Get 2016 Irs K 1 Form
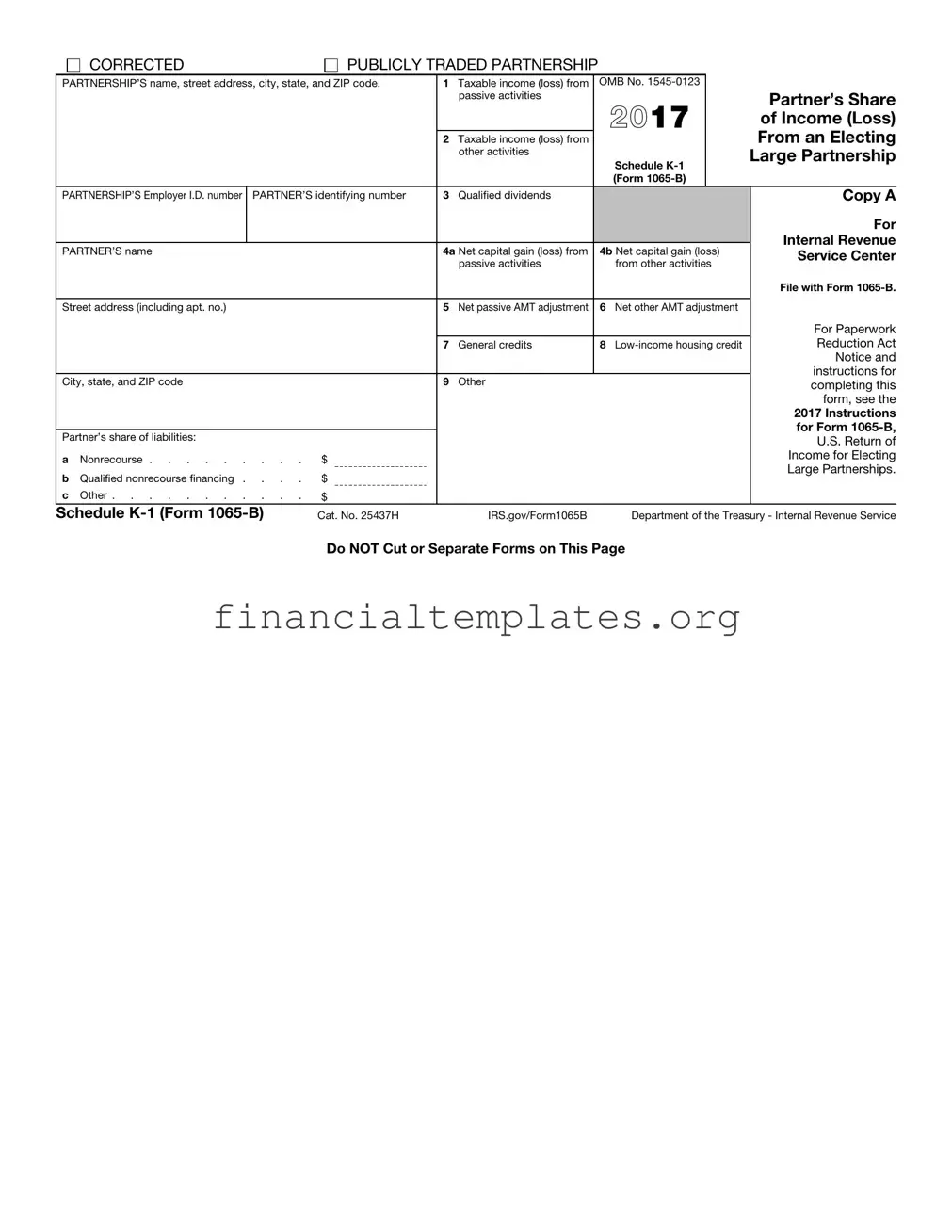
The 2016 IRS K-1 Form plays a crucial role in detailing the financial activities and tax responsibilities for individuals and entities involved in partnerships, especially those that are publicly traded. Known more formally as Schedule K-1 (Form 1065-B), this document serves multiple purposes, including reporting the share of partnership income, losses, dividends, and credits to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Specifically designed for Electing Large Partnerships, the form meticulously breaks down categories of income and losses—such as taxable income from passive and other activities, net capital gains, and dividends. It also addresses adjustments related to the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) and outlines the partner's liabilities and credits. Essential details such as the partnership’s and partner's names, addresses, and identification numbers are prominently featured, ensuring that each form is accurately matched to its respective partners and their potential tax liabilities. Being tagged with the 'CORRECTED' box option, the form accommodates revisions to previously submitted information, indicating the IRS's allowance for updates. Properly understanding and filling out this form is paramount for partners, as it directly affects tax obligations and compliance with federal tax laws.
