting Codes
42Recalcitrant
43Recalcitrant
44Recalcitrant
45Recalcitrant
46Recalcitrant
47Nonparticipating FFI Pool
48U.S. Payees Pool
49
Box 13j. LOB Code (enter the code that best describes the applicable limitation on benefits (LOB) category that qualifies the taxpayer for the requested treaty benefits).
LOB Code |
LOB Treaty Category |
02Government – contracting state/political subdivision/local authority
03Tax exempt pension trust/Pension fund
04Tax exempt/Charitable organization
05Publicly traded corporation
06Subsidiary of publicly traded corporation
07Company that meets the ownership and base erosion test
08Company that meets the derivative benefits test
09Company with an item of income that meets the active trade or business test
10Discretionary determination
11Other
10Codes 27 through 32 should only be used by a QI, QSL, WP, or WT. A QI acting as a QDD may use code 27 or 28.
11This code should only be used if income is paid to an account that is excluded from the definition of financial account under Regulations section
12This code should only be used when the withholding agent has received a certification on the FFI withholding statement of a participating FFI or registered deemed- compliant FFI that maintains the account that the FFI has reported the account held by the passive NFFE as a U.S. account (or U.S. reportable account) under its FATCA requirements. The withholding agent must report the name and GIIN of such FFI in boxes 15d and 15e.
13This code should only be used by a withholding agent that is reporting a payment (or portion of a payment) made to a QI with respect to the QI’s recalcitrant account holders.
Form |
|
Foreign Person’s U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding |
2021 |
|
|
OMB No. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/Form1042S for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
|
Copy E |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Internal Revenue Service |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UNIQUE FORM IDENTIFIER |
|
AMENDED |
|
|
|
AMENDMENT NO. |
|
|
for Withholding Agent |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1 Income |
2 Gross income |
|
3 Chapter indicator. Enter “3” or “4” |
|
|
13e Recipient’s U.S. TIN, if any |
|
|
|
13f |
Ch. 3 status code |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3a Exemption code |
|
|
4a Exemption code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13g Ch. 4 status code |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
3b Tax rate |
. |
|
4b Tax rate |
. |
|
13h Recipient’s GIIN |
13i Recipient’s foreign tax identification |
13j LOB code |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
number, if any |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
5 Withholding allowance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
6 Net income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
7a Federal tax withheld |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13k Recipient’s account number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
7b Check if federal tax withheld was not deposited with the IRS because |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
escrow procedures were applied (see instructions) |
|
|
13l Recipient’s date of birth (YYYYMMDD) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
7c Check if withholding occurred in subsequent year with respect to a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
partnership interest |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
8 Tax withheld by other agents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14a Primary Withholding Agent’s Name (if applicable) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
9Overwithheld tax repaid to recipient pursuant to adjustment procedures (see instructions)
( |
) |
|
14b Primary Withholding Agent’s EIN |
15 Check if |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
10 Total withholding credit (combine boxes 7a, 8, and 9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15a Intermediary or |
|||
11Tax paid by withholding agent (amounts not withheld) (see instructions)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15d Intermediary or |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12a |
Withholding agent’s EIN |
|
12b Ch. 3 status code |
12c Ch. 4 status code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15e |
Intermediary or |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
12d Withholding agent’s name |
15f Country code |
15g Foreign tax identification number, if any |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
12e |
Withholding agent’s Global Intermediary Identification Number (GIIN) |
15h |
Address (number and street) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
12f |
Country code |
12g |
Foreign tax identification number, if any |
15i |
City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
12h |
Address (number and street) |
16a |
Payer’s name |
|
|
|
16b Payer’s TIN |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
12i City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code |
16c |
Payer’s GIIN |
|
|
16d Ch. 3 status code |
|
16e Ch. 4 status code |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
13a |
Recipient’s name |
|
|
13b Recipient’s country code |
17a |
State income tax withheld |
17b Payer’s state tax no. |
17c Name of state |
||||||
13c Address (number and street)
13d City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see instructions. |
Form |
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Form Purpose | The IRS 1042-S form is used to report income paid to foreign persons including non-resident aliens, foreign partnerships, foreign corporations, foreign estates, and foreign trusts. |
| Income Types | This form covers various types of income, such as interest, dividends, rents, royalties, and scholarship or fellowship grants. |
| Withholding Requirements | Form 1042-S is used to report amounts paid that are subject to withholding under Chapter 3 of the Internal Revenue Code, which pertains to U.S. source income of foreign persons. |
| Tax Treaties | The form can reflect the application of reduced rates of withholding at source as facilitated by income tax treaties between the U.S. and foreign countries. |
| Filing Entity | U.S. withholding agents, such as individuals, businesses, or institutions, that pay income to foreign persons must file Form 1042-S. |
| Deadlines | Form 1042-S must be filed with the IRS and furnished to the recipient by March 15 following the calendar year in which the income was paid. |
| Electronic Filing | Filers who must submit 250 or more Forms 1042-S must file them electronically through the IRS FIRE (Filing Electronic Returns Electronically) system. |
| Penalties | Failure to file or incorrect filing of Form 1042-S can result in penalties, which may include fines and interest on unpaid taxes. |
| Duplicate Reporting | Income reported on Form 1042-S must not be reported on Form 1099, to avoid duplicate reporting of the same income. |
Guide to Writing IRS 1042-S
Filling out the IRS 1042-S form is a detailed process that involves providing specific information to the Internal Revenue Service regarding payments made to foreign individuals or entities. This task is mandatory for entities that engage in such financial activities. It's essential to approach this form with care to ensure all information is accurate and complete. The following steps are designed to guide you through the process of filling out this form systematically.
