Get Accommodations Tax Form
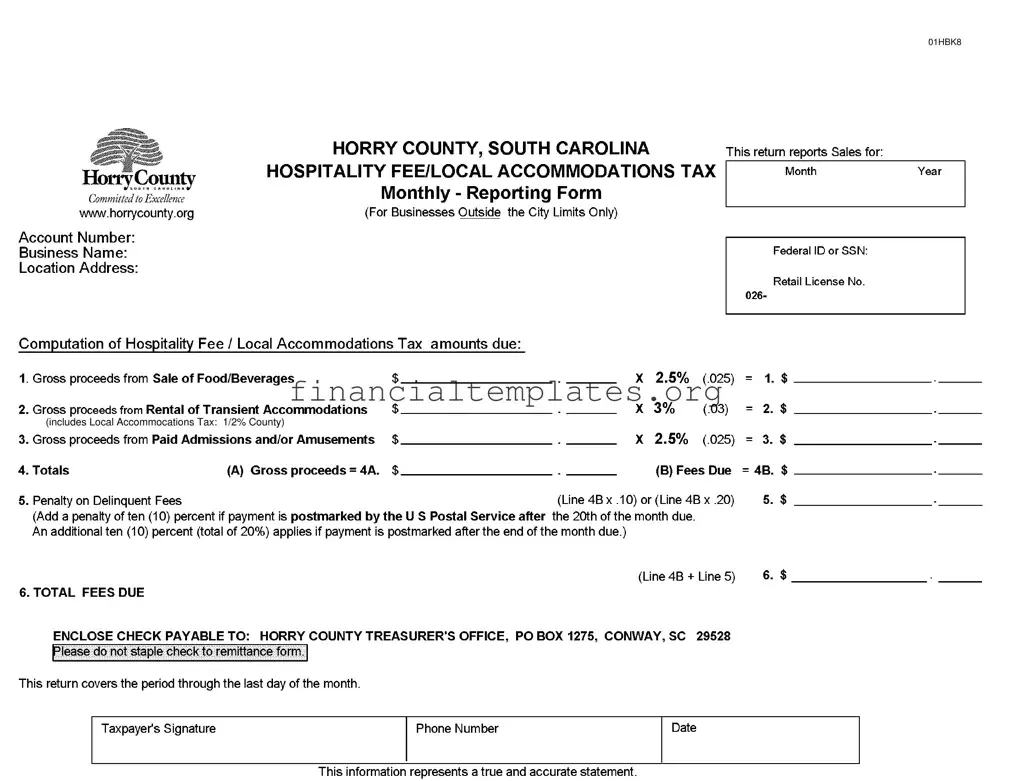
In the vast array of forms and documents that businesses in Horry County, South Carolina, must navigate, the Accommodations Tax form stands out as a crucial tool for reporting monthly hospitality fees and local accommodations taxes. Specifically tailored for businesses operating outside the city limits, this form captures a snapshot of revenues generated from various sources including the sale of food and beverages, rental of transient accommodations, and paid admissions and/or amusements. The detailed sections demand precise figures for gross proceeds, which are then subject to calculated percentages to derive the tax amounts due. Crucially, it underscores the financial obligations these businesses owe to the county, with clear stipulations on penalties for late submissions that emphasize the importance of timely compliance. The requirement for a taxpayer's signature attests to the accuracy of the reported figures, reinforcing the legal responsibility of businesses to contribute to local governance through tax payments. By directing remittances to the Horry County Treasurer’s Office, the form serves as a direct link between local enterprises and the funding of county services, showcasing the interconnectedness of business operations and community welfare.