2016 Irs K 1 Example

CORRECTED
PUBLICLY TRADED PARTNERSHIP
PARTNERSHIP’S name, street address, city, state, and ZIP code. |
1 |
Taxable income (loss) from |
OMB No. |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
passive activities |
|
|
Partner’s Share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
of Income (Loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
From an Electing |
|
|
|
|
|
2 Taxable income (loss) from |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
other activities |
|
|
Large Partnership |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Schedule |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Form |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
PARTNERSHIP’S Employer I.D. number |
PARTNER’S identifying number |
3 |
Qualified dividends |
|
|
Copy A |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal Revenue |
PARTNER’S name |
|
4a Net capital gain (loss) from |
4b Net capital gain (loss) |
|||||
|
Service Center |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
passive activities |
from other activities |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
File with Form |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Street address (including apt. no.) |
|
5 Net passive AMT adjustment |
6 Net other AMT adjustment |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For Paperwork |
|
|
|
|
7 |
General credits |
8 |
Reduction Act |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notice and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
instructions for |
City, state, and ZIP code |
|
9 |
Other |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
completing this |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
form, see the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2017 Instructions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for Form |
Partner’s share of liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
U.S. Return of |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
Nonrecourse |
$ |
|
|
|
|
Income for Electing |
|
|
|
|
|
Large Partnerships. |
||||
b |
Qualified nonrecourse financing . . . . |
$ |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
c |
Other |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Schedule |
Cat. No. 25437H |
|
IRS.gov/Form1065B |
Department of the Treasury - Internal Revenue Service |
||||
Do NOT Cut or Separate Forms on This Page

CORRECTED (if checked)
PUBLICLY TRADED PARTNERSHIP (if checked)
PARTNERSHIP’S name, street address, city, state, and ZIP code. |
1 |
Taxable income (loss) from |
OMB No. |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
passive activities |
|
|
Partner’s Share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
of Income (Loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
From an Electing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 Taxable income (loss) from |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
other activities |
|
|
Large Partnership |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Schedule |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Form |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
PARTNERSHIP’S Employer I.D. number |
PARTNER’S identifying number |
3 |
Qualified dividends |
|
|
Copy B |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For Partner |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See the separate |
|||
PARTNER’S name |
|
|
|
4a Net capital gain (loss) from |
4b Net capital gain (loss) |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
passive activities |
from other activities |
Partner’s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Instructions for |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Schedule |
Street address (including apt. no.) |
|
|
|
5 Net passive AMT adjustment |
6 Net other AMT adjustment |
(Form |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This is important tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
information and is |
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
General credits |
8 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
being furnished to the |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal Revenue |
City, state, and ZIP code |
|
|
|
9 |
Other |
|
|
Service. If you are |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
required to file a return, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a negligence penalty or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
other sanction may be |
Partner’s share of liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
imposed on you if this |
||
a |
Nonrecourse |
. |
. |
$ |
|
|
|
|
income is taxable and |
|
|
|
|
|
the IRS determines that |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
Qualified nonrecourse financing . . |
. |
. |
$ |
|
|
|
|
it has not been |
|
c |
Other |
. |
. |
$ |
|
|
|
|
reported. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Schedule |
|
(Keep for your records.) |
|
IRS.gov/Form1065B |
Department of the Treasury - Internal Revenue Service |
|||||

CORRECTED
PUBLICLY TRADED PARTNERSHIP
PARTNERSHIP’S name, street address, city, state, and ZIP code. |
1 |
Taxable income (loss) from |
OMB No. |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
passive activities |
|
|
Partner’s Share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
of Income (Loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
From an Electing |
|
|
|
|
|
2 Taxable income (loss) from |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
other activities |
|
|
Large Partnership |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Schedule |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Form |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
PARTNERSHIP’S Employer I.D. number |
PARTNER’S identifying number |
3 |
Qualified dividends |
|
|
Copy C |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For Electing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Large Partnership |
PARTNER’S name |
|
|
4a Net capital gain (loss) from |
4b Net capital gain (loss) |