- Begin by gathering all necessary documentation related to the payments made to the foreign individuals or entities, including their identifying information and the total amount paid during the fiscal year.
- Enter the payer's information in the top section of the form. This includes the payer's name, address, and the employer identification number (EIN).
- Fill in the recipient’s information. This section requires the name, address, country of citizenship, and the taxpayer identification number (TIN) of the recipient.
- Specify the type of income that was paid to the recipient in the appropriate box. This generally includes but is not limited to, wages, dividends, or scholarship funds.
- Input the total amount of income paid to the foreign individual or entity during the reporting year in the currency in which the payment was made.
- Calculate and enter any tax withheld from the payments. This requires understanding the applicable tax treaty rates or the default rate as prescribed by U.S. tax law.
- If there are any exemptions applied due to treaty benefits, clearly indicate this in the specified area by noting the applicable article and paragraph of the treaty.
- Review the information for accuracy and completeness. Mistakes can lead to compliance issues or delays in processing.
- Sign and date the form at the bottom to certify that the information provided is correct to the best of your knowledge.
- Finally, submit the form to the IRS by the required deadline to avoid penalties. Depending on your situation, the form may be submitted either electronically or in paper form.
Completing the IRS 1042-S form accurately is crucial for compliance with U.S. tax laws concerning payments to foreign entities or individuals. Taking your time to fill out each section carefully, and double-checking your work, can prevent potential issues. Remember, if there's any confusion about how to complete the form or if you need to clarify specific regulations, consulting a tax professional is always a wise decision.
Understanding IRS 1042-S
-
What is a Form 1042-S?
Form 1042-S is a tax document used by the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to report certain types of income paid to foreign individuals and entities. This includes, but is not limited to, salaries, dividends, royalties, and scholarship or fellowship grants that come from sources within the United States. The form serves both to report income and any applicable withholdings that might have been taken out for tax purposes.
-
Who needs to file Form 1042-S?
Form 1042-S must be filed by any U.S. entity that makes payments of the types described above to foreign individuals or entities. This can include universities, employers, or financial institutions, among others. The form is required for each recipient of such payments, meaning an entity may need to file multiple forms if it makes payments to more than one foreign individual or entity.
-
What information do I need to complete Form 1042-S?
To complete Form 1042-S, you'll need detailed information about both the payer (usually the U.S. entity making the payment) and the recipient (the foreign individual or entity receiving the payment). This includes the full name and address of each, the recipient's country of tax residence, and their U.S. taxpayer identification number (TIN), if they have one. Additionally, you'll need details of the payments made, including the total amount and the type of income paid. If any withholding was done, this must also be reported on the form.
-
What if I don't have a TIN?
Foreign individuals or entities receiving payment may not always have a U.S. Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN). In such cases, it's essential to make a note of this on Form 1042-S, following the specific instructions provided by the IRS for these situations. Depending on the circumstances, recipients might be encouraged to apply for a TIN to comply with U.S. tax laws and potentially avoid higher withholding rates.
-
When is Form 1042-S due?
Form 1042-S is generally due by March 15th of the year following the payment. If March 15th falls on a weekend or a public holiday, the due date is extended to the next business day. It's crucial to adhere to this deadline to avoid penalties for late filing. Copies of the form also need to be provided to the income recipient by the same date, allowing them to correctly file their tax returns if necessary.