Accommodations Tax Example
01HBK8
(inc udes Local Acc mocatio Tax: 1/2% County)
Document Specifics
| Fact Number | Fact Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | The Accommodations Tax Form is specific to Horry County, South Carolina. |
| 2 | It is designed for monthly reporting by businesses located outside city limits. |
| 3 | The form reports on three main categories: Sale of Food/Beverages, Rental of Transient Accommodations, and Paid Admissions/Amusements. |
| 4 | Gross proceeds from Rental of Transient Accommodations include a 1/2% Local Accommodations Tax for the County. |
| 5 | Taxes are calculated as a percentage of gross proceeds, with specific rates applied to each category of revenue. |
| 6 | A penalty is added to delinquent fees, starting at 10% if payment is postmarked after the 20th of the due month, increasing to a total of 20% if after the month's end. |
| 7 | Payments are to be made to the Horry County Treasurer’s Office, highlighting the need for checks to be made payable to this entity. |
| 8 | The form requires a declaration that the information provided represents a true and accurate statement by the taxpayer. |
Guide to Writing Accommodations Tax
The Accommodations Tax form is essential for businesses in Horry County, South Carolina, operating outside city limits. This form is used to report sales related to hospitality fees and local accommodations tax. Organizations must accurately complete and submit this form to comply with local tax regulations. The instructions provided aim to guide you through the process of filling out the form correctly and ensuring timely submission to avoid any penalties. Careful adherence to these steps can help maintain compliance and support the local infrastructure through tax contributions.
- Locate the section at the top of the form and enter your business's account number, name, and location address in the designated fields.
- In the "Federal ID or SSN" field, input your Federal Identification Number or Social Security Number.
- Next to "Retail License No.", fill in your business's retail license number.
- Under the "Computation of Hospitality Fee / Local Accommodations Tax amounts due" section, report the gross proceeds from the sale of food and beverages in the first field.
- In the subsequent field, enter the gross proceeds from the rental of transient accommodations. Include any local accommodations tax at the county rate of 0.5%.
- Report the gross proceeds from paid admissions and/or amusements in the designated field.
- Calculate the totals of the above amounts and input the sum in the "Totals" field.
- For the penalty on delinquent fees, if applicable, calculate 10% (or 20% for later submissions) of the fees due and report this amount.
- Add the penalty to the total fees due to find the final amount payable and write this in the appropriate field.
- Make your check payable to "Horry County Treasurer’s Office" and address it to PO BOX 1275, CONWAY, SC 29528. Ensure not to staple the check to your remittance form.
- Sign and date the form at the bottom, providing a contact phone number where you can be reached.
Once completed, the form, along with the payment, should be mailed promptly to the address provided. Ensuring the form is filled accurately and submitted before the due date will help avoid any unnecessary penalties. It is critical for businesses to keep a copy of the form and check for their records.
Understanding Accommodations Tax
What is the Accommodations Tax form for Horry County, and who needs to file it?
The Accommodations Tax form is designed for businesses in Horry County, South Carolina, that are outside the city limits to report and remit taxes collected from sales, specifically hospitality fees and local accommodations taxes. These taxes apply to gross proceeds from the sale of food and beverages, rental of transient accommodations, which include a local accommodations tax, and paid admissions or amusements. Entities required to file this form include restaurants, hotels, vacation rentals, and entertainment venues that fall outside city jurisdictions within Horry County.
How is the Hospitality Fee/Local Accommodations Tax calculated?
Calculations for the Hospitality Fee and Local Accommodations Tax are based on the gross proceeds from different sources. For the sale of food and beverages and paid admissions/amusements, a rate of 2.5% is applied. For the rental of transient accommodations, a 3% rate is used. The total of these amounts, after applying the respective percentages, defines the fees due. Additionally, penalties for late payment are calculated as a percentage of these fees.
What penalties apply for late payments of the Accommodations Tax?
Late payments attract a penalty, which is determined by how delayed the remittance is. A penalty of 10 percent is added if payment is postmarked by the U.S. Postal Service after the 20th of the month due, and this penalty increases to a total of 20 percent if the payment is postmarked after the end of the month due.
What information is needed to complete the Accommodations Tax form?
To accurately fill out the Accommodations Tax form for Horry County, you'll need your Account Number, Business Name, Location Address, Federal ID or SSN, and Retail License No. Additionally, you're required to have detailed records of your gross proceeds from the sale of food and beverages, rental of transient accommodations, and paid admissions or amusements to compute the tax owed.