||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
passive activities |
from other activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For Paperwork |
Street address (including apt. no.) |
|
|
5 Net passive AMT adjustment |
6 Net other AMT adjustment |
||||
|
|
Reduction Act |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notice and |
|
|
|
|
7 |
General credits |
8 |
instructions for |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
completing this |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
form, see the |
City, state, and ZIP code |
|
|
9 |
Other |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
2017 Instructions |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for Form |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S. Return of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income for Electing |
Partner’s share of liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Large Partnerships. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
Nonrecourse |
. . . |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
b |
Qualified nonrecourse financing . |
. . . |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
c |
Other |
. . . |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
Schedule
IRS.gov/Form1065B |
Department of the Treasury - Internal Revenue Service |
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Detail |
|---|---|
| Form Identification | Schedule K-1 (Form 1065-B) is used for reporting a partner's share of income, losses, deductions, and credits from an electing large partnership. |
| Taxable Activities | It includes separate sections for reporting taxable income (loss) from passive activities, other activities, qualified dividends, and net capital gain (loss). |
| Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) Adjustments | The form requires information about net passive AMT adjustment and net other AMT adjustment to help calculate alternative minimum tax obligations. |
| Credits | General credits, low-income housing credit, and other credits can be reported on this form, reflecting a partner's share of various tax incentives. |
| Partner's Share of Liabilities | Details regarding the partner's share of liabilities, including nonrecourse, qualified nonrecourse financing, and other liabilities, are provided for more accurate tax reporting. |
Guide to Writing 2016 Irs K 1
After receiving the 2016 IRS K-1 Form for an Electing Large Partnership, you'll need to fill it out carefully to ensure accurate reporting of your portion of the partnership's income, deductions, credits, and other items. This form is essential for determining your tax liability associated with partnership activities. Follow these steps to fill out the form correctly:
- Start by entering the PARTNERSHIP'S name, street address, city, state, and ZIP code in the designated area at the top of the form.
- Fill in the PARTNERSHIP’S Employer I.D. number and the PARTNER'S identifying number in their respective fields.
- Next, write the PARTNER'S name and street address (including apt. no.), city, state, and ZIP code in the spaces provided.
- Indicate the Taxable income (loss) from passive activities by entering the dollar amount in line 1.
- For line 2, report the Taxable income (loss) from other activities.
- Enter the amount of Qualified dividends in line 3.
- For lines 4a and 4b, document the Net capital gain (loss) from passive activities and from other activities, respectively.
- Report the Net passive AMT adjustment on line 5 and the Net other AMT adjustment on line 6.
- On lines 7 through 9, fill in the amounts for General credits, Low-income housing credit, and Other credits and deductions as applicable.
- Under the section titled "Partner’s share of liabilities," input the dollar amounts next to Nonrecourse, Qualified nonrecourse financing, and Other.
- If any information has been corrected, make sure to check the CORRECTED box at the top of the form.
- Finally, review all the information you've entered to ensure it’s accurate and complete before submitting the form.
Completing the Schedule K-1 (Form 1065-B) accurately is crucial for meeting your tax obligations. After submitting the form, keep a copy for your records and be prepared to use the information when filing your personal tax return. If you encounter any complexities or uncertainties, consider seeking advice from a tax professional.
Understanding 2016 Irs K 1
FAQ Section: Understanding the 2016 IRS Form K-1 (1065-B)
-
What is the purpose of the 2016 IRS Form K-1 (1065-B)?
The 2016 IRS Form K-1 (1065-B) is used by publicly traded partnerships to report each partner's share of the partnership's income, deductions, and credits to the IRS. It helps partners determine how much of the partnership's income or loss they should report on their own tax returns.
-
Who needs to file Form K-1 (1065-B)?
Publicly traded partnerships are required to file Form K-1 (1065-B) with the IRS and provide a copy to each partner. Partners are not required to submit the form with their tax return but must utilize the information to complete their individual returns.
-
What information is included on Form K-1 (1065-B)?
- Taxable income or loss from passive activities.
- Taxable income or loss from other activities.
- Qualified dividends.
- Net capital gain or loss, from both passive and other activities.
- Adjustments for Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT), including both passive and other adjustments.
- Various credits, including general and low-income housing credits.
- Partner’s share of liabilities, categorized into nonrecourse, qualified nonrecourse financing, and other liabilities.
-
What should I do if I receive a corrected Form K-1 (1065-B)?
If you receive a corrected Form K-1 (1065-B), you must use the updated information to amend your tax return if you've already filed it. If you have not yet filed, simply use the information from the corrected form. Corrected forms are issued when the partnership realizes there was an error in the information initially reported.