-
How do I file Form 1042-S?
Form 1042-S can be filed electronically or on paper, although the IRS encourages electronic filing for efficiency and security reasons. Filing electronically is mandatory for entities submitting 250 or more forms. The IRS website provides instructions and links for electronic filing. For those who choose or need to file on paper, the forms must be ordered from the IRS, as photocopies are not accepted.
-
What are the penalties for not filing Form 1042-S?
Failure to file Form 1042-S, filing late, or filing an incorrect form can result in penalties. These penalties can vary, potentially including financial fines and interest on any underpaid taxes. The specifics depend on the extent of the delay and the nature of the mistake. The IRS may offer relief from penalties in certain situations if the filer can show that the failure was due to reasonable cause and not willful neglect.
-
Can Form 1042-S be amended?
Yes, if errors are discovered after Form 1042-S has been filed, it is possible, and often necessary, to amend the form. To do this, a new form should be completed with the correct information and marked as "Amended" to distinguish it from the original submission. Detailed instructions on how to properly amend Form 1042-S are available on the IRS website. It's important to correct any mistakes promptly to prevent or minimize penalties.
Common mistakes
Filling out the IRS 1042-S form can be a complex process that requires careful attention to detail. This form is used to report amounts paid to foreign persons, including non-resident aliens, foreign partnerships, and corporations, in the preceding year. Mistakes can lead to delays or incorrect tax withholding and reporting. Here are four common mistakes people make when filling out this form:
-
Incorrect Taxpayer Identification Numbers (TINs): One frequent error is entering incorrect or incomplete Taxpayer Identification Numbers. This can include the Social Security Number (SSN), Employer Identification Number (EIN), or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) of the recipient. Accurate TINs are crucial for ensuring proper reporting and tax withholding.
-
Failing to Choose the Correct Income Code: The IRS 1042-S form requires the payer to select an income code that best describes the type of payment being reported. This code is essential for determining the tax rate and any exemptions that may apply. Choosing the wrong income code can lead to incorrect withholding and reporting.
-
Not Reporting in U.S. Dollars: All amounts must be reported in U.S. dollars, even if the payment was made in another currency. This requires the payer to convert the payment amount to U.S. dollars using the exchange rate in effect on the date of payment. Failing to report in U.S. dollars can lead to inaccuracies in the reported amounts.
-
Omitting or Misreporting Recipient Information: It is critical to provide detailed and accurate information about the recipient of the payment. This includes the recipient's name, address, and country of citizenship. Incomplete or incorrect recipient information can cause problems with the IRS and may result in the form being rejected.
By avoiding these common mistakes, filers can ensure smoother processing of their IRS 1042-S forms and stay compliant with U.S. tax laws. Whether you are a seasoned tax professional or a first-time filer, paying close attention to these details is key to successful tax reporting for payments to foreign persons.
Documents used along the form
When navigating the terrain of U.S. tax reporting and compliance, the IRS 1042-S form plays a pivotal role, especially for those handling foreign persons' U.S. source income subject to withholding. Beyond the 1042-S, understanding complementary forms and documents is key to a smooth process. These additional resources bolster compliance, ensuring that both individuals and organizations meet their tax obligations efficiently. Let's explore some of these essential forms and documents.
- Form W-8BEN: This certificate is used by foreign individuals to claim exemption from withholding on income associated with service payments, dividends, and interest from U.S. sources. It establishes the individual's status as a foreign person and eligibility for reduced rates under income tax treaties.
- Form W-8BEN-E: Tailored for foreign entities, this document serves a similar purpose to the W-8BEN but is specifically designed for corporations and organizations. It helps entities claim special tax treaty benefits, including exemptions and reduced withholding rates.
- Form 8233: This form is for nonresident aliens who receive compensation for personal services performed in the U.S. It allows individuals to claim a withholding exemption based on a tax treaty between the U.S. and their country of residence.
- Form 1042: Often used in tandem with the 1042-S, this annual withholding tax return form is for any U.S. entity that has paid amounts subject to reporting on Form 1042-S. It encompasses the total tax withheld from payments to foreign individuals and entities.
Understanding the interplay between the IRS 1042-S form and these additional documents is crucial for managing nonresident alien tax compliance. Each form has a distinct purpose, catering to different aspects of tax reporting and withholding for foreign individuals and entities. Leveraging these forms correctly not only ensures compliance but also maximizes efficiency in international transactions and payments. As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and prepared with the right documentation will always be a cornerstone of successful tax strategy and execution.