How do businesses submit the Accommodations Tax form and payment?
Businesses are instructed to submit their completed Accommodations Tax form along with a check for the total fees due to the Horry County Treasurer’s Office, at the provided postal address. It's important to ensure that the check is not stapled to the remittance form. The submission covers the period through the last day of the reported month.
Is there a specific deadline each month for submitting the form and payment?
Yes, businesses are required to postmark their Accommodations Tax payment by the 20th of each month. Penalties for late payment apply if the payment is postmarked after this date.
What happens if the submitted information changes or is found to be inaccurate?
If you discover that the information you submitted is inaccurate or needs to be updated, it's imperative to contact the Horry County Treasurer’s Office as soon as possible. Providing a true and accurate statement is crucial, as indicated on the form, to avoid penalties or legal repercussions.
Common mistakes
- Not providing accurate information in fields such as the business name or location address. It is essential that all details reflect current and correct information to ensure the form is processed efficiently.
- Filling in the Federal ID or SSN incorrectly. This number is crucial for identifying the taxpayer's account, and any mistake can lead to processing delays or misidentification.
- Miscalculating the gross proceeds from the sale of food/beverages, rental of transient accommodations, or paid admissions/amusements. Precise calculations are necessary to determine the correct amount of taxes and fees due.
- Misunderstanding the tax rates and applying incorrect percentage rates when calculating the taxes due on the gross proceeds. It is important to apply the specific rates as indicated for each category to ensure accurate tax computation.
- Omitting the calculation of penalties on delinquent fees. If the payment is late, taxpayers must calculate and add a penalty of 10% if postmarked after the 20th of the month due or an additional 10% if after the end of the month, totaling 20%.
- Incorrect addition of the total fees due, including any penalties. It is critical to accurately add these figures to present the correct total amount that needs to be remitted to the Horry County Treasurer’s Office.
- Forgetting to sign the taxpayer's signature at the bottom of the form, which is a certification that the information provided represents a true and accurate statement. An unsigned form may not be processed.
- Attaching the check to the remittance form despite the instructions advising against it. Properly following instructions for payment submission ensures the processing is not delayed.
The Accommodations Tax Form serves as a critical financial document for businesses outside city limits in Horry County, South Carolina. To avoid delays in processing and potential financial penalties, each section of the form should be approached with careful attention to detail. Common mistakes can often be avoided by thoroughly reviewing all entered information, double-checking calculations, and adhering closely to the provided instructions.
Documents used along the form
When handling the Accommodations Tax form, especially in the context of businesses located outside the city limits, it's vital to have a comprehensive understanding of not only the form itself but also the ancillary documents that often accompany it. These documents are pivotal for ensuring accurate reporting, compliance with local regulations, and maximizing the efficacy of financial management for businesses. Detailed below is a list of documents frequently used in conjunction with the Accommodations Tax form. Each plays a significant role in the overarching process of tax submission and financial documentation.
- Business License Application: Prior to remitting accommodations taxes, businesses must be properly licensed. This document initiates the process, detailing the nature of the business, ownership information, and location.
- Retail License: This document, often a prerequisite for the Accommodations Tax form, is issued by the state and confirms the business's authorization to sell goods and services.
- Sales Tax Return: This complements the accommodations tax by reporting the total amount of sales tax collected from customers, offering a broader financial perspective.
- Employee Withholding Tax Form: For businesses with employees, this form reports the amount of income tax withheld from employees' wages, highlighting the business's adherence to payroll tax regulations.
- Zoning Compliance Certificate: Demonstrates that the business location complies with local zoning laws, a requirement that might indirectly influence the validity of tax submissions.
- Quarterly Federal Tax Return (Form 941): For businesses with employees, this form reports payroll taxes to the federal government, including withholdings from employees' paychecks.
- Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return (Form 940): This form is crucial for businesses with employees, as it calculates the employer's contribution to unemployment benefits.