-
How do partner’s shares of liabilities affect their individual tax returns?
The share of liabilities listed on Form K-1 (1065-B) affects a partner's basis in the partnership. The partner's basis is essentially their investment in the partnership, adjusted by their share of income, deductions, and liabilities. Increases in liabilities can increase a partner's basis, while decreases can reduce it, affecting the partner's ability to deduct partnership losses.
-
Where can I find more information or assistance with Form K-1 (1065-B)?
For more detailed instructions on how to interpret or use the information provided on Form K-1 (1065-B), partners should refer to the IRS instructions for Form 1065-B or consult with a tax professional specialized in partnership tax matters.
Common mistakes
Filling out the IRS 2016 K-1 form can sometimes be complex and prone to errors. Here are five common mistakes people make on this form:
Incorrect partnership information: Misreporting the partnership’s name, address, city, state, or ZIP code can lead to processing delays or misdirected correspondence.
Inputting wrong identification numbers: Filling in incorrect Employer Identification Numbers (EIN) for the partnership or incorrect identifying numbers for the partner can cause significant issues with tracking and attributing income properly.
Income and loss misclassification: Not properly distinguishing between taxable income (loss) from passive activities and from other activities may result in inaccurate tax liabilities or benefits.
Misunderstanding capital gains and losses: Combining or incorrectly reporting net capital gain (loss) from passive activities and from other activities can impact tax calculations.
Inaccurately reported partner’s share of liabilities: Failing to correctly detail the partner’s share of nonrecourse, qualified nonrecourse financing, and other liabilities can affect the partner's basis in the partnership and eventual taxable income.
Documents used along the form
When handling business or personal taxes, especially for those involved with partnerships or pass-through entities, the Schedule K-1 (Form 1065-B) is a crucial document for reporting share of income, deductions, credits, etc. To ensure comprehensive and accurate tax reporting, various other forms and documents may be necessary alongside the Schedule K-1. These additional documents help in providing a detailed financial picture and support the information reported.
- Form 1065: U.S. Return of Partnership Income: This form is used by partnerships to report their income, gains, losses, deductions, credits, etc. The Schedule K-1 (Form 1065-B) serves as a component of Form 1065, providing the information necessary for partners to fill out their personal tax returns.
- Form 1040: U.S. Individual Income Tax Return: Individuals receiving a Schedule K-1 due to their involvement in a partnership will often need to file a Form 1040, detailing their overall personal income, which includes what's reported on K-1.
- Form 8949: Sales and Other Dispositions of Capital Assets: If there are capital gains or losses reported on the Schedule K-1, Form 8949 may need to be completed to specify these transactions on the individual’s tax return.
- Form 4562: Depreciation and Amortization: Partnerships utilizing depreciation or amortization to offset income on their Form 1065 can impact the amounts reported on Schedule K-1; individuals receiving a K-1 may also need to file Form 4562 if they have depreciable property.
- Schedule E (Form 1040): Supplemental Income and Loss: Often, portions of the Schedule K-1 information are reported on Schedule E, which is attached to the individual’s Form 1040, covering income or loss from real estate, S-corporations, partnerships, trusts, and royalty income.
- Form 8582: Passive Activity Loss Limitations: If the Schedule K-1 reports income or loss from passive activities, Form 8582 might be needed to report and calculate the limitation of passive activity losses for the individual taxpayer.
Together, these forms and documents ensure a thorough accounting of an individual's tax obligations and investment outcomes. It is important for both the partnership and the individual partners to maintain accurate and consistent records across these documents to fulfill their tax reporting responsibilities fully and to minimize the potential for discrepancies that could catch the attention of the IRS. As each taxpayer's situation can be unique, consulting with a tax professional when preparing these forms is often a wise decision.
Similar forms
The Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement, bears similarities to the 2016 IRS K-1 form as it reports an individual's annual earnings and the taxes withheld from those earnings by their employer. Just like the K-1 form outlines a partner’s share of income, deductions, and credits from a partnership, the W-2 provides detailed financial information but on the employment front. It specifically outlines the employee’s compensation and tax deductions, playing a pivotal role in personal tax return preparation.
Form 1099-MISC, Miscellaneous Income, is akin to the K-1 form in that it is used to report income outside of salaries, wages, and tips. It covers the freelance or contract work, royalties, and rents, very much like how K-1 reports income from partnerships. Both forms cater to the reporting of income from varied sources, though the nature of the income and the source entity differ, focusing on individual and partnership dimensions of income reporting respectively.