Similar forms
The IRS 1042-S form is closely related to the W-2 form, which many U.S. taxpayers are more familiar with. While the 1042-S documents income paid to foreign persons, the W-2 form reports wages, tips, and other compensation paid to employees who are U.S. citizens or resident aliens. Both forms serve to report income to the taxpayer and the IRS, but they cater to different groups of individuals based on their residency status.
Similarly, the 1042-S form echoes the Form 1099 series, especially the 1099-MISC, which reports various types of income other than wages, salaries, and tips. Like the 1042-S, 1099 forms report payments and financial transactions to the IRS and the recipient; however, 1099 forms generally apply to U.S. citizens and resident aliens, whereas the 1042-S is for foreign persons. The distinction lies in both the source of income and the recipient's tax status.
The IRS Form W-8BEN is another document that intersects with the purpose of the 1042-S form. Form W-8BEN is used by foreign individuals to certify their foreign status and claim any applicable treaty benefits for reduced withholding. This form is often submitted to the payer before the 1042-S form is necessitated, effectively preceding the 1042-S in the international taxation documentation process. The connection lies in their mutual aim to properly document and tax foreign individuals' income according to U.S. laws and treaties.
Form 1042, the Annual Withholding Tax Return for U.S. Source Income of Foreign Persons, operates hand in hand with Form 1042-S. While the 1042-S form provides a detailed transaction-level report of income paid to foreign persons, Form 1042 serves as a summary tax return that reports the aggregate amount of U.S. source income paid out and the total tax withheld. Both are essential for compliance in withholding tax obligations towards foreign entities and individuals.
The Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) is utilized in a distinct but related context. It reports income, deductions, and credits of partners in a partnership. Although intended for a different recipient—partners in a partnership rather than foreign persons—the Schedule K-1 shares the 1042-S's underlying purpose of documenting taxable income and activities for tax reporting purposes. Each form ensures accurate tax liability calculation by providing detailed financial information to both the IRS and the tax filer.
Form 8966, the FATCA Report, has a tangential relationship with the 1042-S form. The FATCA Report is used under the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act to report financial accounts held by foreign taxpayers, or by U.S. taxpayers with substantial foreign assets. While the 1042-S focuses on reporting income paid to these individuals, Form 8966 is concerned with the reporting of assets. Both contribute to the U.S. efforts to curb tax evasion by providing transparency in foreign income and assets.
The W-9 form, Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification, parallels the 1042-S in its function of collecting taxpayer information for reporting purposes. U.S. persons use Form W-9 to provide their taxpayer identification number to entities that will pay them income during the tax year. The key difference from the 1042-S form lies in the recipient's tax status—W-9 is for U.S. persons, while 1042-S is for foreign persons—yet both forms are pivotal in ensuring the correct reporting and withholding of taxes.
Last, Form 8233, Exemption From Withholding on Compensation for Independent (and Certain Dependent) Personal Services of a Nonresident Alien Individual, is intricately linked with the 1042-S. This form is used by nonresident aliens to claim exemption from withholding on income for personal services due to a tax treaty. The form’s approval may affect how payments are reported on the 1042-S, demonstrating their interconnected roles in the administration of international taxation under U.S. law.
Dos and Don'ts
When preparing the IRS 1042-S form, used for reporting amounts paid to foreign persons, including non-resident aliens, foreign corporations, and foreign partnerships, certain practices should be followed to ensure accuracy and compliance. Here are essential do's and don'ts:
- Do ensure that all information provided is accurate and matches the documentation for the foreign person or entity. Incorrect information can lead to delays or issues with processing.
- Do utilize the IRS instructions for form 1042-S to guide you through each section. These instructions are updated periodically and provide the necessary details for each box on the form.
- Do report each recipient's income on a separate form 1042-S. This is crucial for keeping records clear and organized, making it easier for both the IRS and the recipient to understand the details of the reported income.
- Do use the official IRS electronic filing system, if possible, for submitting the form 1042-S. Electronic submission is more secure, more efficient, and can reduce the likelihood of errors.
- Do keep copies of the 1042-S form and any related documentation for at least 7 years. This is important in case the IRS has questions or in case of an audit.
- Don't omit any required fields or information. Incomplete forms can be rejected or result in unnecessary processing delays.
- Don't guess on amounts or other details. Use precise figures and double-check all information for accuracy. Estimates or incorrect information can lead to issues with the IRS.