- Financial Statements: Including income statements and balance sheets, these documents provide a comprehensive overview of the business's financial health and are often necessary for internal and external analysis.
- Bank Statements: Offer a direct snapshot of the business's cash flow and financial transactions within a given period, supporting the details reported on the Accommodations Tax form.
- Previous Accommodations Tax Returns: Keeping records of past submissions can provide valuable insights for future filings and help ensure consistency and accuracy over time.
Together, these documents form a robust framework supporting the proper submission of the Accommodations Tax form. By diligently preparing and reviewing these associated forms and documents, businesses can ensure they meet local regulation requirements, maintain good standing within their community, and manage their financial responsibilities effectively. Understanding and utilizing these documents facilitates a smoother tax reporting process, empowering businesses to focus more on their growth and less on bureaucratic hurdles.
Similar forms
The Sales and Use Tax form is one such document that shares similarities with the Accommodations Tax form. Like the Accommodations Tax form, it's used by businesses to report and remit taxes collected, in this case, on general sales and services. Both forms require business identifiers such as Federal ID or SSN, and business name, along with a detailed calculation of taxes owed based on specified rates. They both include penalties for late submissions, emphasizing timely compliance and accurate reporting. The main difference lies in the type of transactions each form covers; the Sales and Use Tax form has a broader application, encompassing a wide range of goods and services, whereas the Accommodations Tax is specifically focused on hospitality-related revenues.
The Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return, more commonly known as Form 941, also parallels the Accommodations Tax form in several ways. This form is used by employers to report income taxes, social security tax, or Medicare tax withheld from employees' paychecks, and to pay the employer's portion of social security or Medicare tax. Similar to the Accommodations Tax form, the Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return requires detailed calculations, the provision of an Employer Identification Number (EIN), and includes penalties for late submissions. Both documents ensure the proper collection and remittance of taxes to the appropriate governmental agencies, though they serve different sectors (employment versus hospitality).
The Property Tax Declaration form is another document with similarities to the Accommodations Tax form. This form, used by property owners to declare the value of their property for tax purposes, also requires detailed reporting and calculation of taxes due. Like the Accommodations Tax form, it demands accurate information regarding the owner (or business) including identification numbers and contact details. Timely submission is crucial to avoid penalties, mirroring the structure seen with accommodations tax. Despite their focus on different types of assets — real property versus hospitality services — both forms play crucial roles in the tax landscape, ensuring fair taxation based on declared values or revenues.
Lastly, the Business License Renewal form shares common traits with the Accommodations Tax form. Both are required for the continued, legal operation of businesses within a specific jurisdiction — the former for general business licensing and the latter for tax compliance related to hospitality services. Detailed business information, including account numbers and identification details, are mandatory on both forms. Additionally, they calculate fees or taxes due based on business activities, with penalties for late submissions reinforcing the importance of adherence to deadlines. Though one focuses on licensing and the other on tax remittance, their role in regulating business operations is fundamental.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Accommodations Tax form, especially if you are handling taxes for a business located outside city limits in Horry County, South Carolina, it is crucial to follow a set of guidelines that will help avoid common mistakes and ensure the process goes smoothly. Here is a list of dos and don'ts to keep in mind:
- Do ensure you report for the correct period by clearly stating the month and year at the top of the form.
- Do double-check the account number, business name, and location address to ensure they match your official records.
- Do accurately calculate the gross proceeds from the sale of food/beverages, rental of transient accommodations, and paid admissions/amusements, as these figures are critical for computing tax amounts due.
- Do apply the correct percentages (2.5% or 3%) to your gross proceeds to calculate the fees due, ensuring you do not mix these rates up.
- Do include the taxpayer's signature and a valid phone number at the bottom of the form for verification purposes.
- Don't forget to add the penalty amount if the payment is postmarked after the 20th of the month. Remember, the penalty increases to 20% if it's after the month's end.
- Don't staple the check to the remittance form when sending your payment to the Horry County Treasurer’s Office.