The Schedule C (Form 1040), Profit or Loss from Business, shares a common purpose with the K-1 form, documenting an individual's business income and expenses throughout the tax year. While K-1 details a partner's financial information from a partnership, Schedule C does so for sole proprietors. They are alike in that they both inform the IRS about the financial status of a business entity related to an individual, crucial for accurate tax liability assessment.
Form 1065, U.S. Return of Partnership Income, directly relates to the K-1 form in the context of partnership reporting. While Form 1065 is used by the partnership to report its income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits to the IRS, the K-1 form, a part of Form 1065, records each partner’s share of these financial elements. In essence, both serve the partnership taxation requirements, but from entity and individual perspectives, respectively.
The Schedule E (Form 1040), Supplemental Income and Loss, is employed for reporting income from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs. It is similar to the K-1 form as it is another means through which a partner in a partnership can report their share of income or loss. Both are integral for disclosing passive income types, ensuring comprehensive tax reporting.
Form 1120S, U.S. Income Tax Return for an S Corporation, although it is for S corporations, parallels the K-1 form’s function for partnerships. The K-1 form details a partner’s share of income and losses, while Form 1120S serves a similar purpose but for shareholders of an S corporation. Each shareholder’s individual share of the corporation's income, deductions, and credits are reported, akin to partnership dynamics in the K-1.
Form 1041, U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts, is used to report income, deductions, and credits of a decedent's estate or a trust. Similar to the K-1 form, which allocates income and losses to partners of a partnership, Form 1041 allocates estate or trust income to beneficiaries. Both forms are essential for ensuring that income from these entities is correctly reported and taxed on the individual level.
Form 8832, Entity Classification Election, while not a direct income reporting form, relates to the K-1 in that it affects how an entity is taxed, which in turn influences the nature of tax reporting documents like the K-1. Entities may choose their tax classification, impacting how partners or owners report their share of business income. The election made on Form 8832 can determine whether owners receive a K-1 or another form of income report.
Form 8865, Return of U.S. Persons With Respect to Certain Foreign Partnerships, is similar to the K-1 form but applies to international partnerships. U.S. persons who are partners in a foreign partnership use Form 8865 to report income, losses, and other financial activities, paralleling the domestic partnership income reporting on the K-1. Both serve to ensure transparency and compliance in the taxation of partnership income, whether domestic or foreign.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the 2016 IRS K-1 form, a critical document for individuals in partnerships, ensuring accuracy and understanding its components are key. Here's a guided list of what you should and shouldn't do:
-
Do:
- Verify your partnership's information, including the correct name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN), at the top of the form.
- Double-check your personal identifying information, such as your Social Security Number (SSN) or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN), to prevent any mishaps.
- Ensure the taxable income or loss reported matches your records, specifically in fields related to passive and other activities.
- Review calculations for net capital gain or loss, both from passive activities and other sources, for accuracy.
- Understand and accurately report your portion of liabilities, including nonrecourse, qualified nonrecourse financing, and other liabilities.
- Pay close attention to credits that may apply to you, such as general credits and low-income housing credits.
- Utilize the instructions provided for the K-1 form to assist in understanding each section and how to complete it.
- Keep a copy of the completed form for your records and for future reference.
- Be on the lookout for any corrected forms issued by the partnership that may affect your tax return.
- Contact a tax professional if you have questions or need clarification on how to report K-1 information on your tax return.
-
Don't:
- Rush through filling out the form without verifying all the information against your own records.
- Ignore the importance of accurately reporting the partnership liabilities section, as this can affect your tax liability.
- Overlook any corrected K-1 forms sent out by the partnership, as failing to report corrected information can lead to issues with the IRS.
- Forget to consider how the K-1 affects your Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) calculations, particularly the adjustments for net passive or other AMT adjustments.
- Assume the information provided by the partnership is correct without conducting your own review.
- Miss the significance of understanding every line item, even those that may not seem immediately relevant to your tax situation.
- Delay consulting with a tax advisor if you're unsure about how to include K-1 form data on your personal tax return, especially for complex situations.
- Dismiss the directions and guidance provided in the instructions for the form, which can offer valuable insights and prevent common mistakes.
- Fail to maintain a copy for your records, as you may need to refer back to this document or provide it to a tax preparer in the future.
- Underestimate the impact that K-1 form data can have on your overall tax liability or refund potential.