- Don't neglect the importance of timely filing. Be aware of the submission deadlines and plan accordingly to avoid late fees or penalties.
- Don't hesitate to consult with a tax professional if you encounter any doubts or confusion. The rules surrounding form 1042-S can be complex, and professional guidance can be invaluable.
Misconceptions
The IRS 1042-S form is a critical document for foreign persons receiving U.S. source income, yet it's surrounded by misconceptions that can lead to confusion or errors in filing. Understanding these myths can help ensure compliance with U.S. tax laws and minimize potential issues.
- Only non-U.S. citizens need to file it: While it's true that the 1042-S form is focused on foreign persons, U.S. entities that make payments to foreign persons must also deal with this form. They are responsible for reporting the income paid and any withholdings to the IRS.
- It's only for reporting wages: This misconception limits the scope of the 1042-S form significantly. In reality, the form covers a wide range of U.S. source income paid to foreign persons, including not just wages but also scholarships, royalties, dividends, and more. Thus, it encompasses a broader array of transactions than many realize.
- It replaces the need for a W-2 or 1099 form: The 1042-S is not a substitute for W-2 or 1099 forms. While they all report income, the 1042-S form is specifically for foreign persons. U.S. citizens and resident aliens will receive a W-2 or 1099 form for their income reporting. Understanding the distinct purpose of each form is crucial for proper tax filing.
- Filing the 1042-S form is the sole responsibility of the foreign person receiving income: This is a common misunderstanding. In fact, it is the responsibility of the U.S. entity that pays the foreign person to file the 1042-S form with the IRS and to furnish a copy to the income recipient. Foreign persons may need to report this income on their own tax returns, but they are not responsible for filing the 1042-S form.
By dispelling these myths, both payers and recipients of U.S. source income to foreign persons can better navigate the complexities of tax reporting and compliance, avoiding common pitfalls that may arise from misconceptions about the 1042-S form.
Key takeaways
Understanding the IRS 1042-S form is essential for entities that pay income to foreign persons, including individuals, corporations, partnerships, trusts, estates, and more. This form is used to report amounts paid from U.S. sources to foreign persons that are subject to income tax reporting—even if not necessarily subject to withholding. Here are eight key takeaways to keep in mind when dealing with the 1042-S form:
- Know Who Must File: The 1042-S form must be filled out by any U.S. entity that pays reportable amounts to foreign individuals or entities. This includes universities, businesses, and financial institutions that have engaged in transactions involving foreign payments.
- Understand What to Report: This form is used for reporting various types of income, such as dividends, royalties, scholarship or fellowship grants, and other types of payments, including compensations for services performed by non-residents.
- Distinguish Between 1042-S and W-8BEN: The recipients of income might need to fill out Form W-8BEN to certify their foreign status and claim any applicable treaty benefits. However, it is the payer's responsibility to complete and file the 1042-S form.
- Be Aware of the Deadline: The 1042-S form, along with Form 1042 (the tax return for U.S. source income of foreign persons), must be filed with the IRS by March 15th of the year following the payment. Extensions are available, but they must be requested.
- Pay Attention to Withholding Requirements: Even if tax was not withheld from payments made to foreign individuals or entities, reporting through the 1042-S form is still required. It's important to understand withholding obligations, as failure to withhold when necessary can lead to penalties.
- Maintain Accurate Records: Keeping detailed records of all transactions and payments made to foreign persons is crucial. This documentation will support the amounts reported on the 1042-S form and can be invaluable in case of an audit.
- Utilize the Right Income and Exemption Codes: The 1042-S form contains a variety of income and exemption codes. Selecting the correct codes is crucial for accurately reporting the nature of the payment and any applicable exemptions under tax treaties.
- Seek Professional Advice: Given the complexity of tax laws and treaties, it is wise to seek advice from a tax professional. They can provide guidance tailored to specific situations, ensuring compliance and minimizing the risk of errors.
Handling the 1042-S form with care and diligence ensures compliance with U.S. tax reporting and withholding requirements for payments made to foreign persons. Awareness and understanding of the obligations it entails can help in avoiding penalties and fostering smooth international dealings.
Popular PDF Documents
Irs Pub 6744 - Its structured scenarios promote not just tax knowledge but also critical thinking and decision-making skills crucial for tax prep.
What Is a Tax Lien - Form 785 explains securing priority for lenders over IRS liens in property transactions.
What Is a 8862 Form - Crucial for those who have previously been denied the Earned Income Credit but have since met the eligibility requirements.