- Don't overlook the line for the Federal ID or Social Security Number and the Retail License No., as these are crucial for identifying your business.
- Don't delay in calculating the total fees due. Include any penalties if applicable, to prevent further delays or additional penalties.
By following these guidelines, businesses can ensure they accurately and efficiently complete the Accommodations Tax form for Horry County, South Carolina, contributing to a smooth tax reporting process. Remembering to double-check computations, include necessary identification details, and submit payments on time will aid in avoiding common pitfalls in tax preparation.
Misconceptions
Understanding the Accommodations Tax Form can sometimes lead to confusion. Here are seven common misconceptions about this form and clarifications for each:
- It applies to all businesses. The form is specifically for businesses outside city limits. Thus, businesses within city limits must adhere to different reporting requirements.
- Only accommodations revenues are taxable. While it's called the Accommodations Tax Form, it also applies to gross proceeds from the sale of food and beverages and paid admissions or amusements, not just transient accommodations.
- The tax rates are uniform. The form outlines different tax rates: 2.5% for sales of food/beverages and paid admissions/amusements, and 3% for transient accommodations, highlighting the need to apply the correct rate to each revenue type.
- Penalties are a flat rate. Penalties for late payment are incremental—10% if postmarked after the due date, with an additional 10% (totaling 20%) if postmarked after the month's end.
- All information needed is financial. In addition to financial calculations, businesses must provide identifying information, such as a Federal ID or SSN and a Retail License Number, which are crucial for correct processing.
- The form is for annual submission. It is a monthly reporting form, designed to cover sales and tax calculations for each month, not annually.
- Electronic submission is available. Currently, there is a physical address provided for mailing the check and form, indicating that this specific form requires a paper submission and does not mention an electronic submission option.
Correcting these misconceptions ensures that businesses can accurately fulfill their tax obligations, thereby avoiding any potential penalties for misfiling.
Key takeaways
Understanding the intricacies of the Accommodations Tax form can enhance compliance and ensure timely payments. Here are key takeaways from the Horry County, South Carolina, Accommodations Tax form, designed to aid businesses located outside city limits.
- The form serves to report sales related to Hospitality Fees and Local Accommodations Tax, specifically focusing on transactions exterior to city boundaries.
- It is essential to include both the account number and the Federal ID or Social Security Number alongside the Retail License Number to properly identify the business entity.
- Businesses are required to accurately report gross proceeds from the sale of food and beverages, rental of transient accommodations, and paid admissions/amusements.
- A notable component is the inclusion of Local Accommodations Tax within the gross proceeds from rentals of transient accommodations, calculated at a rate of 1/2% for the county.
- Tax rates applied are 2.5% for sales of food/beverages and admissions/amusements, and 3% for transient accommodations rentals, which are crucial for determining the tax amounts due.
- Penalties for late payments are structured to increase the burden on the delinquent payer, starting at 10% if payment is postmarked after the 20th of the month due, escalating to a total of 20% if postmarked after the month's end.
- Total fees due are a sum of the calculated fees plus any applicable penalties, emphasizing the importance of timely remittance to avoid additional charges.
- All payments must be directed to the Horry County Treasurer's Office, including the proper handling of the remittance form and payment to ensure swift processing.
- Timeliness is key, with the form covering the reporting period through the last day of the month, underscoring the necessity for businesses to prepare in advance for end-of-month reporting.
- The taxpayer's affirmation of the accuracy and truthfulness of the reported information, through signature and date, underscores the legal responsibility in filing the Accommodations Tax form.
Proper understanding and adherence to the guidelines provided in the Accommodations Tax form will facilitate a smoother process for businesses contributing to Horry County's local economy. As regulations and rates may vary, staying informed of the specific requirements for businesses outside city limits is crucial for accurate and efficient tax reporting.
Popular PDF Documents
IRS 709 - IRS 709 must be filed even when no tax is due, ensuring all sizable gifts are appropriately reported.
Alternative Minimum Tax Credit - Essential for the financial well-being of taxpayers seeking to rectify their tax standing post-AMT payment.