Misconceptions
When navigating tax documents, particularly for partnerships, it's crucial to clear up common misconceptions about the 2016 IRS K-1 form, formally known as Schedule K-1 (Form 1065-B). This form plays a vital role in reporting the financial activities of publicly traded partnerships and ensuring that partners correctly report their share of the partnership's income, deductions, and credits on their own tax returns. Understanding the nuances of this form helps in accurate tax reporting and compliance.
Misconception 1: Schedule K-1 is only for reporting positive income. Many believe that the K-1 form should only be used to report income. However, both profits and losses, including taxable income (loss) from passive activities and other activities, must be reported through Schedule K-1. This includes net capital gains or losses and adjustments related to the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT).
Misconception 2: All partners receive the same K-1. It's a common misunderstanding that every partner gets an identical K-1 form. In reality, each partner receives a Schedule K-1 that reflects their specific share of the partnership's income, deductions, and credits, depending on the partnership agreement and their investment in the partnership.
Misconception 3: Schedule K-1 is filed with the partner's tax return. Although recipients use the information on Schedule K-1 to complete their own tax returns, the form itself is not filed with the individual's tax return. Instead, it's the partnership's responsibility to file Schedule K-1 with the IRS as part of Form 1065-B and provide each partner with their copy for record-keeping and tax preparation purposes.
Misconception 4: The information on Schedule K-1 doesn't affect personal tax returns. Quite the contrary, the information reported on Schedule K-1 has a direct impact on a partner's personal tax obligations. It includes various types of income, such as qualified dividends and net capital gains, which could affect tax liabilities, tax rates, and potential deductions on personal returns.
Misconception 5: Schedule K-1 only covers federal tax obligations. While the primary purpose is to report federal tax information, the data provided on Schedule K-1 may also be necessary for state tax filings, depending on the state's tax laws and the partnership's business locations. Therefore, partners should not overlook the relevance of K-1 information for state tax purposes.
Misconception 6: Corrections to the K-1 form are uncommon and unnecessary. Corrections to Schedule K-1 are more common than many assume. If errors are discovered after the initial filing, a corrected K-1 can be issued. It's crucial for partners to review their K-1 carefully and communicate any discrepancies to the partnership for amendment, ensuring compliance and accuracy in tax reporting.
Understanding these misconceptions about the 2016 IRS K-1 form clarifies the filing process for both partnerships and individuals. This, in turn, promotes accurate tax reporting and helps avoid potential penalties or audits resulting from misinformation or misunderstanding of tax obligations.
Key takeaways
Understanding the complexities of the 2016 IRS K-1 Form is crucial for taxpayers involved in publicly traded partnerships and electing large partnerships. Here are key takeaways to guide you through the process of filling out and utilizing this form properly:
Identification of Income Types: The K-1 form breaks down income into various categories, such as taxable income (loss) from passive activities, taxable income (loss) from other activities, qualified dividends, and net capital gains (loss) from both passive and other activities. Recognizing these distinctions is vital for correctly reporting your share of a partnership’s income or loss.
Reporting Adjustments and Credits: Attention should be paid to specific adjustments like the net passive activity adjustments for the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) and credits, including general credits and low-income housing credits. These elements can influence your tax liability and potential refund, making accurate reporting indispensable.
Partner’s Share of Liabilities: The form also includes sections for reporting the partner’s share of nonrecourse, qualified nonrecourse financing, and other liabilities. Understanding your share of these liabilities is essential for correctly assessing the risk and tax implications associated with your partnership interests.
Compliance and Penalties: A Copy B of the Schedule K-1 is provided for the partner, highlighting the significance of this document for tax compliance. If the income reported on the K-1 is not correctly included on your tax return, it could result in penalties or other sanctions from the IRS. Therefore, it's imperative to ensure all information is accurately reported and filed.
Navigating the intricacies of the Schedule K-1 (Form 1065-B) requires a detailed understanding of its components and their implications for your tax situation. Properly filling out and using this form plays a critical role in managing your tax responsibilities as a partner in a publicly traded or large electing partnership.
Popular PDF Documents
Philly Wage Tax Refund - Philadelphia’s procedure for interdepartmental refunds and permits within the Refund Petition form underscores the importance of departmental authorizations.
Wisconsin State Tax Form - The WT-7 form serves the critical function of aligning reported tax withholdings with actual records.
Schedule 8812 Form 1040 - Form 8812 helps taxpayers calculate additional child tax credit that may lead to a refund even without owing tax.